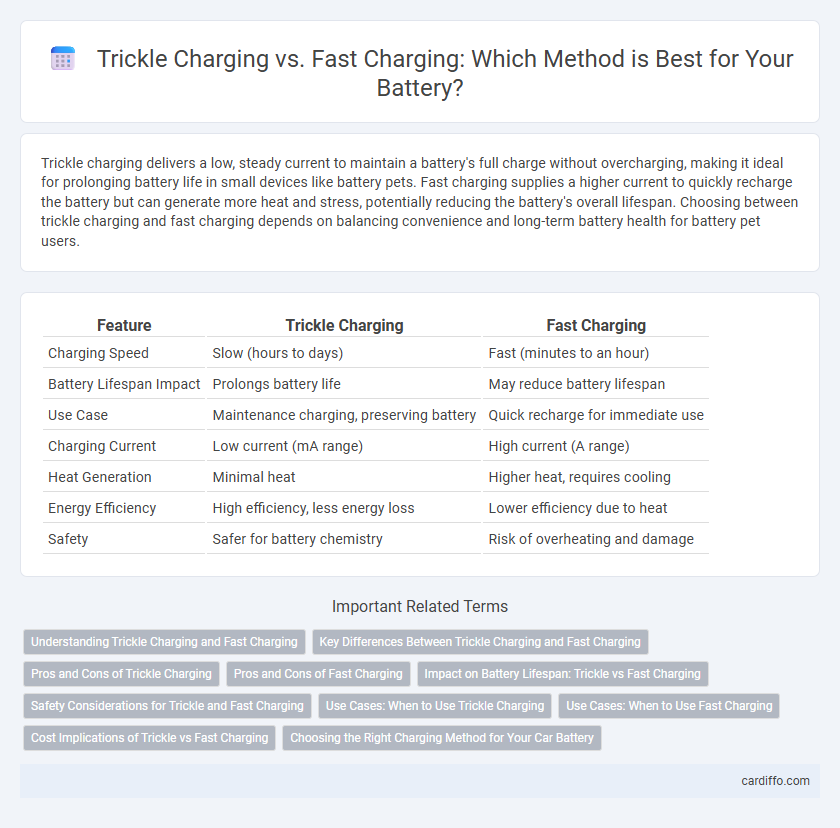
Trickle charging delivers a low, steady current to maintain a battery's full charge without overcharging, making it ideal for prolonging battery life in small devices like battery pets. Fast charging supplies a higher current to quickly recharge the battery but can generate more heat and stress, potentially reducing the battery's overall lifespan. Choosing between trickle charging and fast charging depends on balancing convenience and long-term battery health for battery pet users.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Trickle Charging | Fast Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Slow (hours to days) | Fast (minutes to an hour) |
| Battery Lifespan Impact | Prolongs battery life | May reduce battery lifespan |
| Use Case | Maintenance charging, preserving battery | Quick recharge for immediate use |
| Charging Current | Low current (mA range) | High current (A range) |
| Heat Generation | Minimal heat | Higher heat, requires cooling |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, less energy loss | Lower efficiency due to heat |
| Safety | Safer for battery chemistry | Risk of overheating and damage |
Understanding Trickle Charging and Fast Charging
Trickle charging involves supplying a low, steady current to maintain a battery's full charge without overcharging, making it ideal for long-term battery maintenance and preventing sulfation in lead-acid batteries. Fast charging delivers a high current to rapidly replenish battery capacity, significantly reducing charging time but generating more heat and stress, which can affect battery lifespan. Understanding the trade-offs between these methods helps optimize battery performance and longevity based on usage requirements.
Key Differences Between Trickle Charging and Fast Charging
Trickle charging delivers a low current to maintain a battery's full charge without overcharging, making it ideal for long-term maintenance of lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Fast charging provides a high current to rapidly replenish battery capacity, significantly reducing charging time but generating more heat and potentially reducing battery lifespan if used frequently. The key differences include charging speed, current intensity, heat generation, and suitability for battery health preservation versus quick power restoration.
Pros and Cons of Trickle Charging
Trickle charging maintains a battery's full charge by supplying a low, steady current, which minimizes the risk of overcharging and prolongs battery lifespan. It is ideal for applications requiring long-term maintenance, such as in backup power systems and seasonal vehicles, but it features slower charging times compared to fast charging. However, trickle charging is less efficient for quickly restoring battery capacity, making it unsuitable for situations where rapid energy replenishment is critical.
Pros and Cons of Fast Charging
Fast charging significantly reduces battery recharge time, offering convenience for users who need quick power-ups, especially in mobile devices and electric vehicles. However, it can generate excess heat and stress the battery's chemical components, potentially leading to reduced overall battery lifespan and capacity degradation. While fast charging boosts efficiency, it may require advanced thermal management systems to mitigate damage and maintain safety.
Impact on Battery Lifespan: Trickle vs Fast Charging
Trickle charging delivers a low, steady current that minimizes heat generation, significantly preserving battery lifespan by reducing stress on battery cells. Fast charging increases current flow to rapidly restore battery capacity but accelerates battery degradation due to elevated temperatures and chemical strain. Choosing trickle charging over fast charging extends overall battery longevity by maintaining optimal electrochemical conditions.
Safety Considerations for Trickle and Fast Charging
Trickle charging maintains battery voltage at a low, steady rate to prevent overcharging and overheating, significantly reducing thermal runaway risks and prolonging battery lifespan. Fast charging delivers high current rapidly, which requires advanced battery management systems to monitor temperature and voltage, preventing safety hazards such as swelling, fire, or explosion. Properly designed fast charging protocols incorporate safeguards like temperature sensors and voltage cutoffs to minimize safety concerns inherent in rapid energy transfer.
Use Cases: When to Use Trickle Charging
Trickle charging is ideal for maintaining battery health in devices with low power consumption or during long-term storage, preventing overcharging while ensuring the battery remains fully charged. It is commonly used for lead-acid batteries in vehicles, emergency backup systems, and rechargeable batteries in small electronics like remote controls and cordless phones. This charging method extends battery lifespan by supplying a low, steady current that compensates for self-discharge without stressing the battery.
Use Cases: When to Use Fast Charging
Fast charging is ideal for situations requiring quick battery replenishment, such as emergency travel or tight schedules, where minimal downtime is essential. It suits devices with larger battery capacities, like electric vehicles and high-performance smartphones, that support high current input without significant degradation. However, frequent fast charging may reduce battery lifespan, so it is best reserved for occasional use rather than daily charging routines.
Cost Implications of Trickle vs Fast Charging
Trickle charging offers a low-cost solution by using minimal electricity over extended periods, reducing energy expenses and preventing battery degradation, which lowers replacement costs. Fast charging demands higher power input that increases electricity bills and accelerates battery wear, leading to more frequent battery replacements and higher maintenance costs. Choosing between trickle and fast charging depends on balancing immediate energy costs with long-term battery health and replacement expenses.
Choosing the Right Charging Method for Your Car Battery
Choosing the right charging method for your car battery depends on your usage patterns and battery type. Trickle charging delivers a low, steady current ideal for maintaining battery health during long periods of inactivity, preventing overcharging and extending battery lifespan. Fast charging provides a higher current for rapid energy replenishment, suitable for quick turnarounds but may generate heat that can accelerate battery wear if used excessively.
Trickle Charging vs Fast Charging Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com