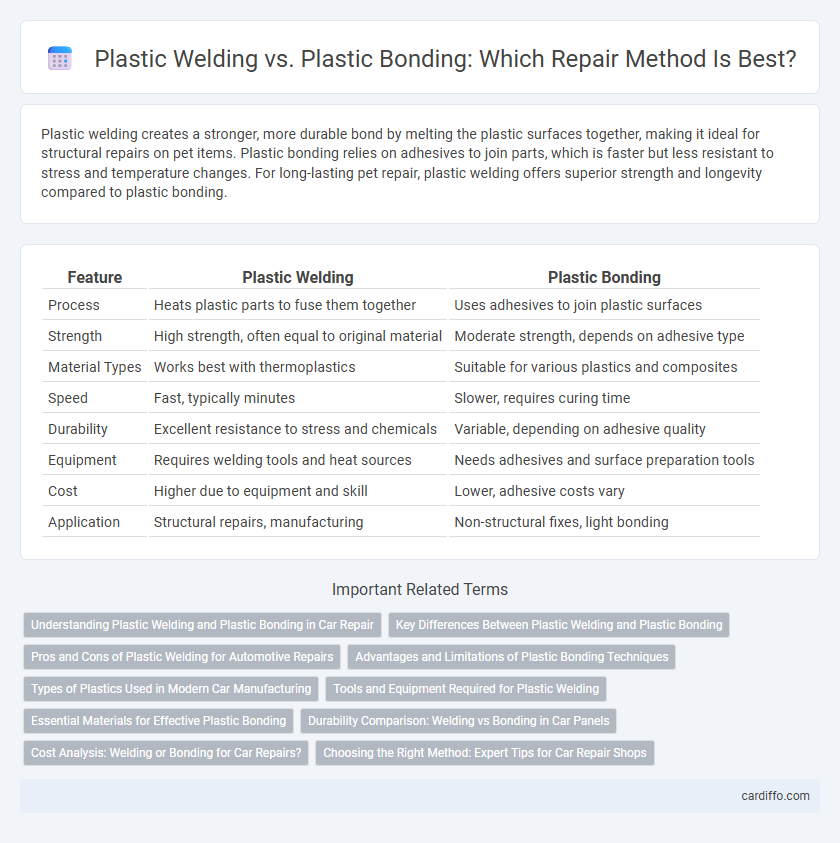
Plastic welding creates a stronger, more durable bond by melting the plastic surfaces together, making it ideal for structural repairs on pet items. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives to join parts, which is faster but less resistant to stress and temperature changes. For long-lasting pet repair, plastic welding offers superior strength and longevity compared to plastic bonding.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Welding | Plastic Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heats plastic parts to fuse them together | Uses adhesives to join plastic surfaces |
| Strength | High strength, often equal to original material | Moderate strength, depends on adhesive type |
| Material Types | Works best with thermoplastics | Suitable for various plastics and composites |
| Speed | Fast, typically minutes | Slower, requires curing time |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to stress and chemicals | Variable, depending on adhesive quality |
| Equipment | Requires welding tools and heat sources | Needs adhesives and surface preparation tools |
| Cost | Higher due to equipment and skill | Lower, adhesive costs vary |
| Application | Structural repairs, manufacturing | Non-structural fixes, light bonding |
Understanding Plastic Welding and Plastic Bonding in Car Repair
Plastic welding in car repair involves using heat or ultrasonic energy to fuse plastic components at the molecular level, creating a strong, durable bond ideal for structural parts like bumpers and dashboards. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives to chemically join plastic surfaces, offering flexibility for fixing intricate shapes or mixed materials but generally yielding less strength than welding. Selecting between plastic welding and bonding depends on factors like plastic type, repair location, and desired strength, with welding preferred for high-stress repairs and bonding suited for cosmetic or less load-bearing fixes.
