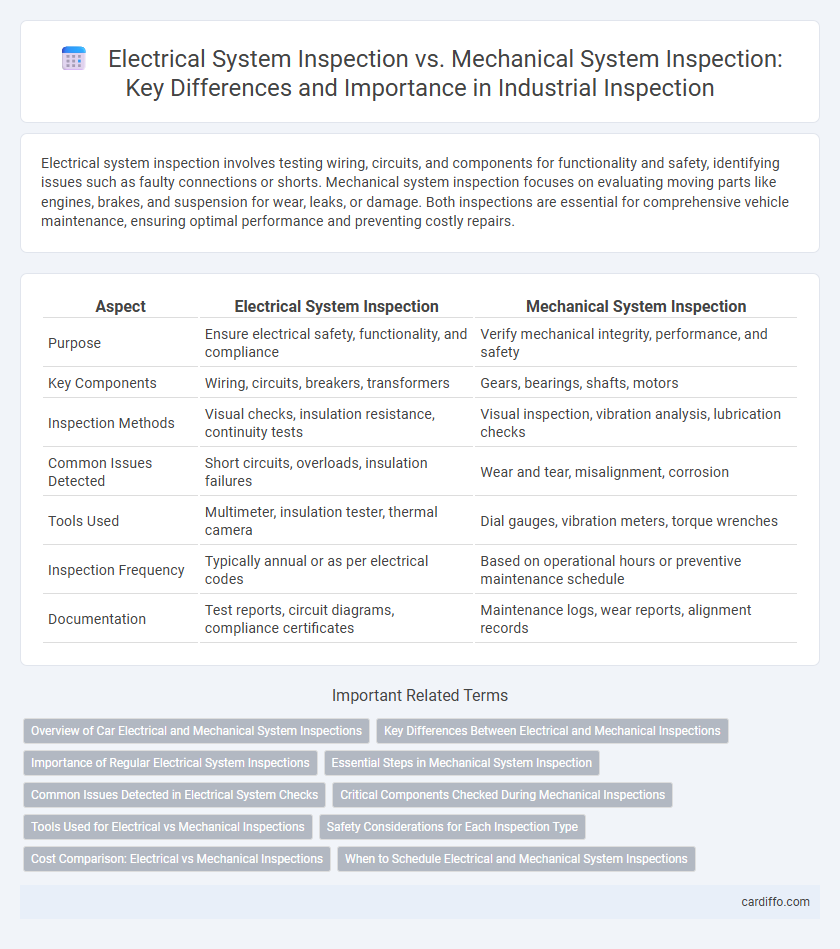
Electrical system inspection involves testing wiring, circuits, and components for functionality and safety, identifying issues such as faulty connections or shorts. Mechanical system inspection focuses on evaluating moving parts like engines, brakes, and suspension for wear, leaks, or damage. Both inspections are essential for comprehensive vehicle maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and preventing costly repairs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Electrical System Inspection | Mechanical System Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure electrical safety, functionality, and compliance | Verify mechanical integrity, performance, and safety |
| Key Components | Wiring, circuits, breakers, transformers | Gears, bearings, shafts, motors |
| Inspection Methods | Visual checks, insulation resistance, continuity tests | Visual inspection, vibration analysis, lubrication checks |
| Common Issues Detected | Short circuits, overloads, insulation failures | Wear and tear, misalignment, corrosion |
| Tools Used | Multimeter, insulation tester, thermal camera | Dial gauges, vibration meters, torque wrenches |
| Inspection Frequency | Typically annual or as per electrical codes | Based on operational hours or preventive maintenance schedule |
| Documentation | Test reports, circuit diagrams, compliance certificates | Maintenance logs, wear reports, alignment records |
Overview of Car Electrical and Mechanical System Inspections
Car electrical system inspections focus on evaluating battery health, wiring integrity, starter and alternator functionality, and electronic control units to ensure optimal power distribution and system reliability. Mechanical system inspections assess engine components, transmission, suspension, brakes, and exhaust systems for wear, alignment, and performance issues that affect vehicle safety and operation. Both inspections are essential for comprehensive vehicle maintenance, with electrical checks targeting circuitry and power management while mechanical inspections address physical wear and mechanical functionality.
