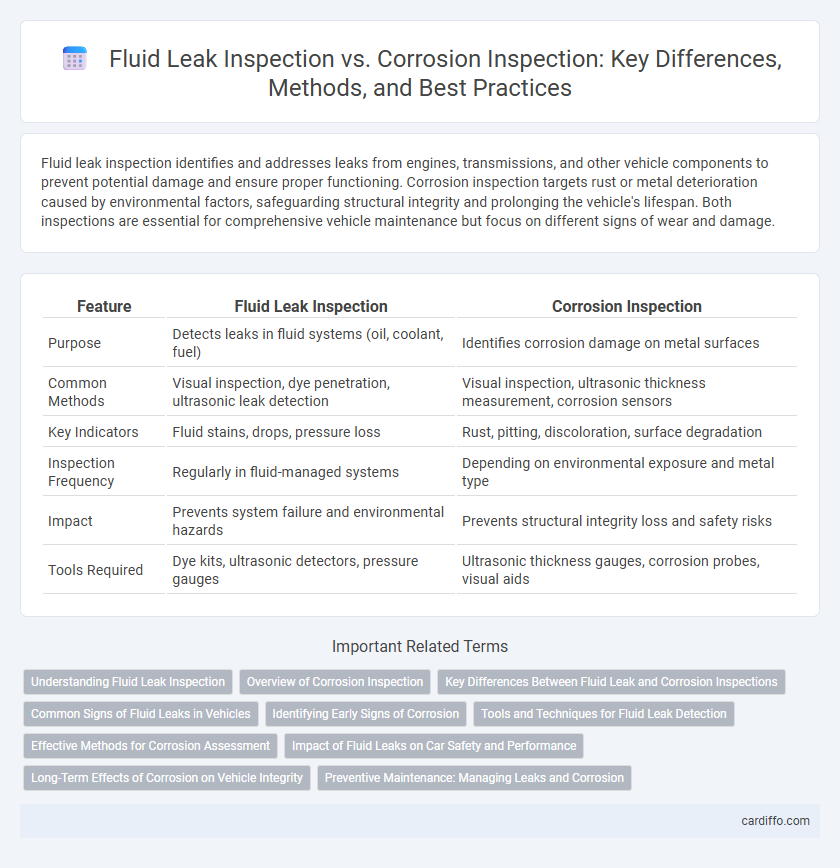
Fluid leak inspection identifies and addresses leaks from engines, transmissions, and other vehicle components to prevent potential damage and ensure proper functioning. Corrosion inspection targets rust or metal deterioration caused by environmental factors, safeguarding structural integrity and prolonging the vehicle's lifespan. Both inspections are essential for comprehensive vehicle maintenance but focus on different signs of wear and damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fluid Leak Inspection | Corrosion Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects leaks in fluid systems (oil, coolant, fuel) | Identifies corrosion damage on metal surfaces |
| Common Methods | Visual inspection, dye penetration, ultrasonic leak detection | Visual inspection, ultrasonic thickness measurement, corrosion sensors |
| Key Indicators | Fluid stains, drops, pressure loss | Rust, pitting, discoloration, surface degradation |
| Inspection Frequency | Regularly in fluid-managed systems | Depending on environmental exposure and metal type |
| Impact | Prevents system failure and environmental hazards | Prevents structural integrity loss and safety risks |
| Tools Required | Dye kits, ultrasonic detectors, pressure gauges | Ultrasonic thickness gauges, corrosion probes, visual aids |
Understanding Fluid Leak Inspection
Fluid leak inspection focuses on detecting and identifying the presence of leaks in fluid systems such as pipelines, tanks, and machinery, using techniques like ultrasonic testing, visual inspection, and infrared thermography. This inspection is critical for preventing system failures, environmental contamination, and safety hazards by locating leaks early and assessing their severity. Unlike corrosion inspection, which evaluates material degradation and structural integrity, fluid leak inspection primarily targets the detection of leak points and fluid loss in operational systems.
