Brake system inspection ensures the safety of your vehicle by checking for worn brake pads, leaking brake fluid, and proper brake responsiveness. Tire tread inspection evaluates the depth and condition of the tire tread to maintain traction and prevent hydroplaning. Both inspections are crucial for vehicle safety but focus on different components affecting stopping performance and road grip.
Table of Comparison
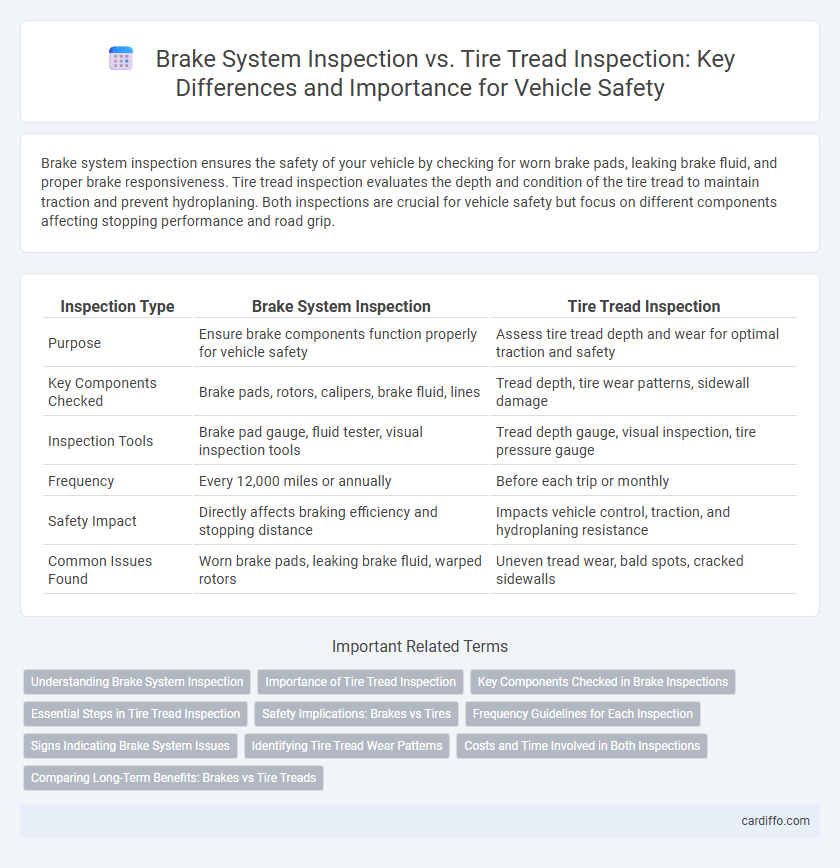
| Inspection Type | Brake System Inspection | Tire Tread Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure brake components function properly for vehicle safety | Assess tire tread depth and wear for optimal traction and safety |
| Key Components Checked | Brake pads, rotors, calipers, brake fluid, lines | Tread depth, tire wear patterns, sidewall damage |
| Inspection Tools | Brake pad gauge, fluid tester, visual inspection tools | Tread depth gauge, visual inspection, tire pressure gauge |
| Frequency | Every 12,000 miles or annually | Before each trip or monthly |
| Safety Impact | Directly affects braking efficiency and stopping distance | Impacts vehicle control, traction, and hydroplaning resistance |
| Common Issues Found | Worn brake pads, leaking brake fluid, warped rotors | Uneven tread wear, bald spots, cracked sidewalls |
Understanding Brake System Inspection
Brake system inspection involves a thorough evaluation of components such as brake pads, rotors, calipers, and brake fluid levels to ensure optimal stopping performance and safety. Unlike tire tread inspection, which primarily assesses tread depth and wear patterns to maintain traction and handling, brake inspections focus on detecting signs of wear, leaks, or corrosion that could impair braking efficiency. Regular brake system inspection is crucial for preventing brake failure and ensuring vehicle safety under various driving conditions.
Importance of Tire Tread Inspection
Tire tread inspection is critical for vehicle safety as it directly affects traction, braking distance, and handling, especially in wet or slippery conditions. Unlike brake system inspection, which ensures the functionality of stopping power, tire tread inspection prevents accidents by maintaining proper grip and reducing the risk of hydroplaning. Regularly checking tread depth and wear patterns helps identify uneven tire wear, which can indicate alignment or suspension issues, ultimately enhancing overall vehicle performance and safety.
Key Components Checked in Brake Inspections
Brake system inspection focuses on critical components such as brake pads, rotors, calipers, brake fluid levels, and hydraulic lines to ensure optimal stopping performance and safety. Tire tread inspection primarily evaluates tread depth, wear patterns, and tire pressure, which impact traction and handling but do not assess braking functionality. Thorough brake inspections detect issues like pad wear, rotor damage, and fluid leaks that directly affect braking efficiency and vehicle safety.
Essential Steps in Tire Tread Inspection
Tire tread inspection requires measuring tread depth using a tread depth gauge to ensure it meets safety standards, generally above 2/32 inch. Visual checks for uneven wear, cracks, and embedded objects are essential to identify potential alignment or inflation issues. Proper tire tread condition directly impacts braking performance, highlighting the need for regular inspections alongside brake system checks.
Safety Implications: Brakes vs Tires
Brake system inspection directly impacts vehicle safety by ensuring optimal stopping power, reducing the risk of accidents caused by brake failure. Tire tread inspection is equally critical as it affects traction, handling, and hydroplaning resistance, particularly in adverse weather conditions. Neglecting either brake or tire inspections significantly compromises road safety, increasing the likelihood of collisions and severe injuries.
Frequency Guidelines for Each Inspection
Brake system inspections should be performed every 12,000 miles or at least once a year to ensure optimal safety and performance. Tire tread inspections require more frequent checks, typically every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, often aligning with oil change intervals for early detection of uneven wear or damage. Following these frequency guidelines helps maintain vehicle safety, prolong component life, and prevent costly repairs.
Signs Indicating Brake System Issues
Signs indicating brake system issues include unusual noises such as squealing or grinding, vibrations during braking, and a spongy brake pedal feel. Brake warning lights on the dashboard and increased stopping distances are critical indicators requiring immediate attention. Unlike tire tread inspection, which focuses on depth measurement and wear patterns, brake inspection prioritizes hydraulic fluid levels, pad thickness, and rotor condition to ensure safe vehicle operation.
Identifying Tire Tread Wear Patterns
Tire tread inspection is crucial for identifying specific wear patterns such as cupping, feathering, or uneven wear that indicate alignment or suspension issues, directly impacting vehicle safety and handling. Brake system inspection focuses on evaluating brake pad thickness, rotor condition, and hydraulic efficiency to ensure reliable stopping power. Accurate identification of tire tread wear patterns allows for targeted maintenance, preventing further damage and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Costs and Time Involved in Both Inspections
Brake system inspection typically incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized tools and potential part replacements, with an average time of 30 to 60 minutes per inspection. Tire tread inspection is more cost-effective, often requiring only visual assessment or simple measurement tools, taking approximately 10 to 15 minutes. Prioritizing tire tread checks can save time and expense, but neglecting brake system inspections may lead to costly repairs and safety risks.
Comparing Long-Term Benefits: Brakes vs Tire Treads
Brake system inspection ensures optimal stopping power and reduces the risk of accidents caused by brake failure, enhancing vehicle safety and longevity. Tire tread inspection maintains traction and prevents hydroplaning, directly impacting fuel efficiency and tire lifespan. Prioritizing regular checks of both components supports long-term cost savings and reliable vehicle performance.
Brake system inspection vs tire tread inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com