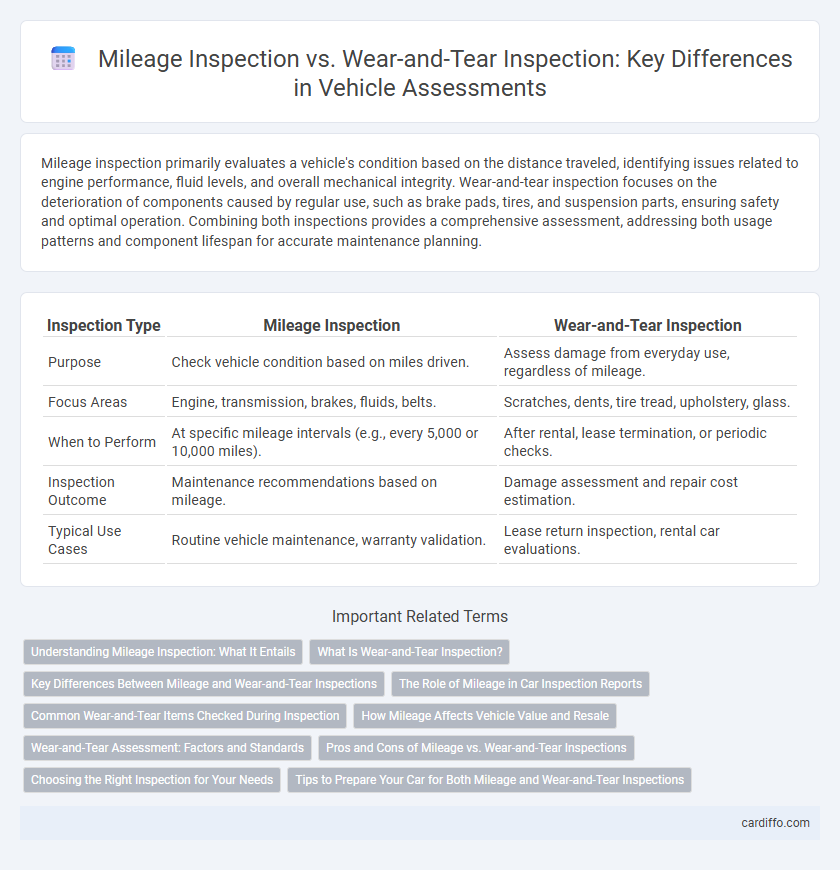
Mileage inspection primarily evaluates a vehicle's condition based on the distance traveled, identifying issues related to engine performance, fluid levels, and overall mechanical integrity. Wear-and-tear inspection focuses on the deterioration of components caused by regular use, such as brake pads, tires, and suspension parts, ensuring safety and optimal operation. Combining both inspections provides a comprehensive assessment, addressing both usage patterns and component lifespan for accurate maintenance planning.
Table of Comparison
| Inspection Type | Mileage Inspection | Wear-and-Tear Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Check vehicle condition based on miles driven. | Assess damage from everyday use, regardless of mileage. |
| Focus Areas | Engine, transmission, brakes, fluids, belts. | Scratches, dents, tire tread, upholstery, glass. |
| When to Perform | At specific mileage intervals (e.g., every 5,000 or 10,000 miles). | After rental, lease termination, or periodic checks. |
| Inspection Outcome | Maintenance recommendations based on mileage. | Damage assessment and repair cost estimation. |
| Typical Use Cases | Routine vehicle maintenance, warranty validation. | Lease return inspection, rental car evaluations. |
Understanding Mileage Inspection: What It Entails
Mileage inspection involves verifying the accuracy of a vehicle's odometer reading to ensure it reflects the true distance traveled, preventing fraud or misrepresentation. This type of inspection checks for discrepancies caused by tampering, rollback, or malfunction of the odometer system, which can impact the vehicle's value and maintenance schedule. It is crucial for maintaining transparency in vehicle history reports and safeguarding buyer trust in the used car market.
What Is Wear-and-Tear Inspection?
