Flooded batteries feature removable caps allowing maintenance through water refilling, offering longer lifespans in deep-cycle applications, whereas sealed batteries are maintenance-free with a closed design that prevents acid spills. Flooded batteries generally provide better tolerance to overcharging and cost less upfront, while sealed batteries excel in compact, leak-proof environments with safer installation options. Choosing between flooded and sealed batteries depends on priorities like maintenance willingness, installation space, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
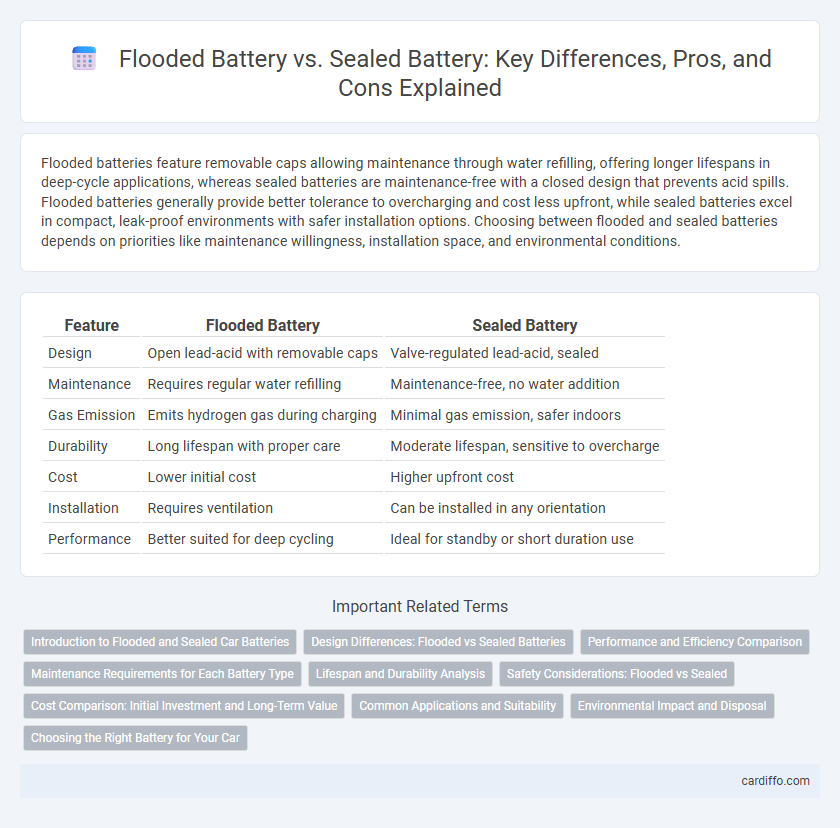
| Feature | Flooded Battery | Sealed Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Open lead-acid with removable caps | Valve-regulated lead-acid, sealed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular water refilling | Maintenance-free, no water addition |
| Gas Emission | Emits hydrogen gas during charging | Minimal gas emission, safer indoors |
| Durability | Long lifespan with proper care | Moderate lifespan, sensitive to overcharge |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Installation | Requires ventilation | Can be installed in any orientation |
| Performance | Better suited for deep cycling | Ideal for standby or short duration use |
Introduction to Flooded and Sealed Car Batteries
Flooded batteries, also known as wet cell batteries, contain liquid electrolyte that requires regular maintenance, including checking water levels and cleaning terminals. Sealed batteries, often called AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) or gel batteries, are maintenance-free and designed to prevent electrolyte spillage, offering enhanced safety and longer lifespan. Both types serve automotive applications but differ in performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness based on usage conditions.
Design Differences: Flooded vs Sealed Batteries
Flooded batteries feature removable caps allowing water refilling and gas release through vents, while sealed batteries have a maintenance-free design with a valve-regulated system to manage internal pressure. The flooded battery's open design enables easy electrolyte inspection and topping up, contrasting with sealed batteries' tightly sealed construction that prevents electrolyte leakage and reduces emissions. These design differences impact durability, maintenance needs, and usability, with flooded batteries suited for heavy-duty applications and sealed batteries preferred for compact, maintenance-free environments.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Flooded batteries exhibit high tolerance for deep discharges and efficient heat dissipation, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications but require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Sealed batteries, such as AGM and Gel types, offer superior efficiency with minimal maintenance due to their spill-proof design and lower self-discharge rates, enhancing longevity in low to moderate load conditions. Performance metrics highlight that flooded batteries provide higher surge currents, while sealed batteries excel in energy retention and vibration resistance, influencing the choice based on specific usage environments.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Battery Type
Flooded batteries require regular maintenance, including checking electrolyte levels and topping off with distilled water to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Sealed batteries, such as AGM and gel types, are maintenance-free, with no need for electrolyte refilling or periodic inspections. Proper maintenance of flooded batteries extends lifespan by preventing sulfation, while sealed batteries offer convenience and reduced risk of leaks or spills.
Lifespan and Durability Analysis
Flooded batteries typically offer a longer lifespan, ranging from 4 to 7 years, due to their ability to be regularly maintained through electrolyte refilling, which enhances durability under heavy usage. Sealed batteries, such as AGM and gel types, provide improved resistance to shock and vibration, resulting in higher durability in mobile or off-road applications but generally have a shorter lifespan averaging 3 to 5 years. The choice between flooded and sealed batteries depends on balancing maintenance capability with the need for robust performance in various environmental conditions.
Safety Considerations: Flooded vs Sealed
Flooded batteries require regular maintenance to prevent acid spills and hydrogen gas buildup, posing risks of corrosion and explosions if improperly handled. Sealed batteries, including AGM and gel types, offer enhanced safety by containing electrolytes within a sealed casing, reducing the likelihood of leaks and harmful gas emissions. Their maintenance-free design and resistance to tropical and cold weather conditions make sealed batteries a safer choice for residential and automotive applications.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Flooded batteries typically have a lower initial investment cost compared to sealed batteries, making them more accessible for budget-conscious buyers. However, sealed batteries offer longer lifespan and require less maintenance, which can translate into better long-term value despite higher upfront expenses. Considering total cost of ownership, sealed batteries often prove more cost-effective due to reduced replacement frequency and maintenance-related downtime.
Common Applications and Suitability
Flooded batteries are commonly used in automotive, marine, and backup power applications due to their durability and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for environments where regular inspection and water refilling are feasible. Sealed batteries, including AGM and gel types, are ideal for applications requiring maintenance-free operation, such as in UPS systems, electric vehicles, and portable electronics, where spill-proof design and vibration resistance are critical. Flooded batteries excel in heavy-duty and high-drain scenarios, while sealed batteries provide enhanced safety and flexibility in confined or sensitive environments.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Flooded batteries require regular maintenance and contain liquid electrolytes that can leak harmful acids, posing environmental hazards during disposal. Sealed batteries, such as AGM and gel types, reduce leakage risks and toxic spill potential, making them safer for the environment. Both types require proper recycling to prevent heavy metal contamination and soil pollution.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Car
Flooded batteries offer easy maintenance and cost-effectiveness with the ability to replace water levels, making them ideal for budget-conscious car owners who can perform regular upkeep. Sealed batteries, including AGM and gel types, provide enhanced durability, spill-proof design, and better resistance to vibration, suited for vehicles requiring low maintenance and improved performance in extreme conditions. Assessing your car's usage patterns, climate, and maintenance willingness is crucial to selecting the right battery that balances reliability, lifespan, and convenience.
Flooded Battery vs Sealed Battery Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com