Key Differences Between Electrical and Mechanical Inspections
Electrical system inspections primarily focus on assessing wiring integrity, circuit functionality, and compliance with safety codes to prevent risks like short circuits and electrical fires. Mechanical system inspections emphasize checking for wear and tear in components such as bearings, gears, and belts, ensuring proper lubrication and mechanical efficiency. Key differences include the nature of potential hazards--electrical faults versus mechanical failures--and the specialized testing methods used, such as thermal imaging for electrical systems and vibration analysis for mechanical systems.
Importance of Regular Electrical System Inspections
Regular electrical system inspections prevent potential hazards such as short circuits, electrical fires, and equipment failures by identifying worn wiring, overloaded circuits, and faulty components early. These inspections ensure compliance with safety standards like the National Electrical Code (NEC) and optimize energy efficiency, reducing operational costs. Unlike mechanical system inspections that focus on moving parts and wear, electrical inspections target circuit integrity and electrical safety, making them crucial for maintaining overall system reliability and occupant safety.
Essential Steps in Mechanical System Inspection
Mechanical system inspection involves critical steps such as visual examination for wear and corrosion, checking alignment and lubrication levels, and testing operational performance under load conditions. Essential assessments include inspecting belts, gears, bearings, and hydraulic components to ensure functionality and safety compliance. Maintaining detailed records of findings and implementing preventive maintenance schedules optimize mechanical system reliability and operational efficiency.
Common Issues Detected in Electrical System Checks
Electrical system inspections commonly detect issues such as faulty wiring, circuit breaker failures, and improper grounding, which can lead to electrical shocks or fire hazards. Overloaded circuits and degraded insulation are frequent problems identified during these checks, impacting overall system safety and efficiency. Identifying loose connections and malfunctioning components early helps prevent costly downtime and ensures compliance with safety standards.
Critical Components Checked During Mechanical Inspections
Mechanical system inspections prioritize critical components such as bearings, gears, and hydraulic systems to ensure operational integrity and prevent failures. Inspectors use vibration analysis, lubrication testing, and thermal imaging to detect wear, misalignment, or leaks in rotating machinery and structural elements. These targeted evaluations reduce downtime and enhance safety compared to electrical system inspections, which focus more on circuitry and connectivity.
Tools Used for Electrical vs Mechanical Inspections
Electrical system inspections utilize specialized tools such as multimeters, megohmmeters, clamp meters, and thermal imaging cameras to measure voltage, resistance, current, and identify hotspots in wiring and components. Mechanical system inspections rely heavily on tools like dial indicators, torque wrenches, ultrasonic testers, and vibration analyzers to assess mechanical wear, alignment, torque specifications, and structural integrity. Each set of tools is optimized for the unique diagnostic requirements of electrical circuits or mechanical assemblies, ensuring accurate detection and preventive maintenance.
Safety Considerations for Each Inspection Type
Electrical system inspections prioritize identifying hazards such as exposed wiring, faulty circuit breakers, and improper grounding to prevent electrical shocks and fire risks. Mechanical system inspections focus on assessing moving parts, lubrication levels, and wear to avoid equipment failures and physical injuries caused by mechanical malfunctions. Both inspection types require strict adherence to safety protocols and use of personal protective equipment to minimize risks during the evaluation process.
Cost Comparison: Electrical vs Mechanical Inspections
Electrical system inspections typically incur lower costs compared to mechanical system inspections due to fewer moving parts and simpler diagnostic tools. Mechanical inspections often require specialized equipment and more time-consuming procedures, leading to higher labor expenses. Budget planning should consider the complexity and scope of each inspection to optimize maintenance expenditures.
When to Schedule Electrical and Mechanical System Inspections
Schedule electrical system inspections annually or whenever there are signs of wear, such as flickering lights or circuit breaker trips, to ensure safety and prevent electrical fires. Mechanical system inspections should occur biannually, ideally before seasonal changes, to maintain HVAC efficiency, detect leaks, and prevent mechanical failures. Timely inspections based on these schedules optimize system performance and extend equipment lifespan.
Electrical system inspection vs mechanical system inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com