Net Cap Cost represents the negotiated price of a leased vehicle after all rebates and incentives are applied, making it the true starting point for lease calculations. Gross Cap Cost, on the other hand, is the vehicle's MSRP plus any additional fees or options before discounts, reflecting the initial selling price. Understanding the difference between Net Cap Cost and Gross Cap Cost helps lessees evaluate the actual cost of the lease and identify potential savings.
Table of Comparison
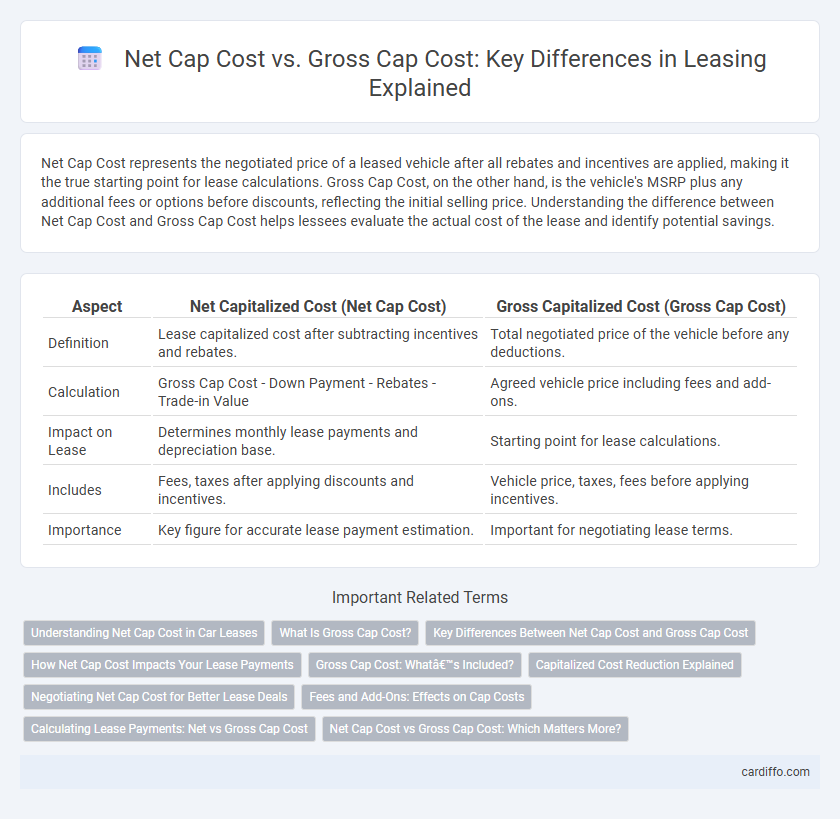
| Aspect | Net Capitalized Cost (Net Cap Cost) | Gross Capitalized Cost (Gross Cap Cost) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease capitalized cost after subtracting incentives and rebates. | Total negotiated price of the vehicle before any deductions. |
| Calculation | Gross Cap Cost - Down Payment - Rebates - Trade-in Value | Agreed vehicle price including fees and add-ons. |
| Impact on Lease | Determines monthly lease payments and depreciation base. | Starting point for lease calculations. |
| Includes | Fees, taxes after applying discounts and incentives. | Vehicle price, taxes, fees before applying incentives. |
| Importance | Key figure for accurate lease payment estimation. | Important for negotiating lease terms. |
Understanding Net Cap Cost in Car Leases
Net Cap Cost in car leases refers to the negotiated price of the vehicle after applying discounts, rebates, and trade-in values, directly affecting monthly lease payments. It represents the actual amount financed by the leasing company, excluding taxes and fees included in the Gross Cap Cost. Understanding Net Cap Cost helps lessees evaluate the true cost of the lease and negotiate better terms.
What Is Gross Cap Cost?