Overview of Corrosion Inspection
Corrosion inspection involves the systematic examination of metal surfaces and structures to detect signs of deterioration caused by chemical or electrochemical reactions. Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and visual inspection are commonly employed to identify corrosion-related damage, ensuring asset integrity and preventing failures. This type of inspection is critical in industries like oil and gas, maritime, and infrastructure where material degradation can lead to costly and hazardous outcomes.
Key Differences Between Fluid Leak and Corrosion Inspections
Fluid leak inspection primarily targets the detection of escaping liquids from pipelines, seals, or equipment using methods like ultrasonic testing, dye penetrant, or visual analysis to prevent operational hazards and environmental contamination. Corrosion inspection focuses on identifying material degradation due to chemical reactions, often employing techniques such as magnetic particle inspection, radiography, or ultrasonic thickness measurement to assess structural integrity. Key differences lie in their objectives: fluid leak inspection aims at finding active leaks and preventing system failures, whereas corrosion inspection evaluates material condition and remaining lifespan, impacting maintenance strategies and safety protocols.
Common Signs of Fluid Leaks in Vehicles
Common signs of fluid leaks in vehicles include visible puddles or stains beneath the car, unexpected drops in fluid levels such as engine oil, transmission fluid, or coolant, and unusual smells like sweet antifreeze or burnt oil. Drivers may also notice damp spots on engine components or hoses, as well as warning lights indicating issues with oil pressure or coolant temperature. Early detection through fluid leak inspection helps prevent severe engine damage and costly repairs.
Identifying Early Signs of Corrosion
Early signs of corrosion often manifest as discoloration, pitting, or surface irregularities detectable during a corrosion inspection, which targets material degradation over time. Fluid leak inspection primarily focuses on identifying breaches or drips in containment systems that can accelerate corrosion if left unaddressed. Combining both inspections enhances the ability to detect and address corrosion proactively, preventing structural failures and costly repairs.
Tools and Techniques for Fluid Leak Detection
Fluid leak inspection primarily employs ultrasonic leak detectors, infrared thermography, and halogen leak detectors to identify escaping fluids with high sensitivity and accuracy. Techniques such as pressure decay testing and tracer gas detection, including helium and hydrogen, are commonly utilized to pinpoint leaks in complex systems. In contrast, corrosion inspection relies more on visual inspection, ultrasonic thickness gauges, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to assess material degradation rather than detecting fluid escape.
Effective Methods for Corrosion Assessment
Fluid leak inspection primarily focuses on detecting escaping liquids through visual checks, ultrasonic testing, and pressure decay methods, ensuring containment integrity. Corrosion inspection employs advanced techniques such as ultrasonic thickness gauging, radiographic testing, and corrosion mapping to assess material degradation and predict lifespan accurately. Combining non-destructive evaluation methods with regular monitoring enhances reliability in preventing structural failures caused by corrosion.
Impact of Fluid Leaks on Car Safety and Performance
Fluid leak inspection is critical for maintaining car safety and performance because leaking fluids such as oil, coolant, or brake fluid can lead to engine overheating, brake failure, and reduced fuel efficiency. Corrosion inspection primarily addresses structural integrity and metal degradation, but fluid leaks directly affect the vehicle's mechanical systems and drivability. Identifying fluid leaks early prevents costly repairs and enhances overall vehicle reliability and safety on the road.
Long-Term Effects of Corrosion on Vehicle Integrity
Corrosion inspection identifies progressive metal degradation that compromises vehicle structural integrity, leading to long-term safety risks and increased maintenance costs. Fluid leak inspection primarily targets immediate containment of hazardous or essential fluids but often misses underlying corrosion damage. Proactive corrosion detection prevents extensive repair needs by preserving chassis strength and preventing critical component failure over time.
Preventive Maintenance: Managing Leaks and Corrosion
Fluid leak inspection identifies and addresses leaks early, preventing equipment failure and costly downtime, while corrosion inspection targets material degradation to maintain structural integrity and safety. Both inspections are critical components of preventive maintenance strategies that extend asset lifespan and optimize operational efficiency. Implementing regular leak and corrosion monitoring reduces unexpected repairs and enhances overall reliability.
Fluid Leak Inspection vs Corrosion Inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com