OBD-II scanning provides a standardized method for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes across most vehicles, enabling quick identification of engine and emissions-related issues. CAN bus diagnostics offer deeper insights by communicating directly with the vehicle's complex network of electronic control units, allowing for real-time monitoring and advanced troubleshooting. Combining both approaches enhances repair accuracy and efficiency by addressing both broad and detailed diagnostic needs.
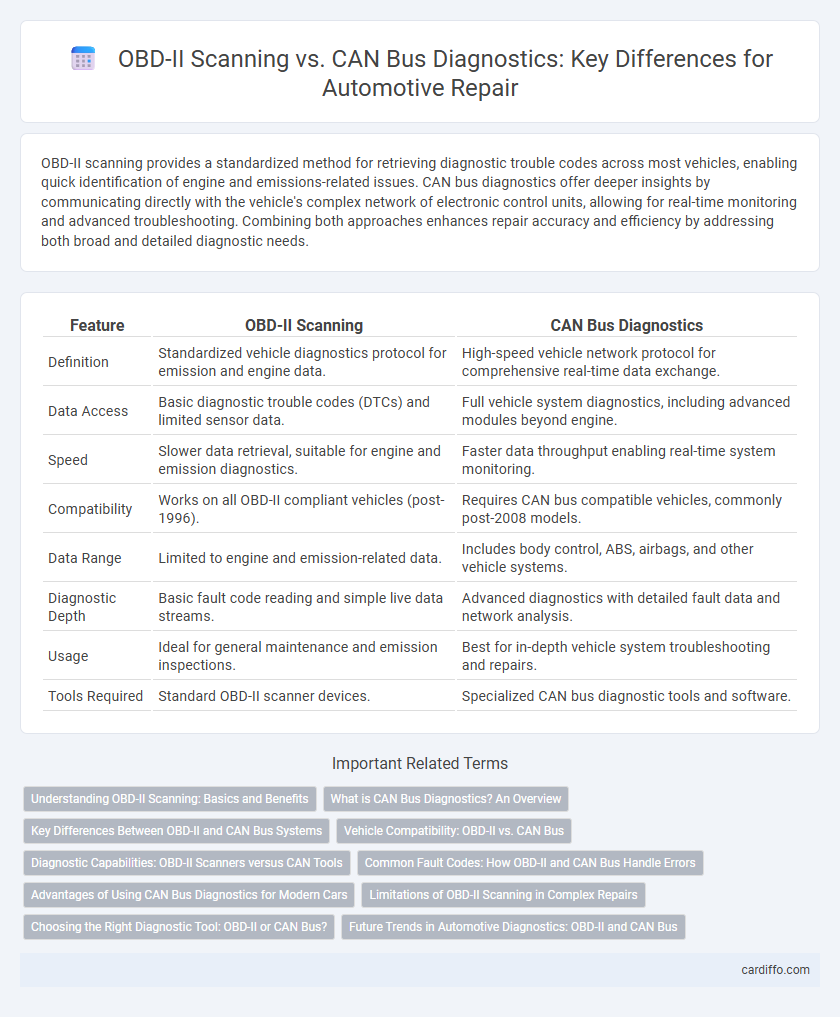
Table of Comparison
| Feature | OBD-II Scanning | CAN Bus Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardized vehicle diagnostics protocol for emission and engine data. | High-speed vehicle network protocol for comprehensive real-time data exchange. |
| Data Access | Basic diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and limited sensor data. | Full vehicle system diagnostics, including advanced modules beyond engine. |
| Speed | Slower data retrieval, suitable for engine and emission diagnostics. | Faster data throughput enabling real-time system monitoring. |
| Compatibility | Works on all OBD-II compliant vehicles (post-1996). | Requires CAN bus compatible vehicles, commonly post-2008 models. |
| Data Range | Limited to engine and emission-related data. | Includes body control, ABS, airbags, and other vehicle systems. |
| Diagnostic Depth | Basic fault code reading and simple live data streams. | Advanced diagnostics with detailed fault data and network analysis. |
| Usage | Ideal for general maintenance and emission inspections. | Best for in-depth vehicle system troubleshooting and repairs. |
| Tools Required | Standard OBD-II scanner devices. | Specialized CAN bus diagnostic tools and software. |
Understanding OBD-II Scanning: Basics and Benefits
OBD-II scanning provides a standardized method to access vehicle diagnostics by reading trouble codes related to engine, transmission, and emissions systems. Unlike CAN bus diagnostics that delve into comprehensive real-time data across multiple vehicle modules, OBD-II focuses on emission control and basic fault detection, making it essential for quick, cost-effective repairs. This method enhances repair efficiency by facilitating early fault identification and simplifying emissions compliance testing.
