Fuse replacement is a straightforward, cost-effective solution for restoring electrical circuit protection after a failure, typically due to short circuits or overloads. Relay replacement involves addressing more complex electrical issues by ensuring proper switching and control within circuits, often necessary when a device fails to operate correctly despite an intact fuse. Understanding the difference between fuse replacement and relay replacement is crucial for accurate diagnostics and maintaining the functionality of electrical systems.
Table of Comparison
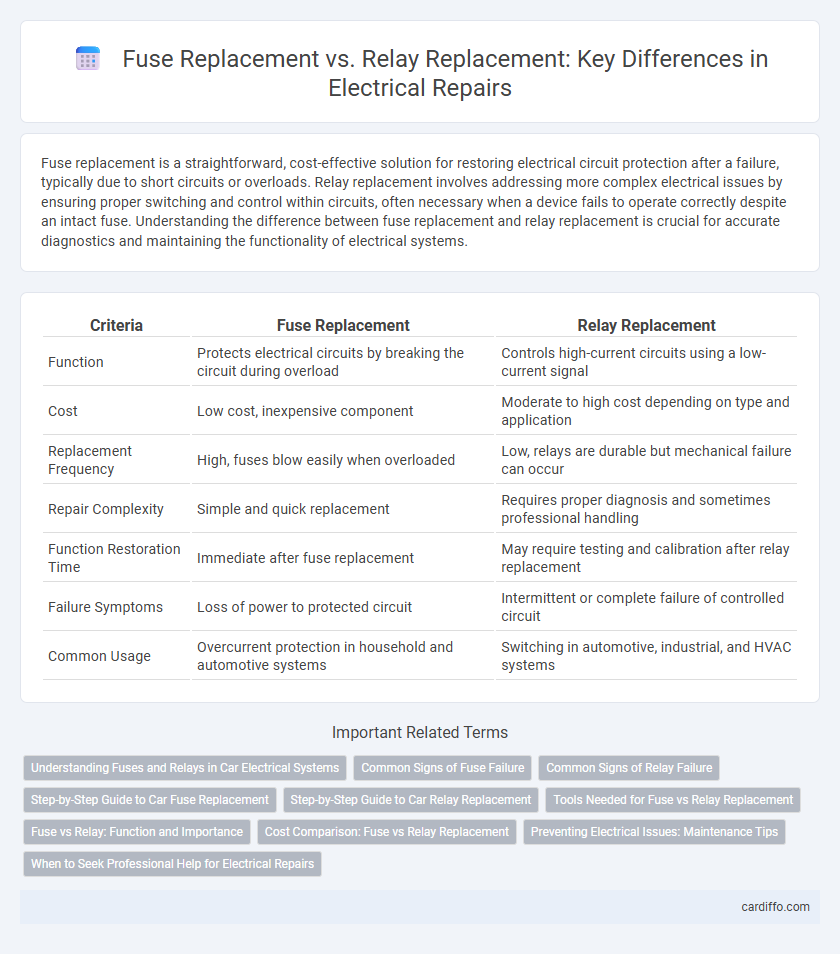
| Criteria | Fuse Replacement | Relay Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Protects electrical circuits by breaking the circuit during overload | Controls high-current circuits using a low-current signal |
| Cost | Low cost, inexpensive component | Moderate to high cost depending on type and application |
| Replacement Frequency | High, fuses blow easily when overloaded | Low, relays are durable but mechanical failure can occur |
| Repair Complexity | Simple and quick replacement | Requires proper diagnosis and sometimes professional handling |
| Function Restoration Time | Immediate after fuse replacement | May require testing and calibration after relay replacement |
| Failure Symptoms | Loss of power to protected circuit | Intermittent or complete failure of controlled circuit |
| Common Usage | Overcurrent protection in household and automotive systems | Switching in automotive, industrial, and HVAC systems |
Understanding Fuses and Relays in Car Electrical Systems
Fuses protect car electrical circuits by breaking the circuit when current flow exceeds safe levels, preventing component damage and fire hazards. Relays control high-current circuits with low-current signals, acting as electrically operated switches to enable efficient power distribution and protection. Correctly diagnosing whether a fuse or relay is faulty is crucial in automotive repair to maintain system integrity and avoid further electrical issues.
