Spot welds create strong, localized joints by fusing overlapping metal surfaces through heat and pressure, ideal for thin sheet metals. Plug welds repair holes or gaps by filling a drilled or punched hole with weld material, providing structural reinforcement. Choosing between spot weld and plug weld depends on the type of repair, metal thickness, and desired joint strength.
Table of Comparison
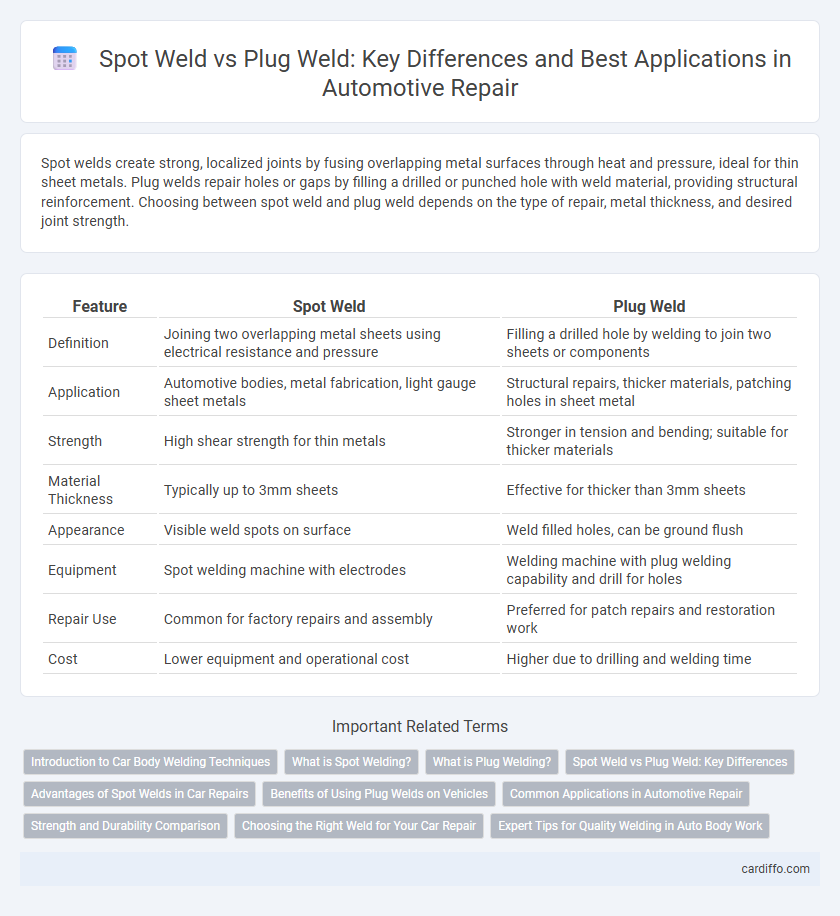
| Feature | Spot Weld | Plug Weld |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joining two overlapping metal sheets using electrical resistance and pressure | Filling a drilled hole by welding to join two sheets or components |
| Application | Automotive bodies, metal fabrication, light gauge sheet metals | Structural repairs, thicker materials, patching holes in sheet metal |
| Strength | High shear strength for thin metals | Stronger in tension and bending; suitable for thicker materials |
| Material Thickness | Typically up to 3mm sheets | Effective for thicker than 3mm sheets |
| Appearance | Visible weld spots on surface | Weld filled holes, can be ground flush |
| Equipment | Spot welding machine with electrodes | Welding machine with plug welding capability and drill for holes |
| Repair Use | Common for factory repairs and assembly | Preferred for patch repairs and restoration work |
| Cost | Lower equipment and operational cost | Higher due to drilling and welding time |
Introduction to Car Body Welding Techniques
Spot welds, commonly used in car body repair, join overlapping metal sheets by applying pressure and heat through an electric current, creating a strong but localized bond ideal for thin metals. Plug welds involve filling holes in one metal sheet with weld material to join it to another, offering a versatile option for connecting different thicknesses or replacing removed spot welds. Understanding these techniques is essential for ensuring structural integrity and durability in automotive body repairs.
