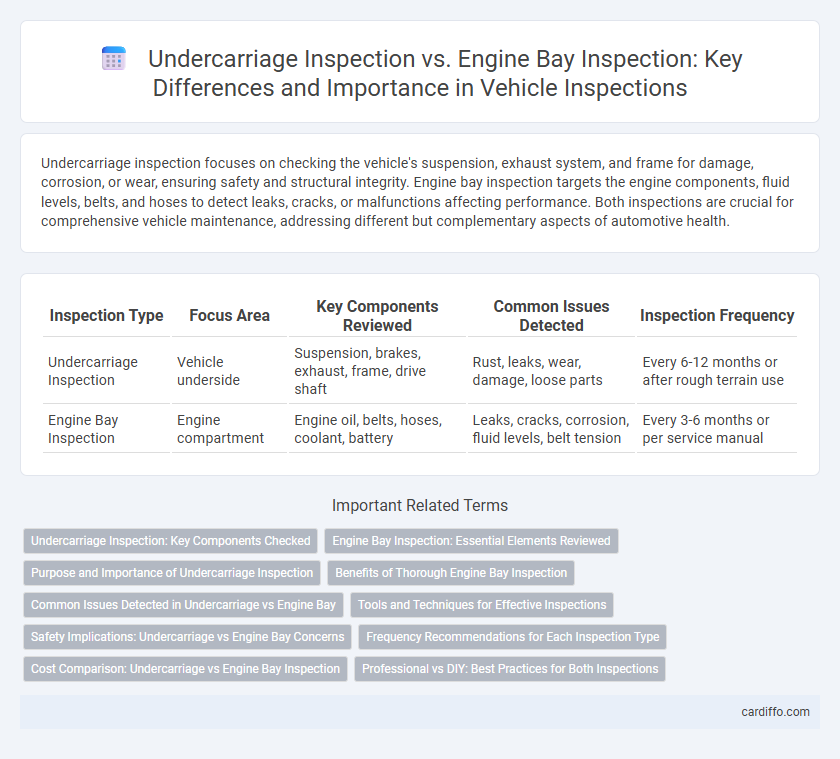
Undercarriage inspection focuses on checking the vehicle's suspension, exhaust system, and frame for damage, corrosion, or wear, ensuring safety and structural integrity. Engine bay inspection targets the engine components, fluid levels, belts, and hoses to detect leaks, cracks, or malfunctions affecting performance. Both inspections are crucial for comprehensive vehicle maintenance, addressing different but complementary aspects of automotive health.
Table of Comparison
| Inspection Type | Focus Area | Key Components Reviewed | Common Issues Detected | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undercarriage Inspection | Vehicle underside | Suspension, brakes, exhaust, frame, drive shaft | Rust, leaks, wear, damage, loose parts | Every 6-12 months or after rough terrain use |
| Engine Bay Inspection | Engine compartment | Engine oil, belts, hoses, coolant, battery | Leaks, cracks, corrosion, fluid levels, belt tension | Every 3-6 months or per service manual |
Undercarriage Inspection: Key Components Checked
Undercarriage inspection focuses on critical components such as suspension systems, steering linkages, brake lines, and exhaust systems, which are susceptible to wear and damage from road debris and environmental exposure. Inspecting for rust, cracks, leaks, and loose or broken parts ensures vehicle safety and performance by preventing structural failures and fluid leaks. Regular undercarriage inspections help maintain alignment and extend the lifespan of essential mechanical components compared to engine bay inspections that primarily assess engine health.
Engine Bay Inspection: Essential Elements Reviewed
Engine bay inspection focuses on critical components such as the battery, belts, hoses, fluid levels, and electrical connections, ensuring optimal engine performance and safety. Inspecting for leaks, corrosion, and wear within the engine bay helps prevent costly repairs and vehicle breakdowns. This detailed examination complements undercarriage inspection by addressing internal mechanical and electrical systems vital for engine operation.
Purpose and Importance of Undercarriage Inspection
Undercarriage inspection focuses on identifying damage, rust, and wear in critical components such as the suspension, exhaust system, and frame, ensuring vehicle safety and structural integrity. It plays a crucial role in detecting hidden issues like fluid leaks or compromised protective coatings that could lead to costly repairs or failure. This inspection complements engine bay checks by addressing areas prone to road debris impact and corrosion, thereby extending the vehicle's operational lifespan.
Benefits of Thorough Engine Bay Inspection
Thorough engine bay inspection enhances vehicle reliability by detecting leaks, corrosion, and worn components that may lead to costly repairs. It ensures optimal engine performance through early identification of issues like faulty belts, hoses, or fluid levels. Compared to undercarriage inspection, engine bay inspection provides critical insights into the heart of the vehicle's functionality, preventing breakdowns and extending engine lifespan.
Common Issues Detected in Undercarriage vs Engine Bay
Common issues detected during undercarriage inspection include worn suspension components, damaged exhaust systems, and corrosion on frame parts. In engine bay inspection, frequent problems involve oil leaks, deteriorated hoses, and faulty belts affecting engine performance. Both inspections are crucial for identifying maintenance needs but address different vehicle systems and potential failure points.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Inspections
Undercarriage inspection relies heavily on specialized tools such as creepers, hydraulic lifts, and bright LED worklights to access and illuminate hard-to-reach areas, enabling detailed examination of suspension components, exhaust systems, and chassis integrity. Engine bay inspection requires precision instruments including diagnostic scanners, infrared thermometers, and borescopes to assess engine performance, detect leaks, and identify overheating issues without disassembly. Employing these targeted tools and techniques ensures comprehensive evaluations by addressing the unique challenges and critical points of each inspection area.
Safety Implications: Undercarriage vs Engine Bay Concerns
Undercarriage inspection reveals critical safety issues such as frame damage, fluid leaks, and suspension wear that directly impact vehicle stability and accident risk. Engine bay inspection focuses on detecting overheating hazards, electrical faults, and fluid contamination that can cause engine failure or fire. Prioritizing both inspections ensures comprehensive vehicle safety by addressing structural integrity and operational risks.
Frequency Recommendations for Each Inspection Type
Undercarriage inspections should be performed every 6,000 to 12,000 miles, depending on operating conditions such as off-road use or exposure to corrosive environments. Engine bay inspections are recommended at shorter intervals, typically every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, to monitor fluid levels, belts, and hoses for wear or leaks. Adhering to these frequency guidelines ensures optimal vehicle performance and prevents costly repairs.
Cost Comparison: Undercarriage vs Engine Bay Inspection
Undercarriage inspection generally incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized lifts and equipment to access the vehicle's underside, whereas engine bay inspection is typically more affordable since it can be performed with standard tools and less extensive setup. Labor costs also tend to be greater for undercarriage inspections because of the complexity and time required to thoroughly examine components like suspension, exhaust, and drivetrain. The price difference reflects the variability in inspection complexity, with undercarriage evaluations averaging 20-40% more than engine bay inspections in professional automotive service centers.
Professional vs DIY: Best Practices for Both Inspections
Professional undercarriage inspections utilize advanced diagnostic tools and lift equipment to detect hidden damage, rust, or fluid leaks, ensuring precise assessment and safety compliance. DIY engine bay inspections emphasize thorough visual checks for loose connections, fluid levels, and signs of wear, with best practices including following manufacturer manuals and using proper lighting. Both inspection types benefit from systematic approaches, but professionals offer deeper analysis for undercarriage integrity, while DIY methods effectively maintain engine health through regular monitoring.
Undercarriage inspection vs engine bay inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com