Copper radiators offer superior thermal conductivity and durability, making them ideal for high-performance cooling systems, whereas aluminum radiators are lighter and more cost-effective, providing efficient heat dissipation in everyday applications. Copper's ability to withstand corrosion enhances longevity but adds weight and expense compared to aluminum. Choosing between copper and aluminum radiators depends on balancing budget constraints with specific cooling requirements and long-term maintenance considerations.
Table of Comparison
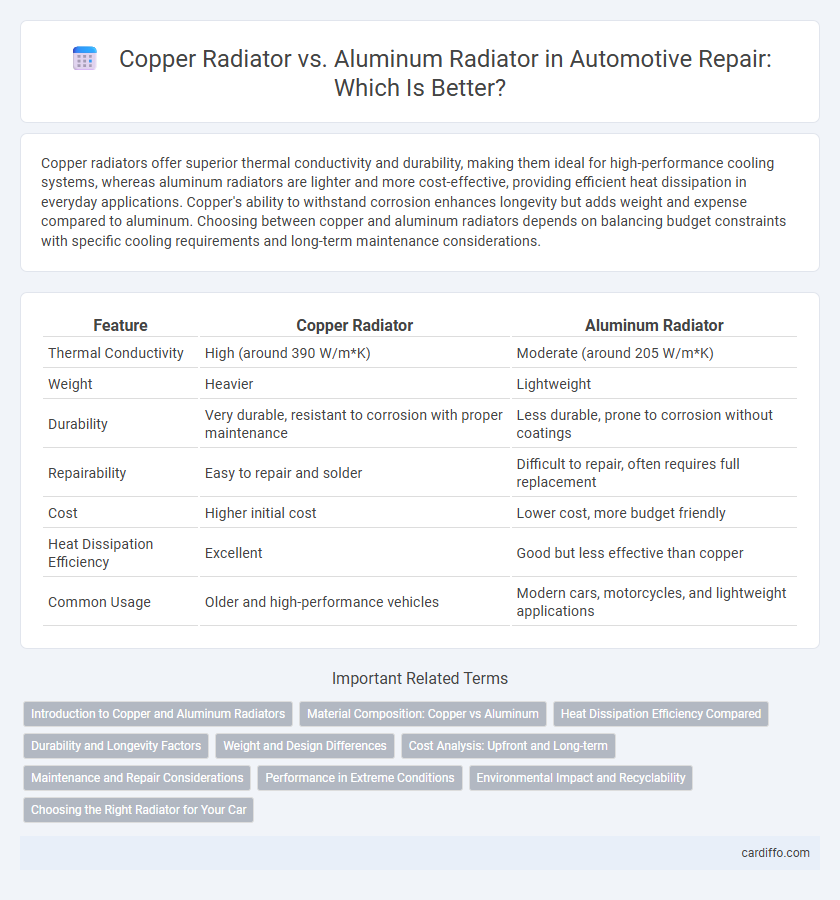
| Feature | Copper Radiator | Aluminum Radiator |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (around 390 W/m*K) | Moderate (around 205 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to corrosion with proper maintenance | Less durable, prone to corrosion without coatings |
| Repairability | Easy to repair and solder | Difficult to repair, often requires full replacement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, more budget friendly |
| Heat Dissipation Efficiency | Excellent | Good but less effective than copper |
| Common Usage | Older and high-performance vehicles | Modern cars, motorcycles, and lightweight applications |
Introduction to Copper and Aluminum Radiators
Copper radiators consist of copper tubes and fins, offering excellent thermal conductivity and durability, making them a popular choice for high-performance cooling systems. Aluminum radiators, made from lightweight aluminum alloys, provide efficient heat dissipation with reduced weight, commonly used in modern vehicles for improved fuel efficiency. Both radiator types have distinct advantages in repair scenarios, with copper radiators being easier to solder and aluminum radiators requiring specialized welding techniques.
Material Composition: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper radiators offer superior thermal conductivity, enabling more efficient heat dissipation compared to aluminum radiators, which have lower thermal conductivity but benefit from lighter weight and cost-effectiveness. Copper's durability and resistance to corrosion often make it ideal for heavy-duty cooling systems, while aluminum radiators are commonly preferred in automotive applications for their balance of performance and reduced weight. Material composition directly affects radiator lifespan, cooling efficiency, and overall system performance depending on the specific repair and operational requirements.
Heat Dissipation Efficiency Compared
Copper radiators exhibit superior heat dissipation efficiency due to copper's higher thermal conductivity of approximately 400 W/mK, enabling faster heat transfer from the engine coolant to the surrounding air. Aluminum radiators, while lighter and more cost-effective, have a thermal conductivity around 237 W/mK, resulting in comparatively lower heat dissipation performance. This difference makes copper radiators more effective in maintaining optimal engine temperatures under heavy-duty or high-performance conditions.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Copper radiators offer superior durability due to their resistance to corrosion and high thermal conductivity, which ensures efficient heat dissipation over time. Aluminum radiators, while lightweight and cost-effective, tend to be more susceptible to wear from oxidation and physical damage under extreme conditions. Longevity factors favor copper radiators in repair scenarios where extended lifespan and minimal maintenance are critical for optimal performance.
Weight and Design Differences
Copper radiators are heavier due to the higher density of copper, which provides superior heat conductivity but increases overall vehicle weight, potentially affecting fuel efficiency. Aluminum radiators are significantly lighter, offering better weight reduction benefits and enhanced performance in modern vehicle designs where efficiency and aerodynamics are prioritized. The intricate design complexity in copper radiators allows for easier repair and durability, while aluminum radiators favor sleek, compact designs with improved corrosion resistance but can be more challenging to repair.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term
Copper radiators generally have a higher upfront cost compared to aluminum radiators due to the material's superior thermal conductivity and durability. Over the long term, copper radiators tend to offer better corrosion resistance and repairability, potentially reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Aluminum radiators are more cost-effective initially but may incur higher long-term costs due to susceptibility to corrosion and less efficient heat dissipation in some conditions.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Copper radiators offer superior corrosion resistance and easier soldering for repairs, making maintenance more straightforward in the long term. Aluminum radiators require specialized welding techniques and are more prone to galvanic corrosion, which can complicate repairs and increase maintenance frequency. Choosing between copper and aluminum impacts repair costs and downtime due to differences in ease of fixing leaks and material durability.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Copper radiators offer superior thermal conductivity, allowing for faster heat dissipation and enhanced cooling performance in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and heavy engine loads. Aluminum radiators are lighter and more resistant to corrosion but may not cool as efficiently under severe stress due to lower thermal conductivity. For demanding applications, copper radiators provide better reliability and temperature regulation, ensuring engine stability in harsh environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Copper radiators offer higher recyclability rates due to copper's valuable and reusable nature, reducing environmental waste compared to aluminum radiators. Aluminum radiators, while lightweight and energy-efficient during vehicle operation, often face challenges in recycling because aluminum alloys can vary and require more complex processing. Choosing copper radiators supports better circular economy practices in automotive repair and promotes sustainable resource management.
Choosing the Right Radiator for Your Car
When choosing the right radiator for your car, consider copper radiators for their superior heat dissipation and durability under high temperatures, which excels in older or high-performance vehicles. Aluminum radiators offer lighter weight and improved corrosion resistance, making them ideal for modern cars aimed at fuel efficiency and longevity. Evaluate compatibility with your vehicle's engine size and cooling requirements to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating.
Copper radiator vs Aluminum radiator Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com