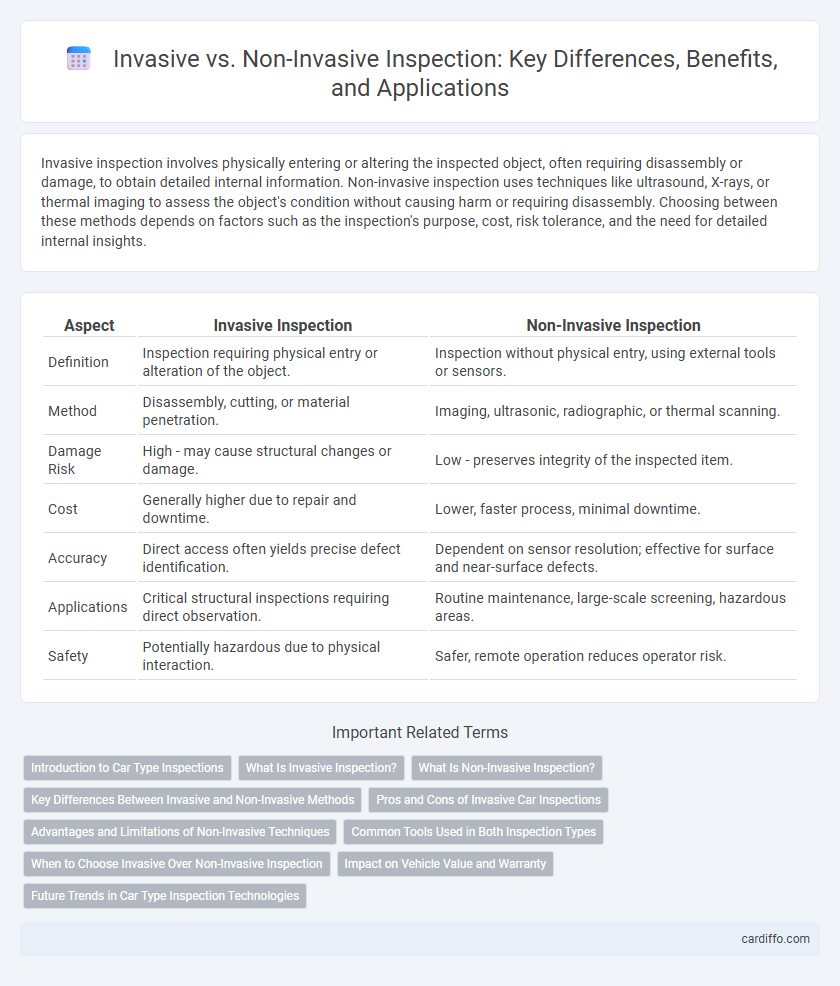
Invasive inspection involves physically entering or altering the inspected object, often requiring disassembly or damage, to obtain detailed internal information. Non-invasive inspection uses techniques like ultrasound, X-rays, or thermal imaging to assess the object's condition without causing harm or requiring disassembly. Choosing between these methods depends on factors such as the inspection's purpose, cost, risk tolerance, and the need for detailed internal insights.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Invasive Inspection | Non-Invasive Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inspection requiring physical entry or alteration of the object. | Inspection without physical entry, using external tools or sensors. |
| Method | Disassembly, cutting, or material penetration. | Imaging, ultrasonic, radiographic, or thermal scanning. |
| Damage Risk | High - may cause structural changes or damage. | Low - preserves integrity of the inspected item. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to repair and downtime. | Lower, faster process, minimal downtime. |
| Accuracy | Direct access often yields precise defect identification. | Dependent on sensor resolution; effective for surface and near-surface defects. |
| Applications | Critical structural inspections requiring direct observation. | Routine maintenance, large-scale screening, hazardous areas. |
| Safety | Potentially hazardous due to physical interaction. | Safer, remote operation reduces operator risk. |
Introduction to Car Type Inspections
Invasive inspection for car types involves physically accessing internal components, allowing for detailed assessment of parts like engines, transmissions, and wiring, which is critical for diagnosing hidden faults. Non-invasive inspection uses technologies such as ultrasonic testing, infrared thermography, and electromagnetic sensors to evaluate vehicle conditions without disassembly, preserving integrity while identifying surface and sub-surface defects. Both methods complement each other in comprehensive automotive diagnostics, improving safety and maintenance outcomes.
