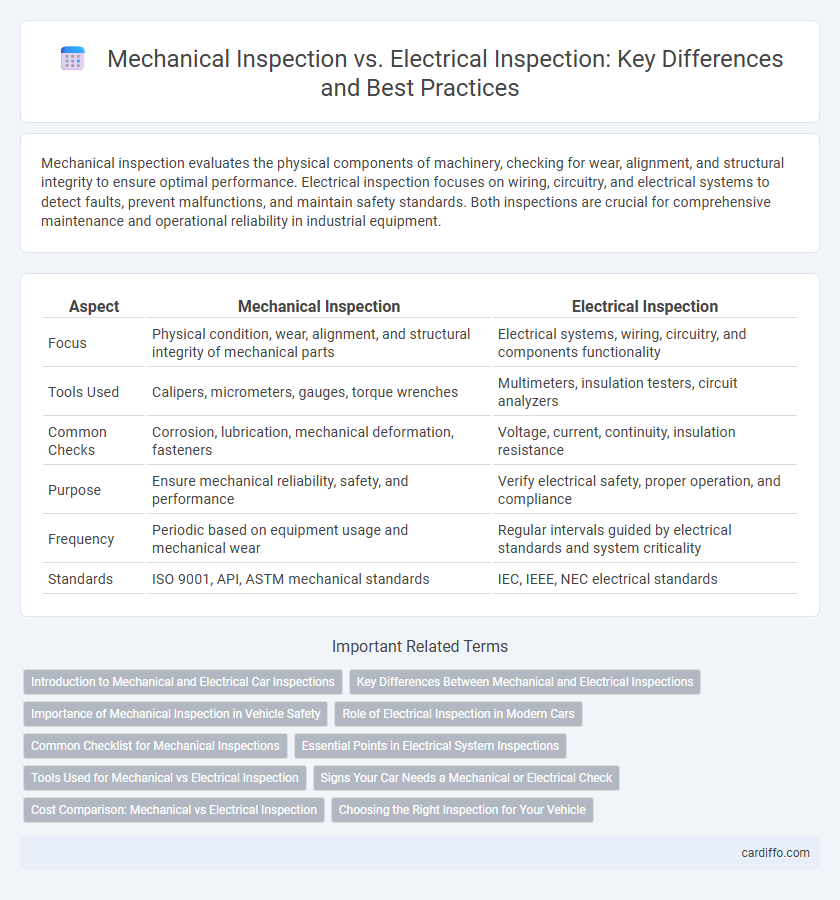
Mechanical inspection evaluates the physical components of machinery, checking for wear, alignment, and structural integrity to ensure optimal performance. Electrical inspection focuses on wiring, circuitry, and electrical systems to detect faults, prevent malfunctions, and maintain safety standards. Both inspections are crucial for comprehensive maintenance and operational reliability in industrial equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mechanical Inspection | Electrical Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Physical condition, wear, alignment, and structural integrity of mechanical parts | Electrical systems, wiring, circuitry, and components functionality |
| Tools Used | Calipers, micrometers, gauges, torque wrenches | Multimeters, insulation testers, circuit analyzers |
| Common Checks | Corrosion, lubrication, mechanical deformation, fasteners | Voltage, current, continuity, insulation resistance |
| Purpose | Ensure mechanical reliability, safety, and performance | Verify electrical safety, proper operation, and compliance |
| Frequency | Periodic based on equipment usage and mechanical wear | Regular intervals guided by electrical standards and system criticality |
| Standards | ISO 9001, API, ASTM mechanical standards | IEC, IEEE, NEC electrical standards |
Introduction to Mechanical and Electrical Car Inspections
Mechanical car inspections focus on assessing the vehicle's engine, transmission, brakes, suspension, and exhaust systems to ensure optimal performance and safety. Electrical inspections evaluate the car's battery, wiring, lighting, sensors, and electronic control units to detect faults or malfunctions affecting vehicle operation. Understanding the distinct roles of mechanical and electrical inspections helps maintain overall vehicle reliability and prevents costly repairs.
