Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in improved fuel atomization and more precise control over the air-fuel mixture, which enhances engine efficiency and power output. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, allowing better fuel-air mixing before entering the combustion chamber, which often leads to smoother engine operation and reduced carbon buildup on intake valves. Combining direct injection with port injection can optimize combustion performance, lower emissions, and improve fuel economy by leveraging the advantages of both systems.
Table of Comparison
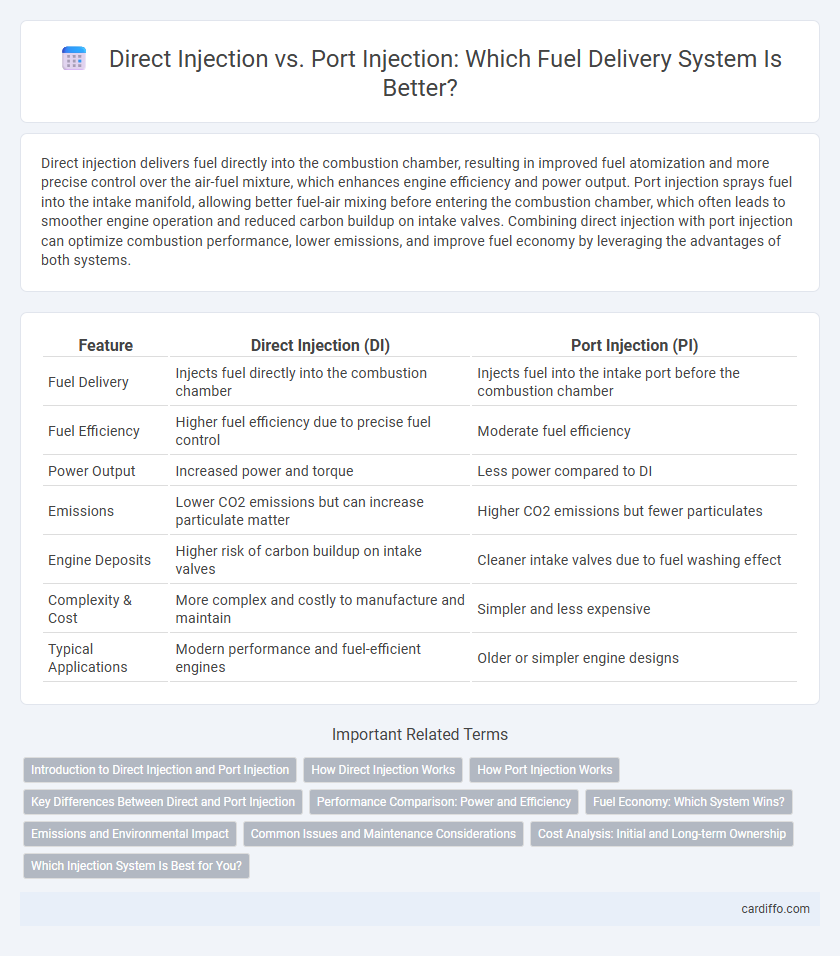
| Feature | Direct Injection (DI) | Port Injection (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber | Injects fuel into the intake port before the combustion chamber |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency due to precise fuel control | Moderate fuel efficiency |
| Power Output | Increased power and torque | Less power compared to DI |
| Emissions | Lower CO2 emissions but can increase particulate matter | Higher CO2 emissions but fewer particulates |
| Engine Deposits | Higher risk of carbon buildup on intake valves | Cleaner intake valves due to fuel washing effect |
| Complexity & Cost | More complex and costly to manufacture and maintain | Simpler and less expensive |
| Typical Applications | Modern performance and fuel-efficient engines | Older or simpler engine designs |
Introduction to Direct Injection and Port Injection
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel atomization and combustion efficiency, which improves power output and reduces emissions. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, allowing better mixing with air before entering the combustion chamber, promoting smoother engine operation and reduced carbon buildup. Both systems influence fuel economy and engine performance differently, with direct injection favored in modern high-performance engines and port injection commonly found in older or simpler designs.
How Direct Injection Works
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure, creating a precise air-fuel mixture that enhances combustion efficiency and power output. This method allows for better control of fuel atomization and timing, reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to port injection systems. The precise injection timing and localized fuel delivery improve thermal efficiency, resulting in optimized engine performance and lower particulate emissions.
How Port Injection Works
Port injection delivers fuel directly into the intake ports, allowing precise fuel atomization before entering the combustion chamber. This method improves air-fuel mixing, enhances throttle response, and reduces emissions by ensuring more complete combustion. Port injection systems typically operate at lower pressures compared to direct injection, resulting in simpler maintenance and lower injector wear.
Key Differences Between Direct and Port Injection
Direct injection sprays fuel directly into the combustion chamber, providing precise fuel delivery and improved combustion efficiency, while port injection injects fuel into the intake port, mixing it with air before entering the cylinder. Direct injection enhances power output and fuel economy but may produce higher particulate emissions compared to the smoother combustion of port injection. Engine design, fuel atomization, and emissions control are critical factors distinguishing the performance and environmental impact of these two fuel injection systems.
Performance Comparison: Power and Efficiency
Direct injection systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enabling precise fuel metering and improved combustion efficiency, which typically results in higher power output and better fuel economy compared to port injection. Port injection sprays fuel into the intake manifold, allowing for better air-fuel mixing but often at the expense of lower peak power and efficiency. Engines with direct injection benefit from enhanced throttle response and reduced fuel consumption, especially under high-load conditions.
Fuel Economy: Which System Wins?
Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing combustion efficiency and resulting in better fuel economy compared to port injection, which sprays fuel into the intake manifold. Studies show vehicles equipped with direct injection systems can achieve fuel savings of up to 10-15% due to precise fuel metering and improved air-fuel mixture control. However, some engines combine both systems, known as dual injection, to optimize fuel economy across different operating conditions.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Direct injection engines produce lower CO2 emissions due to improved fuel atomization and combustion efficiency, resulting in better fuel economy compared to port injection systems. However, direct injection can generate higher particulate matter (PM) and NOx emissions, which require advanced after-treatment technologies such as particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction to meet emission standards. Port injection engines typically emit fewer particulates and NOx but have higher overall fuel consumption and CO2 emissions, impacting long-term environmental sustainability.
Common Issues and Maintenance Considerations
Direct injection systems often face carbon buildup on intake valves due to fuel not washing over them, causing rough idling and reduced fuel efficiency, whereas port injection systems typically avoid this issue. Maintenance for direct injection includes regular use of specialized cleaning additives and occasional professional walnut blasting to remove carbon deposits, while port injection systems primarily require routine fuel filter and injector cleanings. Both systems need timely fuel filter replacements and careful monitoring of fuel quality to prevent injector clogging and maintain optimal engine performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Ownership
Direct injection systems generally have higher initial costs due to advanced fuel injectors and more complex engine components, leading to increased repair expenses over time. Port injection systems tend to be less expensive upfront and offer lower maintenance costs, as their simpler design reduces the likelihood of issues like carbon buildup. Long-term ownership costs often favor port injection for budget-conscious drivers, while direct injection may provide better fuel efficiency and performance that offset some costs depending on usage patterns.
Which Injection System Is Best for You?
Direct injection offers improved fuel efficiency and precise control of fuel delivery, making it ideal for high-performance engines and modern vehicles focused on power and emissions. Port injection, known for its reliability and simpler maintenance, is often preferred for older engines or applications valuing consistent fuel-air mixing and lower complexity. Choosing the best injection system depends on your priorities such as fuel economy, engine type, maintenance ease, and driving conditions.
direct injection vs port injection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com