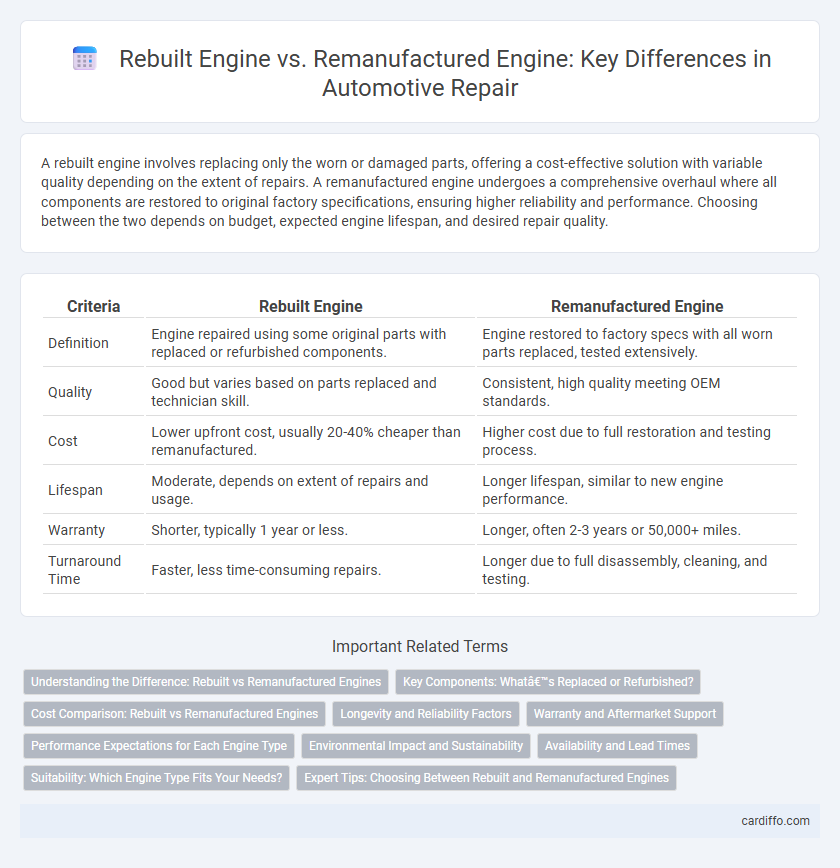
A rebuilt engine involves replacing only the worn or damaged parts, offering a cost-effective solution with variable quality depending on the extent of repairs. A remanufactured engine undergoes a comprehensive overhaul where all components are restored to original factory specifications, ensuring higher reliability and performance. Choosing between the two depends on budget, expected engine lifespan, and desired repair quality.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Rebuilt Engine | Remanufactured Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engine repaired using some original parts with replaced or refurbished components. | Engine restored to factory specs with all worn parts replaced, tested extensively. |
| Quality | Good but varies based on parts replaced and technician skill. | Consistent, high quality meeting OEM standards. |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, usually 20-40% cheaper than remanufactured. | Higher cost due to full restoration and testing process. |
| Lifespan | Moderate, depends on extent of repairs and usage. | Longer lifespan, similar to new engine performance. |
| Warranty | Shorter, typically 1 year or less. | Longer, often 2-3 years or 50,000+ miles. |
| Turnaround Time | Faster, less time-consuming repairs. | Longer due to full disassembly, cleaning, and testing. |
Understanding the Difference: Rebuilt vs Remanufactured Engines
Rebuilt engines are repaired using used components that are cleaned, inspected, and replaced as needed to restore functionality, whereas remanufactured engines are completely disassembled, inspected, and rebuilt with both new and reconditioned parts to meet OEM specifications. Rebuilt engines often vary in quality depending on the extent of repairs and parts used, while remanufactured engines typically undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and performance similar to new engines. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed decisions based on budget, expected engine lifespan, and warranty coverage.
Key Components: What’s Replaced or Refurbished?
