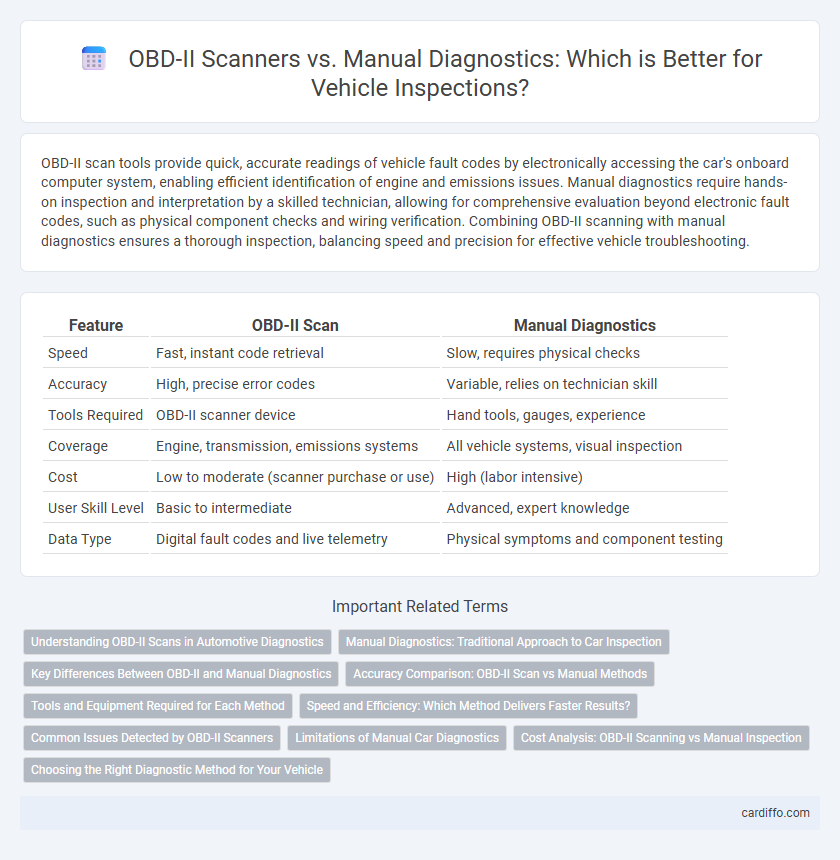
OBD-II scan tools provide quick, accurate readings of vehicle fault codes by electronically accessing the car's onboard computer system, enabling efficient identification of engine and emissions issues. Manual diagnostics require hands-on inspection and interpretation by a skilled technician, allowing for comprehensive evaluation beyond electronic fault codes, such as physical component checks and wiring verification. Combining OBD-II scanning with manual diagnostics ensures a thorough inspection, balancing speed and precision for effective vehicle troubleshooting.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | OBD-II Scan | Manual Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast, instant code retrieval | Slow, requires physical checks |
| Accuracy | High, precise error codes | Variable, relies on technician skill |
| Tools Required | OBD-II scanner device | Hand tools, gauges, experience |
| Coverage | Engine, transmission, emissions systems | All vehicle systems, visual inspection |
| Cost | Low to moderate (scanner purchase or use) | High (labor intensive) |
| User Skill Level | Basic to intermediate | Advanced, expert knowledge |
| Data Type | Digital fault codes and live telemetry | Physical symptoms and component testing |
Understanding OBD-II Scans in Automotive Diagnostics
OBD-II scans provide real-time data and standardized error codes that streamline the identification of vehicle issues, enabling faster and more accurate diagnostics compared to manual methods. This system probes the vehicle's computer for faults in critical systems such as the engine, transmission, and emissions, reducing guesswork and enhancing repair precision. Understanding OBD-II scan results allows technicians to pinpoint specific problems, improving maintenance efficiency and ensuring compliance with emission standards.