Wear-and-tear inspection evaluates the physical condition of a vehicle by examining components that naturally degrade over time, such as tires, brakes, suspension, and upholstery. Unlike mileage inspection, which primarily assesses the distance traveled to estimate usage, wear-and-tear inspections focus on the actual damage and deterioration resulting from normal use. This inspection helps identify maintenance needs and potential safety issues based on the vehicle's real-world condition rather than just its odometer reading.
Key Differences Between Mileage and Wear-and-Tear Inspections
Mileage inspection primarily assesses a vehicle's odometer readings to confirm accurate mileage data for resale or maintenance schedules, while wear-and-tear inspection evaluates physical components such as tires, brakes, and suspension for deterioration from usage. Mileage inspections rely on digital or mechanical odometer verification to detect discrepancies or fraud, contrasting with wear-and-tear inspections that involve visual and functional checks to identify damage and replace parts accordingly. These inspections differ in purpose, with mileage focusing on verifying distance traveled and wear-and-tear centering on assessing the vehicle's mechanical condition and safety risks.
The Role of Mileage in Car Inspection Reports
Mileage serves as a critical metric in car inspection reports, providing quantifiable insight into a vehicle's usage and potential maintenance needs. Wear-and-tear inspections evaluate physical conditions like tire tread, brake pad thickness, and fluid levels, but mileage offers a standardized measure to predict component lifespan and schedule upcoming services. Accurate mileage data enhances the reliability of inspection reports by correlating wear patterns with expected vehicle performance over time.
Common Wear-and-Tear Items Checked During Inspection
Common wear-and-tear items checked during inspections include brake pads, tire tread depth, suspension components, fluid levels, and battery condition. These elements are critical indicators of a vehicle's overall health and are often overlooked in mileage-based inspections alone. Regular assessment of these components helps prevent unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of the vehicle.
How Mileage Affects Vehicle Value and Resale
Mileage inspection measures the total distance a vehicle has traveled, directly impacting its market value and resale potential because higher mileage typically indicates more extensive use and accelerated depreciation. Wear-and-tear inspection evaluates the condition of key components like tires, brakes, and suspension, providing insights into maintenance quality and potential repair costs that also influence resale value. Vehicles with lower mileage and minimal wear-and-tear usually command higher resale prices due to perceived reliability and reduced future expenses.
Wear-and-Tear Assessment: Factors and Standards
Wear-and-tear inspection evaluates vehicle condition based on factors such as tire tread depth, brake pad thickness, suspension performance, and interior wear, adhering to industry standards like ISO 10083 for vehicle inspection. This assessment helps determine maintenance needs and potential repairs by comparing observed wear levels to regulatory benchmarks and manufacturer guidelines. Unlike mileage inspection, which records distance traveled, wear-and-tear inspection provides a qualitative analysis of component degradation critical for vehicle safety and performance.
Pros and Cons of Mileage vs. Wear-and-Tear Inspections
Mileage inspections offer precise tracking by correlating vehicle usage with service intervals, ensuring timely maintenance that prevents unexpected breakdowns and extends engine life. Wear-and-tear inspections provide a comprehensive evaluation of components affected by environmental factors, driving styles, and road conditions, highlighting issues that mileage alone might overlook. However, mileage inspections may miss latent damage not tied to distance, while wear-and-tear assessments can be subjective and require expert interpretation, balancing thoroughness with potential variability in evaluation.
Choosing the Right Inspection for Your Needs
Mileage inspection assesses vehicle components based on distance traveled, crucial for tracking maintenance intervals tied to engine health and fluid changes. Wear-and-tear inspection focuses on identifying physical deterioration of parts such as tires, brakes, and suspension, highlighting damage from usage or environmental factors. Selecting the right inspection depends on whether your priority is monitoring mileage-dependent maintenance or detecting external damage affecting vehicle safety and performance.
Tips to Prepare Your Car for Both Mileage and Wear-and-Tear Inspections
Ensure your vehicle's maintenance records are up to date, highlighting timely oil changes, tire rotations, and brake checks to support mileage accuracy. Inspect critical components such as tires, brakes, and suspension for visible wear, addressing minor repairs before the wear-and-tear inspection. Clean your car thoroughly, including under the hood, to present a well-maintained vehicle that reflects both proper mileage care and minimal wear.
Mileage inspection vs wear-and-tear inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com