Visual inspection relies on human observation to identify surface defects, corrosion, or misalignments, making it essential for detecting obvious and superficial issues. Mechanical inspection utilizes specialized tools and instrumentation to measure dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties, providing precise and quantifiable data. Combining both methods enhances overall accuracy in assessing structural integrity and operational safety.
Table of Comparison
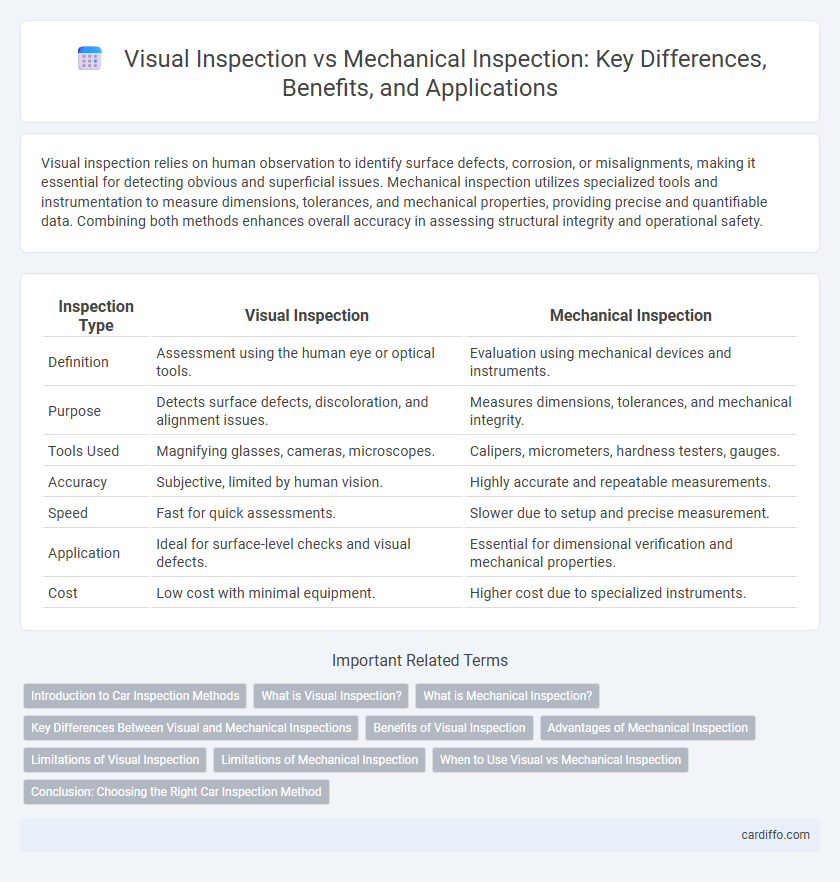
| Inspection Type | Visual Inspection | Mechanical Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment using the human eye or optical tools. | Evaluation using mechanical devices and instruments. |
| Purpose | Detects surface defects, discoloration, and alignment issues. | Measures dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical integrity. |
| Tools Used | Magnifying glasses, cameras, microscopes. | Calipers, micrometers, hardness testers, gauges. |
| Accuracy | Subjective, limited by human vision. | Highly accurate and repeatable measurements. |
| Speed | Fast for quick assessments. | Slower due to setup and precise measurement. |
| Application | Ideal for surface-level checks and visual defects. | Essential for dimensional verification and mechanical properties. |
| Cost | Low cost with minimal equipment. | Higher cost due to specialized instruments. |
Introduction to Car Inspection Methods
Visual inspection involves examining a vehicle's exterior and interior components using the naked eye or basic tools to identify obvious defects such as dents, scratches, or fluid leaks. Mechanical inspection requires specialized equipment and expertise to assess engine performance, brake systems, suspension, and other mechanical parts for wear, functionality, and safety compliance. Combining both inspection methods ensures a comprehensive evaluation of the car's overall condition and roadworthiness.
What is Visual Inspection?
Visual inspection is a non-destructive testing method that involves examining the surface of materials or components using the naked eye or optical aids like magnifying glasses and cameras. It detects surface defects such as cracks, corrosion, misalignment, and contamination without requiring complex tools or equipment. Visual inspection is widely used in manufacturing, construction, and maintenance due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to provide immediate results.
What is Mechanical Inspection?
Mechanical inspection involves assessing the physical and functional condition of machinery and components using specialized tools and techniques such as ultrasonic testing, vibration analysis, and torque measurement. It identifies internal defects, misalignments, wear, and structural integrity issues that are not visible through visual inspection. This method ensures accurate diagnosis of equipment health, enhancing preventive maintenance and operational reliability.
Key Differences Between Visual and Mechanical Inspections
Visual inspection relies on human observation to detect surface defects, discolorations, and general wear, requiring minimal equipment and offering rapid assessments. Mechanical inspection involves the use of instruments and devices such as micrometers, gauges, or ultrasonic testers to measure physical properties and structural integrity with higher precision. Key differences include the level of accuracy, dependence on technology, and suitability for detecting surface versus subsurface or dimensional issues.
Benefits of Visual Inspection
Visual inspection offers rapid, non-destructive assessment that identifies surface defects such as cracks, corrosion, and misalignment without the need for specialized equipment. This method enhances safety by allowing quick detection of potential hazards while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Visual inspections also support real-time decision-making by providing immediate feedback on asset conditions, which is crucial for preventative maintenance strategies.
Advantages of Mechanical Inspection
Mechanical inspection offers precise measurements and quantifiable data, enhancing accuracy and reliability in defect detection. It enables thorough evaluation of internal components and structural integrity that visual inspection might miss. This method reduces human error and provides consistent, repeatable results critical for quality control in manufacturing and maintenance.
Limitations of Visual Inspection
Visual inspection often faces limitations due to its reliance on human perception, making it prone to errors, inconsistencies, and fatigue. It can fail to detect subsurface defects or small imperfections that require specialized tools or mechanical methods. Mechanical inspection, in contrast, utilizes instruments and sensors to provide more precise, objective, and repeatable measurements, overcoming the subjectivity inherent in visual methods.
Limitations of Mechanical Inspection
Mechanical inspection faces limitations in detecting surface defects and subtle material inconsistencies that visual inspection can identify, such as cracks, corrosion, or discoloration. It often requires calibration and can be less effective for complex geometries or when inspecting areas that are difficult to access. In contrast, visual inspection provides immediate, non-invasive assessment but may lack the precision of mechanical tools for dimensional accuracy.
When to Use Visual vs Mechanical Inspection
Visual inspection is ideal for detecting surface flaws, color variations, and obvious deformities, especially in applications requiring quick assessments or when non-destructive testing is a priority. Mechanical inspection becomes necessary for measuring dimensional accuracy, internal features, or material properties where precise quantification is crucial, such as in quality control of machined parts or structural components. Selecting between visual and mechanical inspection depends on the inspection accuracy required, the nature of the defect, and whether the process needs to be non-invasive or quantitatively detailed.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Car Inspection Method
Visual inspection offers a quick, cost-effective way to detect surface-level defects and signs of wear in vehicles, making it ideal for routine checks. Mechanical inspection provides a thorough evaluation of internal components and systems, essential for identifying hidden issues and ensuring overall vehicle safety. Selecting the right car inspection method depends on the inspection purpose, with visual methods suited for regular maintenance and mechanical methods necessary for comprehensive diagnostics.
Visual inspection vs mechanical inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com