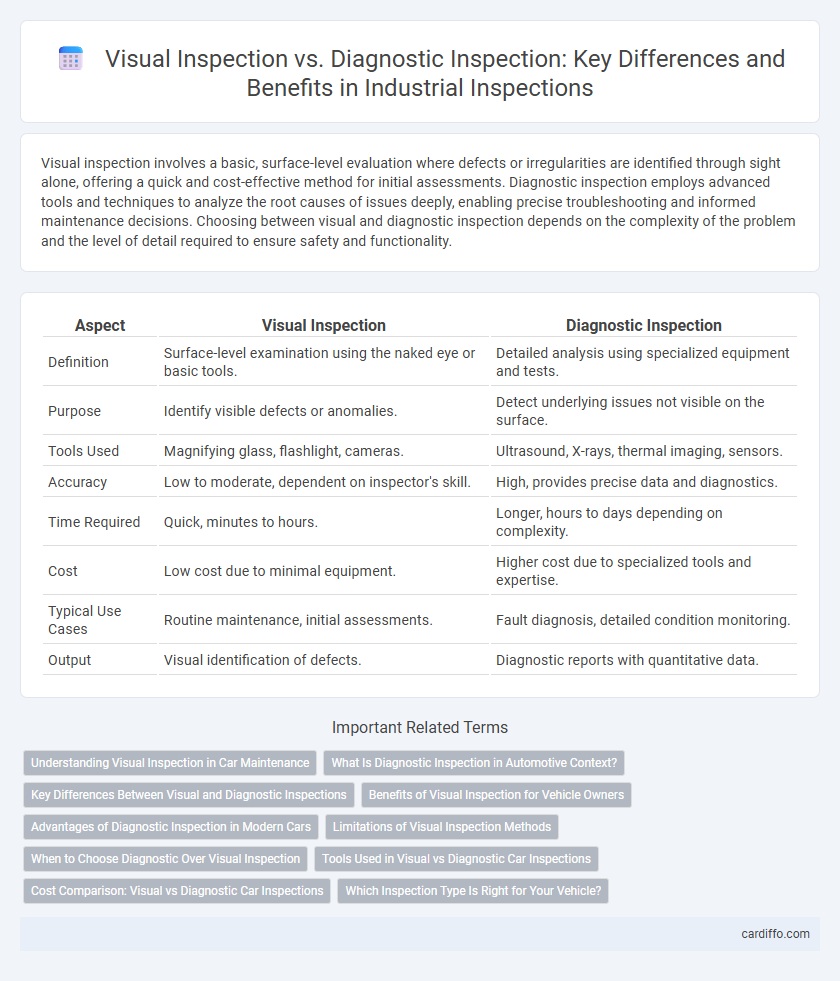
Visual inspection involves a basic, surface-level evaluation where defects or irregularities are identified through sight alone, offering a quick and cost-effective method for initial assessments. Diagnostic inspection employs advanced tools and techniques to analyze the root causes of issues deeply, enabling precise troubleshooting and informed maintenance decisions. Choosing between visual and diagnostic inspection depends on the complexity of the problem and the level of detail required to ensure safety and functionality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Visual Inspection | Diagnostic Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surface-level examination using the naked eye or basic tools. | Detailed analysis using specialized equipment and tests. |
| Purpose | Identify visible defects or anomalies. | Detect underlying issues not visible on the surface. |
| Tools Used | Magnifying glass, flashlight, cameras. | Ultrasound, X-rays, thermal imaging, sensors. |
| Accuracy | Low to moderate, dependent on inspector's skill. | High, provides precise data and diagnostics. |
| Time Required | Quick, minutes to hours. | Longer, hours to days depending on complexity. |
| Cost | Low cost due to minimal equipment. | Higher cost due to specialized tools and expertise. |
| Typical Use Cases | Routine maintenance, initial assessments. | Fault diagnosis, detailed condition monitoring. |
| Output | Visual identification of defects. | Diagnostic reports with quantitative data. |
Understanding Visual Inspection in Car Maintenance
Visual inspection in car maintenance involves systematically examining the vehicle's exterior and interior components to identify obvious issues such as leaks, corrosion, or worn parts. This process relies on trained technicians' observational skills to detect irregularities without specialized tools, making it a cost-effective first step in preventive maintenance. Unlike diagnostic inspection, which uses electronic equipment to analyze complex system malfunctions, visual inspection provides immediate, crucial insights into the vehicle's physical condition.