What is CAN Bus Diagnostics? An Overview
CAN Bus diagnostics is a communication protocol used in modern vehicles to enable real-time data exchange between electronic control units (ECUs). Unlike traditional OBD-II scanning that primarily reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), CAN Bus diagnostics provides detailed information on sensor data, control signals, and system status, allowing for precise fault detection and system monitoring. This advanced diagnostic method enhances vehicle repair efficiency by delivering comprehensive insights into the vehicle's networked electronic systems.
Key Differences Between OBD-II and CAN Bus Systems
OBD-II scanning provides standardized diagnostic codes and data primarily for emission-related issues, making it compatible with a wide range of vehicle models. CAN bus diagnostics enable real-time communication between multiple electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle, offering more detailed and comprehensive system-level information. Unlike OBD-II's single-wire protocol, CAN bus uses a two-wire differential signaling system, enhancing data transmission speed and robustness in modern automotive networks.
Vehicle Compatibility: OBD-II vs. CAN Bus
OBD-II scanning provides broad vehicle compatibility across most cars manufactured from 1996 onward, using standardized protocols for emissions and engine diagnostics. CAN bus diagnostics offer enhanced compatibility for newer vehicles, leveraging the Controller Area Network to communicate with numerous electronic control units (ECUs) for more comprehensive system analysis. Understanding vehicle compatibility is crucial, as OBD-II scanners may not fully access data in modern CAN bus-equipped vehicles, impacting diagnostic accuracy.
Diagnostic Capabilities: OBD-II Scanners versus CAN Tools
OBD-II scanners primarily read generic fault codes standardized across most vehicles, enabling basic engine and emission system diagnostics. CAN bus diagnostic tools provide deeper access to vehicle-specific data, including real-time parameters and module communication, supporting advanced troubleshooting beyond engine control units. This expanded diagnostic capability allows CAN tools to identify complex faults in subsystems such as ABS, airbag, and transmission modules, which OBD-II scanners often cannot detect.
Common Fault Codes: How OBD-II and CAN Bus Handle Errors
OBD-II scanners detect common fault codes by accessing standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) across all vehicle systems, allowing identification of engine, transmission, and emission issues. CAN bus diagnostics provide real-time data by communicating with multiple control modules and sensors, enabling more precise fault isolation through network-wide error code analysis. While OBD-II offers broad compatibility for basic error retrieval, CAN bus systems enhance diagnostic accuracy with detailed, module-specific fault information critical for advanced vehicle repairs.
Advantages of Using CAN Bus Diagnostics for Modern Cars
CAN bus diagnostics offer faster and more accurate data transmission compared to traditional OBD-II scanning, enabling real-time monitoring of vehicle systems. This advanced communication protocol supports multi-node fault detection, which enhances troubleshooting efficiency for complex modern car electronics. Greater diagnostic coverage and the ability to access proprietary manufacturer codes make CAN bus diagnostics essential for comprehensive vehicle repair.
Limitations of OBD-II Scanning in Complex Repairs
OBD-II scanning provides basic diagnostic trouble codes but often lacks the precision needed for complex repairs due to limited access to manufacturer-specific data and advanced system parameters. Unlike CAN bus diagnostics, which offer detailed real-time communication between vehicle electronic control units, OBD-II scanners cannot fully interpret intricate network interactions or sensor data. This limitation can lead to incomplete diagnostics, prolonging repair times and increasing the risk of misdiagnosis in modern vehicles with sophisticated electronic systems.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool: OBD-II or CAN Bus?
Choosing the right diagnostic tool hinges on the vehicle's communication protocol, as OBD-II scanners provide broad compatibility with most cars manufactured after 1996, offering standardized trouble code reading and emission testing. CAN bus diagnostics deliver deeper access to complex systems in modern vehicles, enabling real-time data monitoring and module-specific troubleshooting beyond basic OBD-II codes. Selecting between OBD-II and CAN bus tools depends on the vehicle's make, model, and diagnostic requirements, with CAN bus tools preferred for advanced diagnostics in newer vehicles equipped with Controller Area Network systems.
Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics: OBD-II and CAN Bus
Future trends in automotive diagnostics emphasize enhanced integration of OBD-II scanning with CAN bus diagnostics, enabling real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance. Advances in wireless communication and cloud-based platforms improve the accuracy and speed of fault detection while reducing diagnostic time. Emerging technologies also facilitate deeper insights into complex vehicle systems, boosting repair efficiency and minimizing downtime.
OBD-II scanning vs CAN bus diagnostics Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com