Manual Diagnostics: Traditional Approach to Car Inspection
Manual diagnostics remains a critical approach in car inspection, utilizing hands-on techniques and expert knowledge to identify vehicle issues beyond what an OBD-II scan can detect. This method allows mechanics to assess physical components, perform sensory evaluations, and analyze symptoms that electronic scanners may overlook. Despite advances in OBD-II technology, manual diagnostics provides a comprehensive understanding of automotive problems through direct interaction with the vehicle.
Key Differences Between OBD-II and Manual Diagnostics
OBD-II scan tools provide real-time data retrieval and standardized trouble codes, making vehicle diagnostics faster and more consistent compared to manual diagnostics. Manual diagnostics rely heavily on technician expertise and visual inspections, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. OBD-II scans streamline the identification of engine and system malfunctions, while manual methods offer deeper insight into mechanical issues not captured by electronic sensors.
Accuracy Comparison: OBD-II Scan vs Manual Methods
OBD-II scans provide precise fault codes from the vehicle's computer, enabling rapid identification of issues with engine, transmission, and emission systems, ensuring higher accuracy in diagnostics. Manual diagnostics rely heavily on technician expertise and physical inspection, which can be subjective and less consistent, especially for complex electronic faults. Combining OBD-II scan data with manual diagnostics enhances overall accuracy by verifying computer-generated codes and detecting issues not captured electronically.
Tools and Equipment Required for Each Method
OBD-II scan tools require a compatible scan device capable of reading onboard diagnostic codes and real-time data from the vehicle's ECU, often including Bluetooth or USB connectivity for advanced diagnostics. Manual diagnostics depend heavily on traditional tools such as multimeters, test lights, pressure gauges, and mechanical inspection instruments to physically evaluate vehicle systems. While OBD-II scanners provide faster, data-driven fault detection, manual diagnostics demand extensive toolsets and hands-on expertise to interpret and verify vehicle condition accurately.
Speed and Efficiency: Which Method Delivers Faster Results?
OBD-II scan tools provide faster diagnostic results by quickly retrieving real-time data and standardized trouble codes from a vehicle's onboard computer system, reducing inspection time significantly compared to manual diagnostics. Manual diagnostics require thorough physical inspection and component testing, which can be time-consuming and depends heavily on the technician's expertise. For speed and efficiency, OBD-II scanners deliver quicker fault identification, enabling prompt decision-making during vehicle inspections.
Common Issues Detected by OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II scanners quickly identify common issues such as engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, and catalytic converter efficiency problems by reading standardized trouble codes stored in the vehicle's onboard computer. Unlike manual diagnostics, which rely on visual inspection and mechanical testing to detect symptoms like worn spark plugs or vacuum leaks, OBD-II provides precise fault codes that streamline troubleshooting and repair. This technology enhances accuracy in diagnosing emission control system faults, fueling system malfunctions, and sensor irregularities, significantly reducing diagnostic time.
Limitations of Manual Car Diagnostics
Manual car diagnostics often rely heavily on the technician's experience and subjective interpretation, which can lead to inconsistent results and missed issues. Unlike OBD-II scans that provide precise error codes and real-time data from the vehicle's onboard computer, manual methods lack this level of detail and accuracy. This limitation can result in longer inspection times and incomplete assessments of complex electronic or sensor-related problems.
Cost Analysis: OBD-II Scanning vs Manual Inspection
OBD-II scanning significantly reduces diagnostic labor costs by providing instant access to detailed fault codes and live data from the vehicle's onboard computer system, minimizing the need for extensive manual probing. Manual inspection requires more technician time and specialized tools, increasing overall expense due to labor-intensive processes and potential trial-and-error troubleshooting. Cost analysis reveals that OBD-II scanners offer a more economical solution for early fault detection and routine maintenance diagnostics.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Method for Your Vehicle
OBD-II scan tools quickly read error codes from a vehicle's onboard computer, providing precise insights into engine performance, emissions, and system faults. Manual diagnostics rely on the technician's expertise to interpret symptoms and perform physical inspections, crucial for detecting issues not logged in the OBD system. Selecting the right diagnostic method depends on the vehicle's make, age, complexity, and the nature of the problem, balancing efficiency with thoroughness to ensure accurate vehicle inspection.
OBD-II scan vs manual diagnostics Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com