Composite bumper repair involves restoring plastic or fiberglass materials that require specialized adhesives and heat treatments to ensure flexibility and durability. Metal bumper repair focuses on welding, reshaping, and rust prevention techniques to restore strength and maintain structural integrity. Choosing between composite and metal bumper repair depends on the material properties and damage extent, influencing repair cost and longevity.
Table of Comparison
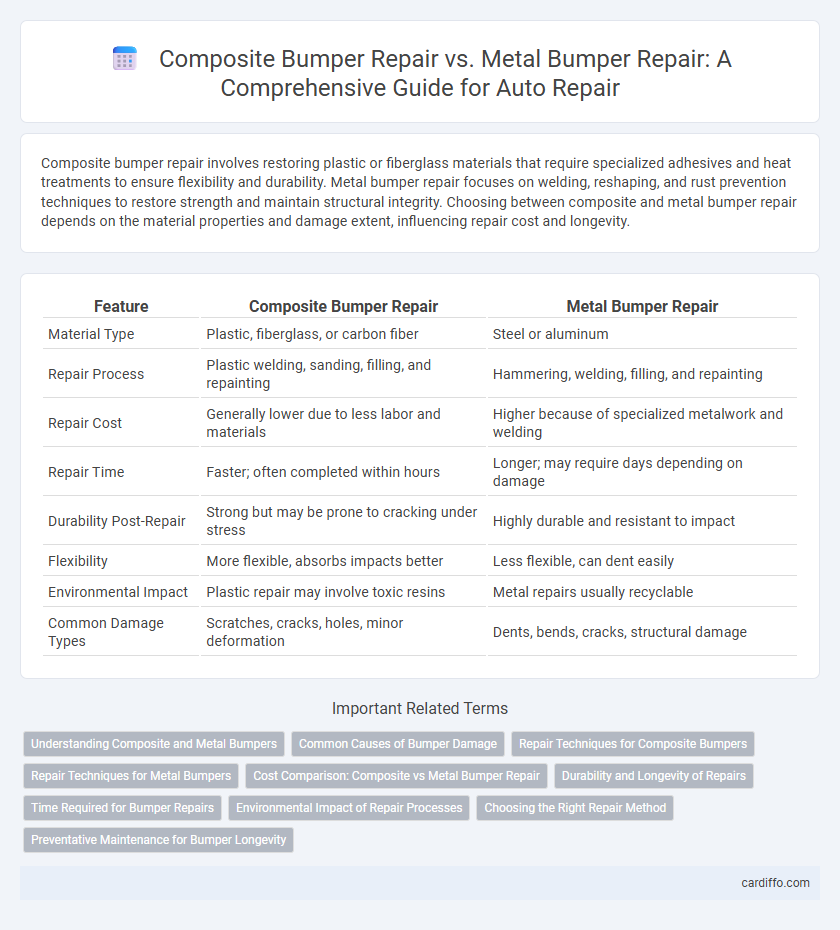
| Feature | Composite Bumper Repair | Metal Bumper Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Plastic, fiberglass, or carbon fiber | Steel or aluminum |
| Repair Process | Plastic welding, sanding, filling, and repainting | Hammering, welding, filling, and repainting |
| Repair Cost | Generally lower due to less labor and materials | Higher because of specialized metalwork and welding |
| Repair Time | Faster; often completed within hours | Longer; may require days depending on damage |
| Durability Post-Repair | Strong but may be prone to cracking under stress | Highly durable and resistant to impact |
| Flexibility | More flexible, absorbs impacts better | Less flexible, can dent easily |
| Environmental Impact | Plastic repair may involve toxic resins | Metal repairs usually recyclable |
| Common Damage Types | Scratches, cracks, holes, minor deformation | Dents, bends, cracks, structural damage |
Understanding Composite and Metal Bumpers
Composite bumpers, typically made from plastic materials such as polypropylene or polyurethane, offer lightweight durability and flexibility, making them resistant to minor impacts and easier to repair without extensive tools. Metal bumpers, composed primarily of steel or aluminum, provide superior strength and impact resistance but often require specialized welding and painting techniques during repair to restore structural integrity and appearance. Understanding the material composition and repair requirements of composite versus metal bumpers is essential for choosing the most cost-effective and efficient repair approach.