What Is Invasive Inspection?
Invasive inspection involves physically accessing the internal components of a system or structure, often requiring disassembly or the use of tools to penetrate surfaces. This type of inspection allows for detailed examination and direct measurement of internal conditions, which is crucial for identifying hidden defects or damage. Industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, and infrastructure routinely employ invasive inspection methods to ensure safety and reliability.
What Is Non-Invasive Inspection?
Non-invasive inspection refers to techniques used to evaluate the condition or integrity of a material, structure, or system without causing any damage or requiring disassembly. Common methods include ultrasonic testing, radiography, thermography, and visual inspection, which provide valuable data while preserving the inspected object's functionality. These techniques are essential in industries like aerospace, manufacturing, and infrastructure for maintaining safety and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Invasive and Non-Invasive Methods
Invasive inspection involves physically penetrating or altering the material or structure being examined, often requiring disassembly or damage for detailed internal analysis. Non-invasive inspection techniques utilize technologies such as ultrasound, X-rays, or thermography to assess components without causing harm or disruption. Key differences include the extent of material interaction, risk of damage, and suitability for real-time monitoring or delicate structures.
Pros and Cons of Invasive Car Inspections
Invasive car inspections provide a thorough evaluation by physically accessing critical components, allowing detection of hidden defects such as internal engine wear or structural damage. The primary advantages include high accuracy and the ability to perform detailed repairs or maintenance assessments. However, this method can be time-consuming, costly, and may cause temporary vehicle disassembly, posing risks of further damage or contamination.
Advantages and Limitations of Non-Invasive Techniques
Non-invasive inspection techniques offer significant advantages such as preserving the integrity of the inspected object, reducing downtime, and enabling real-time analysis without causing damage. These methods, including ultrasonic testing, infrared thermography, and radiography, provide high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting subsurface defects or anomalies. However, limitations include reduced effectiveness on complex geometries, material restrictions, and potential difficulties in interpretation requiring skilled operators.
Common Tools Used in Both Inspection Types
Common tools used in invasive inspection include borescopes, ultrasonic thickness gauges, and radiographic equipment, which enable direct access to internal structures and detailed defect analysis. Non-invasive inspection commonly utilizes infrared thermography cameras, electromagnetic sensors, and acoustic emission devices to detect anomalies without damaging the component. Advanced software for data analysis and imaging integration supports both inspection types, enhancing accuracy and diagnostic capabilities.
When to Choose Invasive Over Non-Invasive Inspection
Invasive inspection is chosen over non-invasive methods when detailed internal assessment or precise measurement is required, particularly for complex machinery or critical structural components where surface-level inspection cannot detect subsurface flaws. Industries such as aerospace, petrochemical, and manufacturing often rely on invasive techniques like ultrasonic testing or material sampling to ensure safety and performance standards. Selecting invasive inspection becomes essential when the risk of undetected defects could lead to catastrophic failure or costly downtime.
Impact on Vehicle Value and Warranty
Invasive inspection often involves disassembling vehicle components, which can lead to visible wear and potential pressure on the vehicle's resale value, whereas non-invasive inspection methods preserve the vehicle's original condition and maintain its market value. Warranty agreements frequently favor non-invasive inspections since they avoid tampering or damage that might void warranty coverage, while invasive processes risk triggering clauses that reduce or nullify the warranty benefits. The choice between invasive and non-invasive inspections directly influences both the protection of vehicle value and the integrity of manufacturer warranty terms.
Future Trends in Car Type Inspection Technologies
Future trends in car type inspection technologies emphasize the integration of advanced AI-powered non-invasive inspection methods such as high-resolution imaging and hyperspectral scanning, enabling rapid detection of defects without dismantling components. Invasive inspection techniques are evolving with precision robotics and micro-sensor arrays that provide detailed internal diagnostics while minimizing physical intrusion. Emerging hybrid inspection systems combine data from both invasive sensors and non-invasive imaging, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency in automotive quality control.
Invasive inspection vs non-invasive inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com