What Is Diagnostic Inspection in Automotive Context?
Diagnostic inspection in the automotive context involves using specialized tools and equipment, such as OBD-II scanners, to identify and analyze vehicle faults beyond surface-level issues detected by visual inspection. This process targets electronic systems, engine performance, emissions, and sensor data to pinpoint underlying problems accurately. Diagnostic inspection enables precise troubleshooting, improving repair accuracy and minimizing vehicle downtime.
Key Differences Between Visual and Diagnostic Inspections
Visual inspections involve a surface-level examination to identify obvious defects such as cracks, corrosion, or misalignments using the naked eye or basic tools, while diagnostic inspections employ advanced tools and sensors like ultrasonic testing or infrared thermography to detect internal faults and measure precise conditions. The key difference lies in the depth and accuracy of assessment, where visual inspection offers quick, preliminary checks and diagnostic inspection provides detailed, quantifiable data critical for predictive maintenance. Visual methods are less costly and faster but may miss hidden issues that diagnostic techniques can reveal, ensuring more comprehensive asset integrity evaluations.
Benefits of Visual Inspection for Vehicle Owners
Visual inspection enables vehicle owners to quickly identify obvious issues such as fluid leaks, tire wear, and visible damage without specialized equipment. This cost-effective approach allows for early detection of potential problems, reducing the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs. Regular visual checks enhance safety and maintenance by ensuring components like lights, brakes, and mirrors function properly.
Advantages of Diagnostic Inspection in Modern Cars
Diagnostic inspection in modern cars offers precise identification of underlying issues through advanced onboard computer systems and sensors, enabling targeted repairs that improve vehicle reliability. Unlike visual inspection, it detects internal faults not visible to the naked eye, reducing diagnostic time and minimizing unnecessary part replacements. This method enhances safety and cost-efficiency by providing real-time data and comprehensive system analysis, crucial for complex automotive technologies.
Limitations of Visual Inspection Methods
Visual inspection methods are limited by their reliance on the inspector's experience and ability to detect surface-level defects, often missing subsurface or internal issues. These methods cannot quantify the severity of defects or predict potential failures, making them insufficient for thorough diagnostic purposes. Factors such as poor lighting, accessibility constraints, and operator fatigue further reduce the accuracy and reliability of visual inspections.
When to Choose Diagnostic Over Visual Inspection
Diagnostic inspection is preferred over visual inspection when detailed understanding of internal or non-visible defects is required, such as in complex machinery or electronic systems. It utilizes advanced tools like ultrasonic testing, radiography, or thermal imaging to detect issues that visual methods cannot reveal. Selecting diagnostic inspection ensures higher accuracy in identifying hidden faults, preventing costly failures and enhancing safety.
Tools Used in Visual vs Diagnostic Car Inspections
Visual inspection tools include basic equipment such as flashlights, mirrors, and magnifying glasses to identify obvious defects or wear on vehicle components. Diagnostic inspections rely on advanced tools like OBD-II scanners, multimeters, and thermal cameras to detect electronic faults, sensor failures, and internal engine issues. Using specialized software and computerized diagnostics enhances the accuracy and scope of fault detection beyond what visual tools can achieve.
Cost Comparison: Visual vs Diagnostic Car Inspections
Visual inspections typically involve lower upfront costs due to their non-invasive nature and quicker execution time, making them ideal for routine checks and preliminary evaluations. Diagnostic inspections require specialized equipment and software, increasing initial expenses but providing detailed and accurate data that can prevent costly repairs by identifying issues early. Investing in diagnostic inspections may result in higher immediate costs but offers long-term savings by minimizing unexpected breakdowns and ensuring precise maintenance.
Which Inspection Type Is Right for Your Vehicle?
Visual inspection involves a thorough examination of a vehicle's exterior and easily accessible components to identify obvious defects, damage, or wear without specialized tools. Diagnostic inspection uses advanced scanning equipment and sensors to detect underlying mechanical or electronic issues that are not visible to the naked eye, providing a comprehensive analysis of vehicle performance and system health. Choosing the right inspection type depends on your vehicle's symptoms, whether you need a quick safety check or an in-depth assessment to troubleshoot complex problems.
Visual inspection vs Diagnostic inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com