OBD scan tools provide quick and accurate diagnostic information by reading standardized error codes from a vehicle's onboard computer, making them efficient for identifying engine and emission issues. Manual diagnostics rely on technician experience and physical inspection to detect problems that may not trigger OBD codes, such as mechanical wear or electrical faults. Combining OBD scans with thorough manual diagnostics ensures a comprehensive assessment of vehicle health and performance.
Table of Comparison
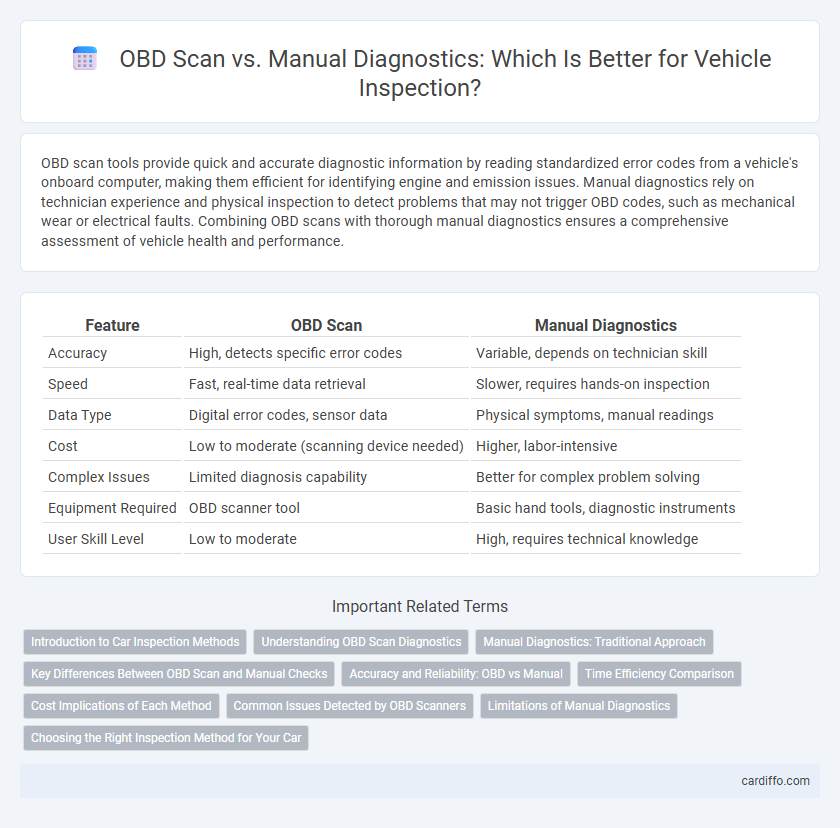
| Feature | OBD Scan | Manual Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, detects specific error codes | Variable, depends on technician skill |
| Speed | Fast, real-time data retrieval | Slower, requires hands-on inspection |
| Data Type | Digital error codes, sensor data | Physical symptoms, manual readings |
| Cost | Low to moderate (scanning device needed) | Higher, labor-intensive |
| Complex Issues | Limited diagnosis capability | Better for complex problem solving |
| Equipment Required | OBD scanner tool | Basic hand tools, diagnostic instruments |
| User Skill Level | Low to moderate | High, requires technical knowledge |
Introduction to Car Inspection Methods
OBD scan tools provide a rapid and precise method for detecting engine and emission system faults by accessing the vehicle's onboard computer data. Manual diagnostics, relying on physical inspection and sensor measurements, offer a hands-on approach to identifying mechanical and electrical issues beyond OBD codes. Combining both techniques enhances the accuracy and efficiency of comprehensive car inspections.
Understanding OBD Scan Diagnostics
OBD scan diagnostics utilize onboard computer systems to quickly identify vehicle issues through error codes, providing precise information about engine and emission systems. This method offers a standardized, efficient approach to detecting faults compared to manual diagnostics, which rely on technician experience and visual inspection. Understanding OBD scan data enhances accurate troubleshooting, reduces diagnostic time, and supports preventative maintenance strategies.
Manual Diagnostics: Traditional Approach
Manual diagnostics relies on hands-on inspection techniques, allowing technicians to identify issues through physical examination and symptom analysis. This traditional approach excels in detecting complex mechanical problems and interpreting subtle signs that OBD scan tools may miss. Skilled technicians utilize experience and intuition to diagnose vehicle malfunctions beyond the scope of digital error codes.
Key Differences Between OBD Scan and Manual Checks
OBD scan tools provide real-time data by electronically accessing a vehicle's onboard computer system, enabling rapid detection of error codes linked to engine performance, emissions, and system malfunctions. Manual diagnostics rely on physical inspection and sensor testing, offering a comprehensive but time-intensive approach to identifying mechanical and electrical issues beyond what OBD sensors can detect. While OBD scans excel in pinpointing software-related faults, manual checks are essential for evaluating components like wiring, fluid levels, and mechanical wear that require expert interpretation and tactile assessment.
Accuracy and Reliability: OBD vs Manual
OBD scan tools provide consistent and precise diagnostic trouble codes, enhancing accuracy by directly interfacing with a vehicle's onboard computer system. Manual diagnostics rely heavily on technician expertise and can introduce variability, potentially affecting reliability and diagnostic consistency. Combining OBD data with manual inspection ensures a comprehensive and reliable assessment of vehicle conditions.
Time Efficiency Comparison
OBD scans provide rapid diagnostic results by quickly reading error codes from the vehicle's computer system, significantly reducing inspection time compared to manual diagnostics. Manual diagnostics often involve detailed physical inspections and component testing, which can extend the time required for identifying issues. Utilizing OBD scan tools enhances time efficiency by delivering immediate data, enabling faster decision-making during vehicle inspections.
Cost Implications of Each Method
OBD scans offer a cost-effective diagnostic solution by quickly identifying error codes, reducing labor time and minimizing the need for expensive manual inspections. Manual diagnostics, while more time-consuming and costly due to technician labor, provide a comprehensive assessment that can detect issues beyond electronic faults. Choosing between OBD scans and manual diagnostics depends on budget constraints and the complexity of the vehicle's issues.
Common Issues Detected by OBD Scanners
OBD scanners efficiently identify common automotive issues such as engine misfires, faulty oxygen sensors, and emission control problems by accessing real-time diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These devices provide data on system malfunctions like catalytic converter efficiency, fuel system errors, and ignition system faults, enabling quicker troubleshooting. Manual diagnostics often require more time and expertise to detect these issues without the precise data OBD scanners deliver.
Limitations of Manual Diagnostics
Manual diagnostics often suffer from human error and limited ability to detect complex electronic issues within modern vehicles. Unlike OBD scans that provide precise error codes and real-time data, manual inspections may overlook subtle faults in engine control units or emission systems. This limitation reduces diagnostic accuracy and prolongs vehicle repair times.
Choosing the Right Inspection Method for Your Car
Selecting the appropriate inspection method depends on your vehicle's complexity and diagnostic needs. OBD scans provide quick, precise fault codes from the car's onboard computer, ideal for identifying electronic and engine-related issues. Manual diagnostics allow experienced technicians to investigate mechanical problems and perform hands-on tests beyond electronic systems, ensuring comprehensive vehicle health assessment.
OBD scan vs manual diagnostics Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com