Float charging maintains a battery at a steady voltage to keep it fully charged without overcharging, ideal for long-term maintenance in battery pets. Equalization charging applies a controlled overcharge to balance the voltage and specific gravity across all cells, preventing sulfation and extending battery life. Understanding the appropriate use of float versus equalization charging ensures optimal performance and longevity of battery pets.
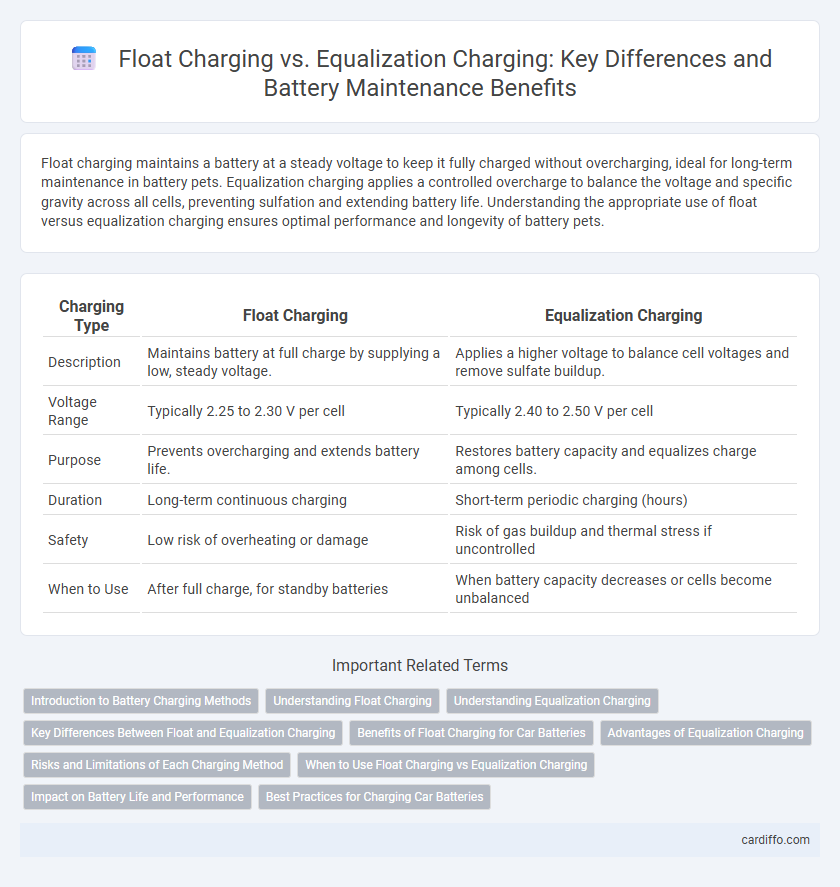
Table of Comparison
| Charging Type | Float Charging | Equalization Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Maintains battery at full charge by supplying a low, steady voltage. | Applies a higher voltage to balance cell voltages and remove sulfate buildup. |
| Voltage Range | Typically 2.25 to 2.30 V per cell | Typically 2.40 to 2.50 V per cell |
| Purpose | Prevents overcharging and extends battery life. | Restores battery capacity and equalizes charge among cells. |
| Duration | Long-term continuous charging | Short-term periodic charging (hours) |
| Safety | Low risk of overheating or damage | Risk of gas buildup and thermal stress if uncontrolled |
| When to Use | After full charge, for standby batteries | When battery capacity decreases or cells become unbalanced |
Introduction to Battery Charging Methods
Float charging maintains a battery at full charge by supplying a continuous, low-level voltage to compensate for self-discharge without overcharging, ideal for standby power applications. Equalization charging applies a controlled overcharge voltage periodically to balance individual cell voltages and prevent sulfation buildup, enhancing battery lifespan and performance. Understanding these distinct charging methods is essential for optimizing battery maintenance in lead-acid and other rechargeable battery technologies.
Understanding Float Charging
Float charging maintains a battery at a constant voltage slightly above its nominal level to keep it fully charged without overcharging or damaging the cells. This method compensates for self-discharge by supplying a continuous low current, ensuring the battery remains at optimal capacity during standby periods. Proper float charging enhances battery lifespan and reliability, especially in backup power systems and renewable energy storage.
Understanding Equalization Charging
Equalization charging is a controlled overcharge applied to lead-acid batteries to balance the charge across all cells, preventing stratification and sulfation. This process typically involves raising the battery voltage above the standard float charge level to ensure uniform electrolyte density and battery health. Proper equalization charging extends battery life and improves overall performance by maintaining optimal cell balance and capacity.
Key Differences Between Float and Equalization Charging
Float charging maintains a battery at full charge by applying a low voltage to prevent overcharging and minimize battery wear, whereas equalization charging involves applying a higher voltage to balance cell voltages and reduce sulfation. Float charging is typically used for long-term maintenance in standby applications, while equalization charging is performed periodically to restore battery capacity and ensure uniform charge distribution. Understanding these key differences helps optimize battery lifespan and performance in various usage scenarios.
Benefits of Float Charging for Car Batteries
Float charging maintains a car battery at a consistent voltage, preventing overcharging and extending battery lifespan by minimizing electrolyte loss and corrosion. It ensures the battery stays fully charged while reducing the risk of overheating, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in vehicles. This method also supports reliable starting power and improves battery readiness during periods of inactivity.
Advantages of Equalization Charging
Equalization charging helps balance the voltage and capacity of individual battery cells, preventing sulfate buildup and extending overall battery life. This method enhances battery performance by correcting imbalances that float charging cannot address, reducing the risk of premature failure. Regular equalization boosts battery efficiency, especially in lead-acid batteries used in solar energy systems and backup power applications.
Risks and Limitations of Each Charging Method
Float charging maintains a constant low voltage to keep the battery fully charged without overcharging, but prolonged float charging can lead to electrolyte stratification and corrosion, reducing battery lifespan. Equalization charging applies a higher voltage to balance cell voltages and remove sulfation but risks overheating, excessive gassing, and water loss if not properly controlled. Each method requires careful monitoring to avoid damage, with float charging suited for standby use and equalization reserved for occasional maintenance cycles.
When to Use Float Charging vs Equalization Charging
Float charging is used to maintain a battery at full charge after it has been fully charged, ideal for standby power systems and backup batteries. Equalization charging, a controlled overcharge process, is applied periodically to balance cell voltages and prevent sulfation in lead-acid batteries, typically done every few months or when voltage imbalance is detected. Use float charging for continuous maintenance and equalization charging for corrective maintenance and battery health optimization.
Impact on Battery Life and Performance
Float charging maintains a battery at full charge by providing a constant low voltage, minimizing overcharge and enhancing battery lifespan through reduced stress on the cells. Equalization charging applies a controlled overcharge to balance cell voltages and chemistry, preventing sulfation but potentially accelerating wear if done excessively. Choosing the appropriate charging method significantly impacts battery performance, as float charging ensures long-term stability while equalization improves capacity and reliability with careful management.
Best Practices for Charging Car Batteries
Float charging maintains a car battery at a consistent voltage of around 13.2 to 13.8 volts to keep it fully charged without overcharging, ideal for long-term storage. Equalization charging involves applying a higher voltage, typically 14.4 to 15.0 volts, for a limited time to balance cell voltages and reduce sulfation in lead-acid batteries. Best practices for car battery charging include using float charging for daily maintenance and performing equalization charging periodically to extend battery life and optimize performance.
Float Charging vs Equalization Charging Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com