Gross Capitalized Cost (Gross Cap Cost) represents the total initial price of a leased vehicle, including the negotiated selling price, taxes, fees, and any add-ons before incentives or trade-in deductions. This figure serves as the baseline for calculating lease payments and determines the overall financial obligation. Understanding Gross Cap Cost is essential for evaluating lease terms and negotiating a favorable deal.
Key Differences Between Net Cap Cost and Gross Cap Cost
Net Cap Cost represents the negotiated price of a leased asset after factoring in down payments, trade-in credits, and incentives, directly impacting monthly lease payments. Gross Cap Cost is the initial agreed-upon price of the asset before any deductions or adjustments are applied. Understanding these key differences is crucial for accurately calculating lease costs and evaluating financing options.
How Net Cap Cost Impacts Your Lease Payments
Net Cap Cost directly influences your monthly lease payments by determining the amount financed after factoring in incentives, trade-in value, and down payment, reducing the principal balance. A lower Net Cap Cost decreases your lease payments, making the lease more affordable throughout the term. Lease agreements with higher Net Cap Cost result in higher depreciation charges, increasing the overall monthly payment.
Gross Cap Cost: What’s Included?
Gross Cap Cost in a lease agreement includes the negotiated price of the vehicle along with all additional fees such as taxes, registration, dealership fees, and any optional add-ons or warranties. It represents the total amount before any deductions like down payments or incentives, serving as the baseline for calculating the lease payments. Understanding Gross Cap Cost is crucial for evaluating the overall lease expense and negotiating better terms.
Capitalized Cost Reduction Explained
Capitalized Cost Reduction, also known as cap cost reduction, lowers the Net Cap Cost by decreasing the initial price of the leased asset, directly impacting monthly lease payments. Gross Cap Cost signifies the total price of the vehicle before any reductions, while Net Cap Cost reflects the final amount financed after applying down payment, trade-in credits, or rebates. This reduction optimizes lease affordability by minimizing depreciation and finance charges embedded in the Net Cap Cost.
Negotiating Net Cap Cost for Better Lease Deals
Negotiating the Net Capitalized Cost, which excludes taxes, fees, and incentives, is essential for securing a more affordable lease payment compared to the Gross Capitalized Cost. Lowering the Net Cap Cost directly reduces your monthly lease payments and overall lease expenses. Understanding and negotiating fees, dealer discounts, and manufacturer incentives that impact the Net Cap Cost can result in significantly better lease deals.
Fees and Add-Ons: Effects on Cap Costs
Net Capitalized Cost reflects the vehicle's gross capitalized cost minus fees, incentives, and add-ons, directly influencing monthly lease payments by lowering the amount financed. Gross Capitalized Cost encompasses the total agreed-upon price of the vehicle plus all fees, add-ons, taxes, and optional extras before any deductions, increasing the base for depreciation and rent charge calculations. Fees and add-ons such as acquisition fees, aftermarket products, and warranty packages elevate the gross cap cost, while rebates, trade-in credits, and negotiated discounts help reduce the net cap cost, impacting overall lease affordability and terms.
Calculating Lease Payments: Net vs Gross Cap Cost
Calculating lease payments involves understanding the distinction between Net Cap Cost and Gross Cap Cost, where Gross Cap Cost represents the vehicle's total price before any incentives or trade-ins, while Net Cap Cost reflects the negotiated price after such deductions. Lease payments are primarily based on the Net Cap Cost, as it determines the actual amount financed over the lease term, directly influencing monthly payment amounts. Accurately calculating payments requires subtracting rebates, trade-in values, and down payments from the Gross Cap Cost to arrive at the Net Cap Cost, ensuring precise payment estimates.
Net Cap Cost vs Gross Cap Cost: Which Matters More?
Net Cap Cost represents the negotiated price of a leased vehicle after applying incentives and trade-ins, whereas Gross Cap Cost reflects the initial price before deductions. The Net Cap Cost is more critical for lessees because it directly affects monthly lease payments and overall lease affordability. Understanding the difference helps consumers negotiate better deals and manage lease expenses effectively.
Net Cap Cost vs Gross Cap Cost Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com