Flat plate batteries provide a cost-effective solution with quick charging capabilities and are commonly used in automotive applications. Tubular plate batteries offer superior durability, longer lifespan, and better deep discharge performance, making them ideal for renewable energy storage and heavy-duty use. Choosing between flat plate and tubular plate batteries depends on the balance between budget constraints and the need for extended reliability and cycle life.
Table of Comparison
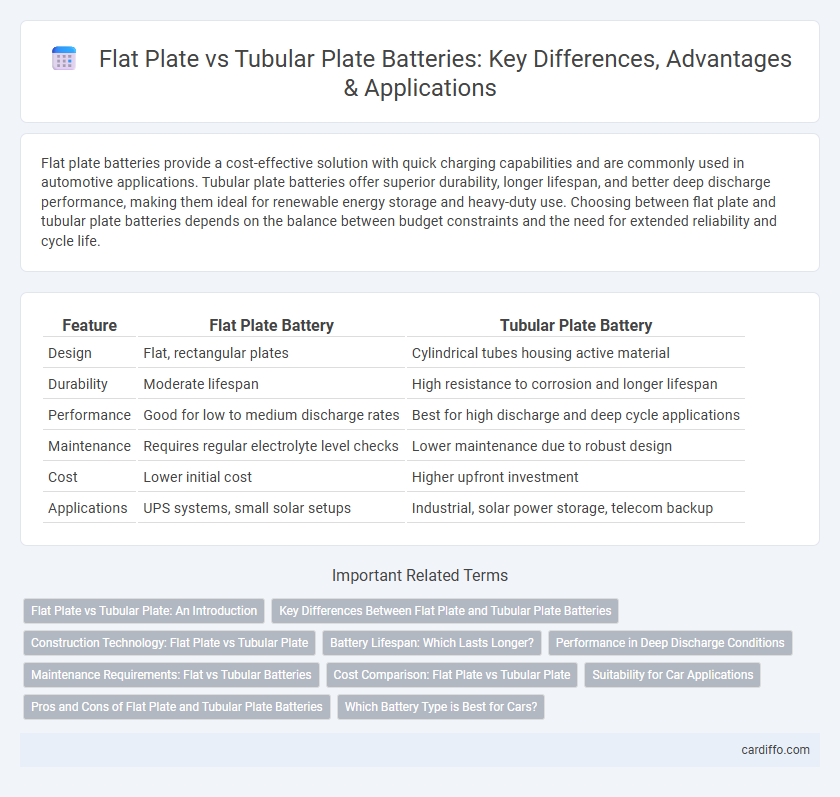
| Feature | Flat Plate Battery | Tubular Plate Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Flat, rectangular plates | Cylindrical tubes housing active material |
| Durability | Moderate lifespan | High resistance to corrosion and longer lifespan |
| Performance | Good for low to medium discharge rates | Best for high discharge and deep cycle applications |
| Maintenance | Requires regular electrolyte level checks | Lower maintenance due to robust design |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Applications | UPS systems, small solar setups | Industrial, solar power storage, telecom backup |
Flat Plate vs Tubular Plate: An Introduction
Flat plate batteries feature flat, rectangular plates that provide a larger surface area for electrolyte contact, enhancing conductivity and efficiency. Tubular plate batteries use cylindrical positive plates that offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for deep-cycle applications. The choice between flat plate and tubular plate batteries depends on the balance between cost, lifespan, and performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Flat Plate and Tubular Plate Batteries
Flat plate batteries use thin, flat lead plates coated with active material, offering lower cost and higher initial power but shorter lifespan and reduced deep discharge resilience. Tubular plate batteries feature cylindrical positive plates with a dense active material, providing superior durability, extended cycle life, and better performance in deep discharge conditions. The tubular design minimizes material shedding and corrosion, making these batteries ideal for high-demand applications like solar and industrial use.
Construction Technology: Flat Plate vs Tubular Plate
Flat plate batteries utilize flat lead plates coated with active materials, offering simpler construction and ease of manufacturing, ideal for low to medium discharge applications. Tubular plate batteries feature cylindrical tubes filled with active material around a central spine, enhancing mechanical strength and durability for deep cycle and high discharge use. The tubular design minimizes shedding of active material, leading to longer battery life and improved performance in demanding conditions.
Battery Lifespan: Which Lasts Longer?
Tubular plate batteries generally offer a longer lifespan compared to flat plate batteries due to their robust design that minimizes active material shedding and corrosion. The tubular structure enhances deep discharge tolerance and maintains consistent performance over extended cycles, resulting in superior durability. Flat plate batteries, while cost-effective, tend to degrade faster under heavy use, reducing overall battery lifespan.
Performance in Deep Discharge Conditions
Flat plate batteries exhibit faster discharge rates but experience quicker capacity loss under deep discharge conditions, making them less ideal for prolonged heavy use. Tubular plate batteries maintain higher capacity and better structural integrity during deep discharge, resulting in longer lifecycle performance and improved reliability. Their design optimizes electrolyte flow and reduces plate degradation, enhancing efficiency in applications requiring frequent deep cycling.
Maintenance Requirements: Flat vs Tubular Batteries
Flat plate batteries demand more frequent maintenance due to their higher susceptibility to corrosion and stratification, requiring regular electrolyte checks and equalization charges. Tubular plate batteries feature robust construction with reinforced grids that reduce water loss and corrosion, significantly lowering maintenance intervals. This durability makes tubular batteries ideal for applications requiring long service life and consistent performance with minimal upkeep.
Cost Comparison: Flat Plate vs Tubular Plate
Flat plate batteries generally offer a lower initial cost compared to tubular plate batteries due to simpler design and manufacturing processes. Tubular plate batteries, while more expensive upfront, provide longer lifespan and better cycle stability, reducing overall cost of ownership in high-demand applications. Cost-effectiveness depends on usage patterns, with flat plates suited for low to moderate use and tubular plates preferred for deep discharge and frequent cycling.
Suitability for Car Applications
Flat plate batteries, commonly used in conventional cars, offer cost-effective and reliable energy storage with moderate charge acceptance and durability. Tubular plate batteries provide superior cyclic performance and enhanced resistance to deep discharges, making them ideal for vehicles requiring high durability and frequent battery cycling, such as commercial or heavy-duty cars. The choice depends on specific car application needs, balancing initial cost against long-term performance and maintenance.
Pros and Cons of Flat Plate and Tubular Plate Batteries
Flat plate batteries offer high initial cost efficiency and easy maintenance but have shorter lifespan and lower deep-cycle durability compared to tubular plate batteries. Tubular plate batteries provide superior cycle stability, longer operational life, and enhanced resistance to wear and tear, making them ideal for high discharge applications despite their higher upfront investment and maintenance complexity. Choosing between flat plate and tubular plate batteries depends on specific energy storage needs, budget constraints, and desired longevity.
Which Battery Type is Best for Cars?
Tubular plate batteries offer higher durability and longer lifespan compared to flat plate batteries, making them ideal for cars subjected to frequent starts and heavy usage. Flat plate batteries are more cost-effective but provide lower deep cycle capability, causing reduced performance in automotive applications requiring sustained power delivery. For cars, especially in demanding conditions, tubular plate batteries provide superior reliability and efficiency.
Flat Plate vs Tubular Plate Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com