Common Signs of Fuse Failure
Common signs of fuse failure include a complete loss of electrical power to a specific circuit, visible burn marks or a broken filament within the fuse, and a noticeable burning smell near the fuse box. Unlike relay replacement which often causes intermittent power issues or clicking sounds, fuse failure typically results in an immediate and consistent electrical cutoff. Identifying these signs quickly helps prevent further damage and ensures timely fuse replacement for safe and reliable repair.
Common Signs of Relay Failure
Common signs of relay failure include intermittent electrical issues, such as flickering lights or unresponsive power windows, indicating poor contact within the relay. Unlike fuse replacement, which addresses simple circuit breaks, relay replacement is necessary when the relay's internal coil or contacts degrade, causing devices to fail intermittently or completely. Diagnosing relay failure often involves checking for clicking sounds or voltage inconsistencies, which are not typical in fuse-related problems.
Step-by-Step Guide to Car Fuse Replacement
Begin car fuse replacement by locating the fuse box, typically found under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. Use the vehicle's manual to identify the specific fuse associated with the malfunctioning component, then carefully remove it using a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers. Insert a new fuse with the exact amperage rating, ensuring a secure fit, and test the circuit function before closing the fuse box.
Step-by-Step Guide to Car Relay Replacement
Car relay replacement involves first locating the faulty relay in the fuse box or relay panel, which is typically found under the hood or inside the dashboard. Next, disconnect the battery to ensure safety, then carefully remove the old relay by pulling it straight out from the socket, avoiding damage to the connectors. Finally, insert the new relay firmly into the socket, reconnect the battery, and test the component to confirm proper functionality.
Tools Needed for Fuse vs Relay Replacement
Fuse replacement requires a basic set of tools, including a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to safely remove and install the fuse, and a multimeter to test for continuity and verify a blown fuse. Relay replacement demands more specialized tools such as a socket set or relay puller to remove the relay securely, along with a multimeter for diagnostic testing of the relay coil and contacts. Both replacements benefit from insulated gloves to ensure safety when working with electrical components.
Fuse vs Relay: Function and Importance
Fuses protect electrical circuits by breaking the circuit when current exceeds a safe level, preventing damage to components. Relays act as electrically operated switches, allowing control of high-current circuits with low-current signals, enabling complex electrical functions. Both are critical in vehicle and electronic system repair, with fuses ensuring circuit safety and relays managing power delivery and system operations.
Cost Comparison: Fuse vs Relay Replacement
Fuse replacement typically costs between $5 and $20, making it a highly affordable repair option due to the simplicity and low price of fuses. Relay replacement, on the other hand, ranges from $30 to $100, reflecting the complexity and higher price of relays in automotive or electrical systems. Choosing between fuse and relay replacement depends on the specific component failure but fuse repairs generally offer a more cost-effective solution.
Preventing Electrical Issues: Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and timely replacement of fuses and relays prevent electrical failures by ensuring consistent circuit protection and proper current flow. Using manufacturer-recommended parts and checking for corrosion or wear on relay contacts enhances system reliability and minimizes risks of short circuits or power surges. Implementing routine maintenance schedules for fuse and relay testing helps detect early faults, reducing downtime and costly repairs in automotive and household electrical systems.
When to Seek Professional Help for Electrical Repairs
Seek professional help for fuse replacement when frequent fuse blows indicate underlying electrical issues beyond simple component failure. Relay replacement requires expert diagnosis if symptoms include intermittent power, unusual noises, or system malfunctions, as these may signal complex wiring or control module problems. Prompt intervention by a certified electrician ensures safety, prevents further damage, and guarantees compliance with electrical codes.
Fuse replacement vs Relay replacement Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com