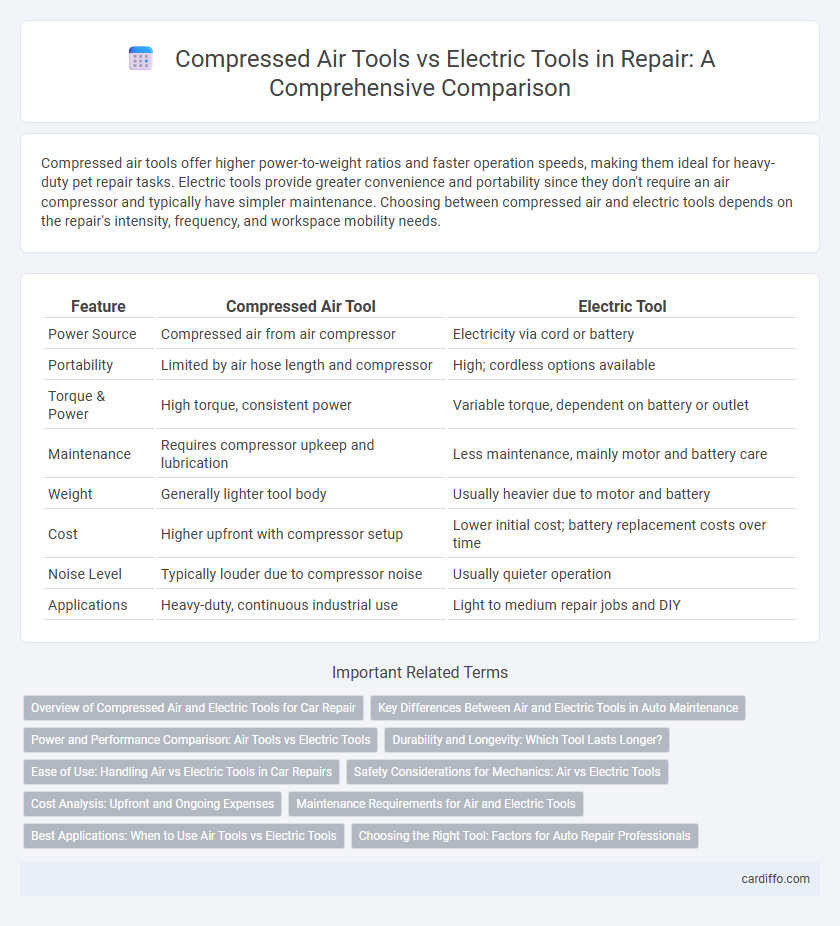
Compressed air tools offer higher power-to-weight ratios and faster operation speeds, making them ideal for heavy-duty pet repair tasks. Electric tools provide greater convenience and portability since they don't require an air compressor and typically have simpler maintenance. Choosing between compressed air and electric tools depends on the repair's intensity, frequency, and workspace mobility needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compressed Air Tool | Electric Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air from air compressor | Electricity via cord or battery |
| Portability | Limited by air hose length and compressor | High; cordless options available |
| Torque & Power | High torque, consistent power | Variable torque, dependent on battery or outlet |
| Maintenance | Requires compressor upkeep and lubrication | Less maintenance, mainly motor and battery care |
| Weight | Generally lighter tool body | Usually heavier due to motor and battery |
| Cost | Higher upfront with compressor setup | Lower initial cost; battery replacement costs over time |
| Noise Level | Typically louder due to compressor noise | Usually quieter operation |
| Applications | Heavy-duty, continuous industrial use | Light to medium repair jobs and DIY |
Overview of Compressed Air and Electric Tools for Car Repair
Compressed air tools and electric tools each play crucial roles in car repair, offering distinct advantages based on power source and application. Compressed air tools, powered by an air compressor, deliver high torque and durability ideal for heavy-duty tasks like impact wrenches and spray guns, ensuring consistent performance in demanding environments. Electric tools, relying on battery or corded power, offer greater portability and precision for tasks such as drilling and grinding, with advancements in lithium-ion technology enhancing their runtime and efficiency.
Key Differences Between Air and Electric Tools in Auto Maintenance
Compressed air tools in auto maintenance offer higher power-to-weight ratios and greater torque for demanding repair tasks, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like impact wrenches and grinders. Electric tools provide portability, consistent power without the need for an air compressor, and easier maintenance, suitable for precision work and light to medium repairs. The choice between compressed air and electric tools depends on factors such as job intensity, workspace setup, and tool longevity.
Power and Performance Comparison: Air Tools vs Electric Tools
Compressed air tools deliver higher power-to-weight ratios, offering superior torque and faster cycle times compared to electric tools, making them ideal for heavy-duty repair tasks. Electric tools provide consistent power output with easier control and require less maintenance, suitable for precision and intermittent use. Performance varies based on compressor capacity and battery technology, influencing tool efficiency and operational cost.
Durability and Longevity: Which Tool Lasts Longer?
Compressed air tools typically offer greater durability and longevity due to their simpler mechanical design and fewer moving parts compared to electric tools. These pneumatic tools resist overheating and wear, making them ideal for heavy-duty and continuous use in repair environments. Electric tools, while convenient and versatile, often have components like brushes and motors that require more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Ease of Use: Handling Air vs Electric Tools in Car Repairs
Compressed air tools offer lightweight construction and reduced vibration, enhancing operator comfort during extended car repair tasks. Electric tools provide straightforward plug-and-play functionality without requiring air compressors, simplifying setup and portability in varied workshop environments. Ergonomic design in both tool types improves precision, but compressed air tools often demand more skill to manage air pressure and hose maneuverability.
Safety Considerations for Mechanics: Air vs Electric Tools
Compressed air tools reduce the risk of electric shock and are less prone to overheating, making them safer for use in wet or oily environments common in automotive repair shops. Electric tools, while offering precise control and quieter operation, require rigorous insulation checks and proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards. Mechanics must also consider the potential for compressed air tools to cause sudden movements or component damage due to high air pressure, necessitating careful handling and appropriate safety gear.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Ongoing Expenses
Compressed air tools typically have lower upfront costs due to simpler construction but require an investment in an air compressor, increasing overall expenses. Electric tools often present higher initial prices but benefit from lower ongoing maintenance and energy costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves comparing compressor energy consumption and maintenance against the durability and efficiency of electric alternatives.
Maintenance Requirements for Air and Electric Tools
Compressed air tools require regular lubrication, filter changes, and moisture removal from the air supply to prevent rust and ensure optimal performance. Electric tools demand routine inspection of cords, brushes, and switches, with occasional cleaning to avoid overheating and electrical faults. Proper maintenance schedules tailored to air and electric tools extend their lifespan and enhance reliability in repair tasks.
Best Applications: When to Use Air Tools vs Electric Tools
Air tools excel in heavy-duty, continuous use scenarios such as automotive repair and manufacturing due to their high power-to-weight ratio and durability. Electric tools are ideal for precision tasks and intermittent use, offering portability and easier maintenance for home repairs and small-scale projects. Selecting the right tool depends on factors like workload intensity, mobility needs, and power source availability.
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors for Auto Repair Professionals
Selecting between compressed air tools and electric tools for auto repair hinges on efficiency, power output, and maintenance needs. Compressed air tools deliver high torque and durability, ideal for repetitive tasks such as impact wrenching and sanding, while electric tools offer precision, portability, and quieter operation suited for delicate repairs and diagnostics. Auto repair professionals must weigh factors like workspace constraints, tool lifespan, and energy costs to optimize functionality and minimize downtime.
compressed air tool vs electric tool Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com