Key Differences Between Mechanical and Electrical Inspections
Mechanical inspection primarily evaluates physical components such as gears, bearings, and shafts for wear, alignment, and structural integrity, while electrical inspection focuses on wiring, circuits, and electrical systems for faults, insulation resistance, and connection quality. Mechanical inspections often involve vibration analysis and lubricant testing, whereas electrical inspections rely on multimeters, insulation testers, and circuit analyzers to identify potential hazards or failures. Both inspections are critical for safety and operational efficiency but require specialized tools and expertise specific to their respective domains.
Importance of Mechanical Inspection in Vehicle Safety
Mechanical inspection is crucial for vehicle safety as it ensures the proper functioning of essential components like brakes, suspension, and steering systems. Regular mechanical checks help detect wear, leaks, and structural damage that could lead to catastrophic failure on the road. Maintaining mechanical integrity reduces the risk of accidents and extends the lifespan of the vehicle's operational systems.
Role of Electrical Inspection in Modern Cars
Electrical inspection in modern cars is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of complex electronic systems such as the battery, alternator, wiring harness, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Unlike mechanical inspection that focuses on physical components like the engine, brakes, and suspension, electrical inspection targets circuitry integrity, voltage regulation, and sensor performance to prevent failures. This inspection helps maintain vehicle safety, optimize energy efficiency, and supports the integration of emerging technologies like electric powertrains and autonomous driving features.
Common Checklist for Mechanical Inspections
A common checklist for mechanical inspections typically includes verifying the condition of bearings, alignment of shafts, lubrication levels, and the integrity of moving parts such as gears and belts. Inspectors also assess the operation of mechanical components under load, check for unusual vibrations or noises, and ensure compliance with manufacturer specifications and safety standards. This checklist ensures machinery reliability, prevents unexpected breakdowns, and maintains optimal performance.
Essential Points in Electrical System Inspections
Electrical system inspections focus on verifying the integrity of wiring, circuit breaker functionality, and grounding systems to prevent electrical hazards and ensure compliance with safety standards. Key points include examining insulation resistance, detecting loose connections, and assessing the performance of protective devices such as fuses and surge protectors. Proper electrical inspections reduce the risk of fire, electrical shock, and equipment failure, making them crucial for maintaining operational safety and reliability.
Tools Used for Mechanical vs Electrical Inspection
Mechanical inspection primarily utilizes tools such as calipers, micrometers, torque wrenches, and dial indicators to measure dimensions, alignment, and mechanical integrity. Electrical inspection relies on multimeters, insulation resistance testers, clamp meters, and circuit analyzers to evaluate voltage, current, resistance, and continuity in electrical systems. Each inspection type employs specialized instruments tailored to detect faults and ensure compliance with respective mechanical or electrical standards.
Signs Your Car Needs a Mechanical or Electrical Check
Unusual engine noises, difficulty starting, or decreased fuel efficiency are key signs your car requires a mechanical inspection, indicating potential issues with the engine, transmission, or other mechanical components. Flickering dashboard lights, malfunctioning power windows, or non-working headlights suggest the need for an electrical inspection to address battery problems, wiring faults, or sensor failures. Regular mechanical and electrical inspections help detect these issues early, ensuring vehicle safety and preventing costly repairs.
Cost Comparison: Mechanical vs Electrical Inspection
Mechanical inspection typically incurs higher costs due to the complexity of machinery and the need for specialized tools and skilled technicians. Electrical inspections often involve less expensive equipment and faster diagnostic procedures, resulting in lower overall expenses. Budget allocation for inspection should consider the frequency and criticality of mechanical versus electrical system assessments.
Choosing the Right Inspection for Your Vehicle
Mechanical inspection evaluates the physical components of a vehicle, such as the engine, transmission, brakes, and suspension, ensuring these systems operate safely and efficiently. Electrical inspection focuses on the vehicle's wiring, battery, lighting, and electronic control units, identifying issues related to circuits, sensors, and onboard computers. Selecting the right inspection type depends on the vehicle's symptoms, age, and usage, with thorough diagnostics often combining both mechanical and electrical assessments for accurate maintenance and repair.
Mechanical inspection vs electrical inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com