What is Spot Welding?
Spot welding is a resistance welding process that joins two or more metal sheets by applying pressure and heat generated from an electric current to a small area, creating a strong bond at the weld spot. Commonly used in automotive repair and manufacturing, spot welding provides quick, efficient, and clean joints without requiring filler material. The process is ideal for thin sheet metals, especially steel and aluminum, ensuring structural integrity and minimal distortion.
What is Plug Welding?
Plug welding is a repair technique used to join two overlapping metal surfaces by filling a drilled or punched hole in the top layer with weld metal, creating a strong, localized weld. Unlike spot welding, which uses electrical resistance to fuse metal surfaces, plug welding relies on molten filler metal to bond the parts together. This method is commonly applied in automotive and structural repairs to reinforce joints where traditional welding is not feasible.
Spot Weld vs Plug Weld: Key Differences
Spot welds join two overlapping metal sheets by applying pressure and heat through electrodes at specific points, creating localized fusion ideal for thin materials. Plug welds involve filling drilled or punched holes in one metal piece with weld material to bond it to an underlying surface, offering greater strength and suitability for thicker metals. Spot welds prioritize speed and minimal deformation, while plug welds provide enhanced structural integrity and resistance to shear forces.
Advantages of Spot Welds in Car Repairs
Spot welds in car repairs offer superior strength and durability by securely joining overlapping metal sheets with minimal heat distortion. This welding technique ensures faster production times and cost efficiency, making it ideal for automotive assembly and structural repairs. Spot welds also provide improved corrosion resistance by maintaining tight, consistent seams, enhancing the vehicle's longevity and safety.
Benefits of Using Plug Welds on Vehicles
Plug welds provide enhanced structural integrity by creating a solid bond between overlapping metal surfaces in vehicle repairs, reducing the risk of weak points compared to spot welds. They offer greater versatility in accessing hard-to-reach areas on vehicle frames and panels, ensuring a thorough and durable connection in complex repair scenarios. The improved corrosion resistance and load distribution of plug welds contribute to longer-lasting repairs and increased safety in automotive restoration.
Common Applications in Automotive Repair
Spot welds are commonly used in automotive repair for joining sheet metal parts, such as body panels and structural components, due to their strength and efficiency in mass production. Plug welds serve as an effective alternative when spot welding is impractical, often applied in repairing holes or joining overlapping metal sections in areas like floor pans and rocker panels. Both welding techniques ensure structural integrity and are selected based on accessibility, thickness, and repair requirements.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Spot welds offer high strength and durability for thin metal sheets by fusing overlapping surfaces with concentrated heat, making them ideal for automotive and sheet metal repairs. Plug welds provide superior strength in thicker materials by filling a hole with weld metal, creating a robust bond that resists shear forces effectively. Both methods ensure structural integrity, but plug welds typically deliver enhanced durability in load-bearing applications due to deeper penetration and greater weld volume.
Choosing the Right Weld for Your Car Repair
Spot welds provide strong, localized bonding ideal for thin metal sheets in automotive repairs, offering quick and efficient joint fastening. Plug welds fill holes and create a more robust structural connection, especially useful when welding thicker materials or overlapping parts. Selecting the right weld depends on the metal thickness, component strength requirements, and accessibility, ensuring durable and safe car repair outcomes.
Expert Tips for Quality Welding in Auto Body Work
Spot welds provide strong, localized joining ideal for overlapping sheet metal in auto body repairs, ensuring structural integrity with minimal distortion. Plug welds, used to fill holes and join thicker materials, offer enhanced strength for repairing rusted or damaged panels by fusing inner and outer layers. Expert tips include proper weld spacing, controlling heat input to prevent warping, and using corrosion-resistant welding materials to maintain durability and appearance in auto body work.
Spot weld vs Plug weld Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com