Patch repair involves applying a new material piece over the damaged area to restore surface integrity, offering increased strength and durability for larger or irregular holes. Plug repair focuses on filling a hole from the inside with a compatible material, typically used for smaller, round defects to ensure a secure fit and prevent further damage. Both methods enhance structural stability but differ in application scope and material usage based on the extent and type of damage.
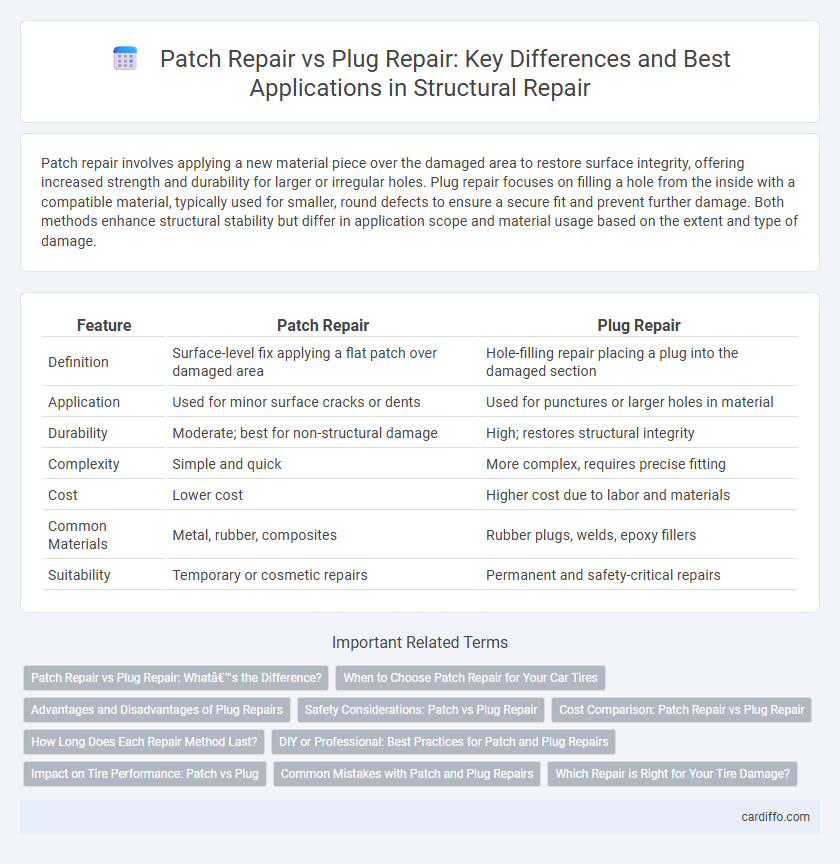
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patch Repair | Plug Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surface-level fix applying a flat patch over damaged area | Hole-filling repair placing a plug into the damaged section |
| Application | Used for minor surface cracks or dents | Used for punctures or larger holes in material |
| Durability | Moderate; best for non-structural damage | High; restores structural integrity |
| Complexity | Simple and quick | More complex, requires precise fitting |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to labor and materials |
| Common Materials | Metal, rubber, composites | Rubber plugs, welds, epoxy fillers |
| Suitability | Temporary or cosmetic repairs | Permanent and safety-critical repairs |
Patch Repair vs Plug Repair: What’s the Difference?
Patch repair involves cutting out a damaged area and replacing it with a large section of new material, ensuring structural integrity and a seamless finish, ideal for extensive or irregular damage. Plug repair, on the other hand, is a smaller, more localized fix where only the damaged portion is removed and filled, commonly used for minor holes or small defects. The choice between patch and plug repair depends on the size, location, and extent of the damage, as well as the desired durability and cosmetic outcome.
When to Choose Patch Repair for Your Car Tires
Patch repair is ideal for small punctures located on the tread area of the tire where the damage does not compromise the tire's structural integrity. It provides a durable and airtight seal by covering the damaged area internally, ensuring safety and longevity. Avoid plug repair when the puncture is near the sidewall or is larger than 1/4 inch, as patch repairs offer a more reliable solution in these cases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plug Repairs
Plug repairs offer the advantage of targeting specific areas of damage, preserving more of the original material and ensuring a durable fix for localized defects such as potholes or cracks. This method typically requires less labor and time compared to full-scale patch repairs, making it cost-effective for small-scale issues. However, plug repairs may be less effective for extensive damage or structural problems, potentially leading to recurring issues if the underlying cause is not fully addressed.
Safety Considerations: Patch vs Plug Repair
Patch repair offers enhanced safety by providing a more secure seal over damaged areas, reducing the risk of further deterioration or leaks in pressure vessels and pipelines. Plug repair, while quicker, may not fully restore structural integrity, potentially compromising safety under high-stress conditions or extreme temperatures. Choosing patch repair aligns better with long-term safety standards and regulatory compliance in critical applications.
Cost Comparison: Patch Repair vs Plug Repair
Patch repair generally incurs higher initial costs due to the extensive surface preparation and materials required, but it offers a longer-lasting solution for larger damages. In contrast, plug repair is more cost-effective for small, localized defects, involving minimal labor and quicker completion times. Budget considerations should weigh the size and severity of the damage against the repair method to optimize overall expense and durability.
How Long Does Each Repair Method Last?
Patch repairs typically offer a long-lasting solution, often extending the life of the damaged area by several years when properly applied with quality materials. Plug repairs tend to be more temporary, serving as a quick fix that may last a few months to a couple of years depending on the extent of the damage and environmental conditions. The durability of both methods depends largely on factors such as surface preparation, repair technique, and exposure to stress or weather.
DIY or Professional: Best Practices for Patch and Plug Repairs
Patch repair provides a reliable method for fixing larger or irregularly shaped holes in materials such as drywall or tires, requiring precise measurements and proper surface preparation to ensure strong adhesion. Plug repair, often preferred for smaller punctures, involves inserting a material strip or plug into the hole to restore integrity quickly and effectively, commonly used in tire maintenance. Both DIY and professional repairs benefit from following manufacturer guidelines, using quality materials, and ensuring thorough curing time to maximize durability and safety.
Impact on Tire Performance: Patch vs Plug
Patch repairs restore the internal structure of the tire by sealing the puncture from the inside, maintaining optimal air retention and overall tire integrity, which results in superior long-term performance. Plug repairs fill the puncture externally but do not address internal damage, potentially leading to air leaks and compromised safety under high-speed or heavy-load conditions. Tire manufacturers and safety experts recommend patch repairs over plug repairs to ensure reliable tire performance and durability.
Common Mistakes with Patch and Plug Repairs
Common mistakes in patch and plug repairs include improper sizing and placement, which can lead to incomplete sealing and further damage. Using incompatible materials or insufficient bonding techniques often results in weak repairs that fail under pressure. Neglecting surface preparation, such as cleaning and drying the area, compromises adhesion and reduces the overall effectiveness of both patch and plug repairs.
Which Repair is Right for Your Tire Damage?
Patch repair is ideal for small punctures located on the tire tread, offering a durable, cost-effective solution that restores air retention without compromising tire integrity. Plug repair suits minor punctures but is less reliable for sidewall damage or larger tears, making it a temporary fix best used when combined with patching. Assess the size, location, and severity of tire damage to determine the appropriate repair method that ensures safety and prolongs tire life.
Patch repair vs plug repair Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com