Rebuilt engines typically have key components like pistons, rings, bearings, and gaskets replaced or machined to restore functionality, often reusing original parts with selective refurbishment. Remanufactured engines, in contrast, undergo a complete teardown with all major parts--including cylinder heads, blocks, and crankshafts--inspected, re-machined or replaced to meet factory specifications. This process ensures critical engine components meet strict tolerances and performance standards, providing a near-new engine quality compared to rebuilt options.
Cost Comparison: Rebuilt vs Remanufactured Engines
Rebuilt engines typically cost 30-50% less than remanufactured engines due to the selective replacement of worn parts rather than comprehensive overhaul. Remanufactured engines undergo complete disassembly and reassembly with new components, which increases labor and material expenses, resulting in higher prices. Choosing a rebuilt engine may save upfront costs, while remanufactured engines often provide longer warranties and enhanced reliability, influencing overall value.
Longevity and Reliability Factors
Rebuilt engines offer moderate longevity and reliability by replacing only worn or damaged parts, which can vary based on the quality of the repair. Remanufactured engines undergo a comprehensive process restoring all components to factory specifications, resulting in higher longevity and consistent reliability. Choosing a remanufactured engine generally ensures extended engine life and reduced risk of failure compared to a rebuilt engine.
Warranty and Aftermarket Support
Rebuilt engines typically come with limited warranties ranging from 3 to 12 months, reflecting the variability in parts replaced and labor quality, while remanufactured engines often include comprehensive warranties lasting up to 3 years or 100,000 miles, ensuring greater reliability and confidence for the buyer. Aftermarket support for rebuilt engines may be inconsistent due to varying shop standards and part sources, whereas remanufactured engines benefit from standardized factory specifications and consistent aftermarket support from established manufacturers. Warranty coverage and strong aftermarket backing make remanufactured engines a preferred option for long-term repair solutions.
Performance Expectations for Each Engine Type
Rebuilt engines typically involve replacing worn components and restoring the engine to a functional condition, offering performance comparable to a used engine but with improved reliability. Remanufactured engines are restored to meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications through extensive machining and the installation of new parts, resulting in superior performance and longevity. Performance expectations favor remanufactured engines for durability and consistency, while rebuilt engines provide a cost-effective solution with satisfactory performance for everyday use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rebuilt engines reuse existing components, reducing waste and conserving raw materials, which lowers the overall environmental footprint compared to manufacturing new engines. Remanufactured engines undergo a thorough process that restores parts to like-new condition, extending engine life and minimizing resource extraction and energy consumption. Both options support sustainability by promoting circular economy practices and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with producing new engine components.
Availability and Lead Times
Rebuilt engines are typically more readily available due to their repair-based process, allowing for quicker turnaround times, often within a few days to a week. Remanufactured engines undergo a complete disassembly and replacement of all worn components, resulting in longer lead times that can range from several weeks to over a month. Choosing between a rebuilt and remanufactured engine often depends on immediate availability needs versus long-term reliability and warranty coverage.
Suitability: Which Engine Type Fits Your Needs?
Rebuilt engines are ideal for vehicles with moderate wear and limited budget, as they use refurbished original parts to restore functionality. Remanufactured engines undergo comprehensive disassembly, replacement of worn components, and rigorous testing, making them suitable for long-term reliability and higher performance. Choosing between rebuilt and remanufactured engines depends on factors like vehicle age, usage intensity, and desired engine lifespan.
Expert Tips: Choosing Between Rebuilt and Remanufactured Engines
Expert tips for choosing between rebuilt and remanufactured engines emphasize understanding the difference in processes: rebuilt engines are repaired using a combination of original and new parts, while remanufactured engines undergo a complete restoration to factory specifications. Consider factors such as warranty length, cost, and vehicle usage to determine the best option; remanufactured engines generally offer longer warranties and more reliability. Evaluating engine history and sourcing engines from reputable suppliers ensures optimal performance and longevity in repairs.
Rebuilt engine vs Remanufactured engine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com