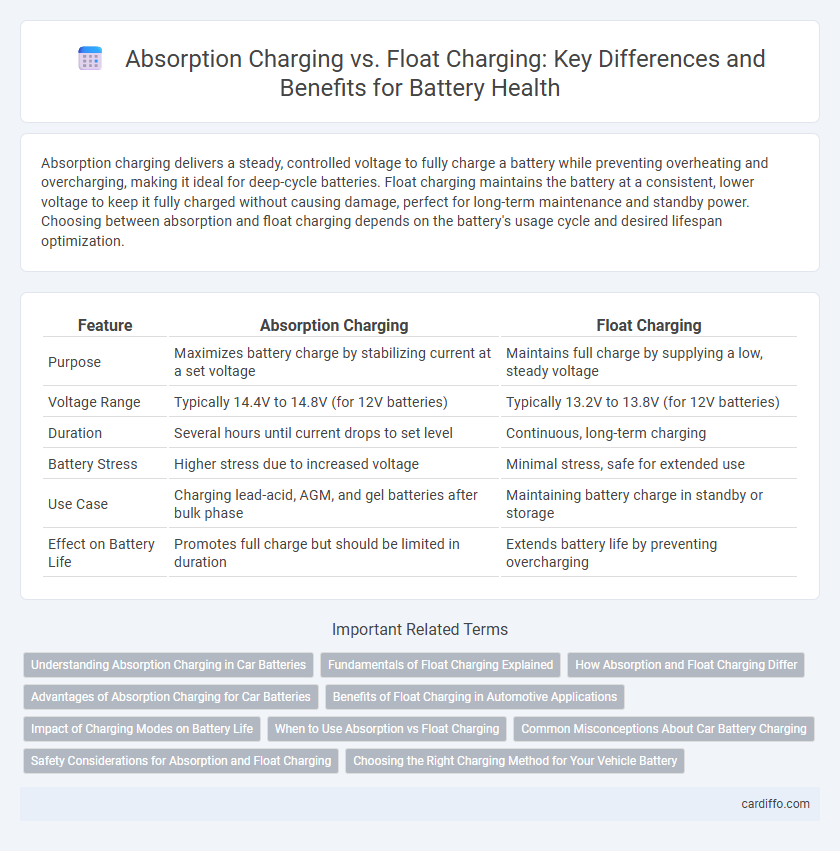
Absorption charging delivers a steady, controlled voltage to fully charge a battery while preventing overheating and overcharging, making it ideal for deep-cycle batteries. Float charging maintains the battery at a consistent, lower voltage to keep it fully charged without causing damage, perfect for long-term maintenance and standby power. Choosing between absorption and float charging depends on the battery's usage cycle and desired lifespan optimization.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Absorption Charging | Float Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Maximizes battery charge by stabilizing current at a set voltage | Maintains full charge by supplying a low, steady voltage |
| Voltage Range | Typically 14.4V to 14.8V (for 12V batteries) | Typically 13.2V to 13.8V (for 12V batteries) |
| Duration | Several hours until current drops to set level | Continuous, long-term charging |
| Battery Stress | Higher stress due to increased voltage | Minimal stress, safe for extended use |
| Use Case | Charging lead-acid, AGM, and gel batteries after bulk phase | Maintaining battery charge in standby or storage |
| Effect on Battery Life | Promotes full charge but should be limited in duration | Extends battery life by preventing overcharging |
Understanding Absorption Charging in Car Batteries
Absorption charging in car batteries involves maintaining a constant voltage while the current gradually decreases, allowing the battery to reach full charge without overcharging. This phase ensures the battery cells achieve optimal chemical balance and maximum capacity by equalizing the charge across all cells. Proper absorption charging extends battery life by preventing overheating and minimizing the risk of sulfation.
Fundamentals of Float Charging Explained
Float charging maintains a battery at full charge by supplying a constant low voltage that compensates for self-discharge without overcharging. The voltage level is carefully regulated, typically around 2.25 to 2.30 volts per cell for lead-acid batteries, ensuring minimal gassing and extending battery life. This method differs from absorption charging, which uses higher voltage to complete the charge rapidly, making float charging ideal for long-term maintenance.
How Absorption and Float Charging Differ
Absorption charging maintains a higher, steady voltage to fully charge the battery by pushing current until it reaches a specified voltage level, preventing overcharging while maximizing energy storage. Float charging holds the battery at a lower voltage to compensate for self-discharge and keep the battery fully charged without causing damage, extending battery lifespan during standby periods. The key difference lies in absorption charging's role in active energy replenishment and float charging's function in maintaining a safe, stable charge level.
Advantages of Absorption Charging for Car Batteries
Absorption charging optimizes the car battery's capacity by delivering a stable voltage at a slower rate, which reduces the risk of overheating and electrolyte loss. This method enhances battery longevity through effective desulfation and ensures a fuller charge compared to float charging. Maintaining optimal charge levels during absorption charging improves overall car battery performance and reliability.
Benefits of Float Charging in Automotive Applications
Float charging maintains a battery at full charge by supplying a low, steady voltage, preventing overcharging and extending battery lifespan in automotive applications. This charging method reduces electrolyte loss and minimizes thermal stress, enhancing overall battery reliability. As a result, float charging ensures consistent power availability for vehicles, especially during periods of inactivity.
Impact of Charging Modes on Battery Life
Absorption charging maintains a higher, steady voltage to fully charge the battery without overcharging, significantly reducing the risk of sulfation and extending battery lifespan. Float charging supplies a lower, consistent voltage to keep the battery at full charge, preventing self-discharge but minimizing wear and stress on battery cells. Choosing the appropriate charging mode directly affects battery health, cycle life, and overall performance by balancing charge efficiency and minimizing degradation.
When to Use Absorption vs Float Charging
Absorption charging is ideal during the final stage of battery charging when the voltage is held constant to fully restore battery capacity without overcharging. Float charging is used after the battery reaches full charge, maintaining it at a low voltage to compensate for self-discharge and keep the battery ready for immediate use. Choosing absorption charging ensures maximum energy storage, while float charging extends battery life by preventing overcharge and sulfation.
Common Misconceptions About Car Battery Charging
Absorption charging maintains a steady voltage to fully charge a car battery without overcharging, while float charging provides a lower voltage to keep the battery at full capacity without causing damage. A common misconception is that float charging can rapidly recharge a dead battery; however, it is designed only to maintain charge over time. Many believe absorption charging is harmful due to higher voltages, but it is essential for safely restoring battery capacity during the charging cycle.
Safety Considerations for Absorption and Float Charging
Absorption charging maintains a higher voltage to fully charge the battery without overcharging, reducing the risk of thermal runaway and electrolyte loss. Float charging uses a lower, constant voltage to keep the battery at full charge while minimizing gassing and battery degradation. Proper management of absorption and float stages ensures battery safety by preventing overheating, reducing corrosion, and extending overall battery life.
Choosing the Right Charging Method for Your Vehicle Battery
Absorption charging delivers a steady voltage to fully charge the vehicle battery while preventing overheating, making it ideal for deep-cycle and lead-acid batteries. Float charging maintains a lower voltage to keep the battery at full capacity without overcharging, suitable for long-term storage and standby power applications. Selecting the correct method depends on usage patterns, battery type, and whether the battery requires full recharge or maintenance charging.
Absorption Charging vs Float Charging Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com