Key Differences Between Plastic Welding and Plastic Bonding
Plastic welding involves melting and fusing plastic components using heat, creating a strong, permanent joint ideal for structural repairs in materials such as polyethylene or polypropylene. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives to chemically bond surfaces without melting, offering versatility for dissimilar plastics and applications where heat could damage the parts. Key differences include welding's requirement for compatible thermoplastics and higher strength joints versus bonding's suitability for complex shapes and a broader range of materials with relatively lower mechanical strength.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Welding for Automotive Repairs
Plastic welding in automotive repairs offers strong, durable joints ideal for structural components and high-stress areas, providing superior resistance to heat and chemicals compared to plastic bonding. However, it requires specialized equipment and skilled operators, increasing initial repair costs and limiting its use to thermoplastic materials. Despite these challenges, plastic welding results in a more permanent fix with reduced risk of adhesive failure, making it preferable for long-term durability in vehicle repairs.
Advantages and Limitations of Plastic Bonding Techniques
Plastic bonding techniques offer advantages such as the ability to join dissimilar materials and provide uniform stress distribution without requiring high heat, making them suitable for heat-sensitive components. Limitations include lower strength compared to welding and sensitivity to environmental factors like moisture and chemicals, which can degrade adhesive performance over time. Optimal surface preparation and selection of adhesives tailored to the specific plastics are essential to maximize bond durability and reliability in repair applications.
Types of Plastics Used in Modern Car Manufacturing
Modern car manufacturing primarily utilizes thermoplastics such as polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), and polycarbonate (PC) due to their excellent durability and impact resistance. Plastic welding is highly effective for these materials because it melts the plastic at the joint, creating a strong, homogeneous bond ideal for structural components. In contrast, plastic bonding suits thermosetting plastics like polyurethane (PU) and epoxy resin, which cannot be melted and require adhesives to form reliable repairs in non-load-bearing parts.
Tools and Equipment Required for Plastic Welding
Plastic welding requires specialized equipment such as heated tools, ultrasonic welders, or hot air guns to melt and join plastic materials. These tools create precise, strong bonds by fusing the plastic at the molecular level, offering greater durability than adhesives used in plastic bonding. Proper calibration and maintenance of welding equipment are essential to ensure consistent weld quality and structural integrity.
Essential Materials for Effective Plastic Bonding
Essential materials for effective plastic bonding include high-quality adhesives specifically formulated for the type of plastic being repaired, such as cyanoacrylate for rigid plastics or epoxy resins for stronger bonds. Surface preparation tools like fine-grit sandpaper and cleaning agents are critical to remove contaminants and enhance adhesive adherence. Proper application equipment, including applicator tips or brushes, ensures precise and uniform distribution of bonding agents for durable and reliable repairs.
Durability Comparison: Welding vs Bonding in Car Panels
Plastic welding creates a stronger, more durable bond by fusing car panel materials at the molecular level, resulting in enhanced resistance to impact and environmental stress. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives that may degrade over time due to exposure to heat, moisture, and chemicals, leading to potential panel separation. For long-term reliability in car panel repair, welding offers superior durability compared to bonding methods.
Cost Analysis: Welding or Bonding for Car Repairs?
Plastic welding for car repairs generally incurs higher initial equipment costs but delivers stronger, more durable joints resistant to stress and environmental factors. Plastic bonding, while more affordable upfront due to lower tool expenses, may require more frequent maintenance or replacement as adhesives can degrade over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors welding for long-term durability, whereas bonding suits budget-conscious repairs with less critical load requirements.
Choosing the Right Method: Expert Tips for Car Repair Shops
Plastic welding offers a stronger, more durable bond by fusing materials through heat, ideal for structural repairs in car bodies, whereas plastic bonding relies on adhesives suitable for surface-level fixes and non-load-bearing parts. Experts recommend selecting plastic welding for high-stress areas like bumpers and panels to ensure longevity and safety, while plastic bonding works well for cosmetic repairs where precision and flexibility are key. Proper assessment of plastic type and damage severity guides car repair shops in choosing the optimal technique, enhancing repair quality and customer satisfaction.
Plastic welding vs Plastic bonding Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com