Common Causes of Bumper Damage
Common causes of composite bumper damage include low-speed collisions, scrapes from curbs or parking barriers, and stress fractures due to environmental exposure. Metal bumpers often sustain dents, corrosion, and bending from higher-impact collisions and rust over time. Understanding these damage types helps determine the appropriate repair techniques and materials for composite versus metal bumpers.
Repair Techniques for Composite Bumpers
Composite bumper repair involves specialized techniques such as plastic welding, epoxy resin application, and heat gun reshaping to restore structural integrity and flexibility. Unlike metal bumper repair, which often requires dent pulling and welding, composite repair emphasizes surface preparation, crack stabilization, and layering with fiberglass or carbon fiber reinforcement. Advanced repair methods ensure durability, color matching, and resistance to environmental damage for composite materials.
Repair Techniques for Metal Bumpers
Metal bumper repair typically involves techniques such as panel beating, welding, and grinding to restore the bumper's original shape and strength. Skilled technicians use specialized tools to remove dents and cracks, ensuring structural integrity and smooth surface finish. Unlike composite bumpers, metal repairs often require precise heat application and metal shaping to prevent further damage and corrosion.
Cost Comparison: Composite vs Metal Bumper Repair
Composite bumper repair generally costs less than metal bumper repair due to lower material prices and simpler labor requirements. Metal bumpers often incur higher expenses because of welding, rust removal, and specialized tools needed for repairs. Insurance premiums can also vary, with composite bumper repairs typically resulting in lower claims costs compared to metal counterparts.
Durability and Longevity of Repairs
Composite bumper repair offers enhanced durability due to its resistance to rust, corrosion, and minor impacts, ensuring longer-lasting results compared to metal bumper repairs. Metal bumper repair, while structurally robust, often requires additional treatment to prevent rust and may experience reduced longevity in harsh weather conditions. Choosing composite material for bumper repairs can result in a more resilient and maintenance-free finish over time.
Time Required for Bumper Repairs
Composite bumper repair typically requires less time compared to metal bumper repair due to the material's flexibility and ease of reshaping. Metal bumpers often need welding, sanding, and repainting, which extend the overall repair process. On average, composite bumper repairs can be completed in a few hours, while metal bumper repairs may take several days to ensure structural integrity and proper finish.
Environmental Impact of Repair Processes
Composite bumper repair generates less environmental waste due to the ability to restore damaged areas with minimal material removal and the use of eco-friendly adhesives and fillers. In contrast, metal bumper repair often involves energy-intensive welding and repainting processes, leading to higher emissions and increased use of hazardous chemicals. Selecting composite repair methods reduces carbon footprint and lowers the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with traditional metal refurbishing.
Choosing the Right Repair Method
Selecting the ideal repair method depends on the bumper material and damage severity; composite bumpers, made from reinforced plastics, often require plastic welding and specialized fillers, while metal bumpers benefit from traditional dent repair and welding techniques. Composite repair offers lightweight durability and corrosion resistance, making it cost-effective for minor to moderate damage, whereas metal repair ensures structural integrity for severe impacts. Evaluating factors like repair cost, longevity, and vehicle make guides the choice between composite or metal bumper restoration.
Preventative Maintenance for Bumper Longevity
Composite bumper repair involves specialized techniques such as plastic welding and resin application that restore flexibility and minimize cracks, enhancing durability. Metal bumper repair requires rust prevention treatments and dent removal to maintain structural integrity and prevent corrosion. Regular inspections and timely maintenance of both materials significantly extend bumper longevity by addressing early signs of damage and wear.
Composite bumper repair vs metal bumper repair Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com