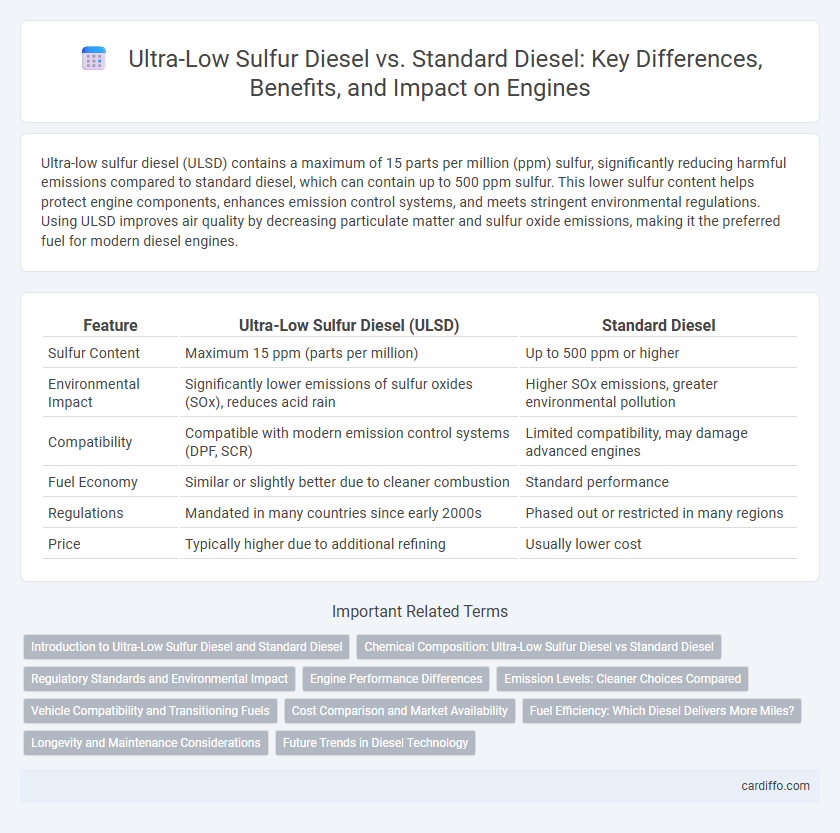
Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) contains a maximum of 15 parts per million (ppm) sulfur, significantly reducing harmful emissions compared to standard diesel, which can contain up to 500 ppm sulfur. This lower sulfur content helps protect engine components, enhances emission control systems, and meets stringent environmental regulations. Using ULSD improves air quality by decreasing particulate matter and sulfur oxide emissions, making it the preferred fuel for modern diesel engines.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) | Standard Diesel |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur Content | Maximum 15 ppm (parts per million) | Up to 500 ppm or higher |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx), reduces acid rain | Higher SOx emissions, greater environmental pollution |
| Compatibility | Compatible with modern emission control systems (DPF, SCR) | Limited compatibility, may damage advanced engines |
| Fuel Economy | Similar or slightly better due to cleaner combustion | Standard performance |
| Regulations | Mandated in many countries since early 2000s | Phased out or restricted in many regions |
| Price | Typically higher due to additional refining | Usually lower cost |
Introduction to Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel and Standard Diesel
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) contains a maximum of 15 parts per million (ppm) sulfur, significantly lower than the 500 ppm found in standard diesel, reducing harmful emissions and improving air quality. ULSD is designed to meet stringent environmental regulations and is compatible with advanced emission control technologies such as diesel particulate filters (DPF) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. Standard diesel, while commonly used, produces higher sulfur emissions that contribute to acid rain and respiratory problems, making ULSD the preferred choice for modern diesel engines and environmental compliance.
Chemical Composition: Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel vs Standard Diesel
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) contains a maximum sulfur content of 15 parts per million (ppm), significantly lower than Standard Diesel's sulfur levels, which can reach up to 5,000 ppm. This reduction in sulfur drastically decreases sulfur oxide emissions, enhancing environmental performance. Chemically, ULSD maintains similar hydrocarbon chains to Standard Diesel but undergoes additional refining processes like hydrotreatment to remove sulfur compounds.
Regulatory Standards and Environmental Impact
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) meets stringent regulatory standards by limiting sulfur content to 15 parts per million, significantly lower than Standard Diesel's typical 500 parts per million. This reduction in sulfur drastically decreases harmful emissions, including sulfur oxides (SOx), which contribute to acid rain and respiratory problems. Compliance with environmental regulations such as the EPA's Tier 3 standards ensures ULSD supports cleaner air quality and reduced environmental impact compared to Standard Diesel.
Engine Performance Differences
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) significantly reduces sulfur content to 15 ppm compared to standard diesel's higher sulfur levels, enhancing engine performance by improving combustion efficiency and reducing injector deposits. ULSD supports advanced emission control technologies like diesel particulate filters (DPF) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR), leading to lower engine wear and improved fuel economy. Engines running on ULSD exhibit smoother operation, decreased maintenance costs, and extended longevity compared to those using standard diesel.
Emission Levels: Cleaner Choices Compared
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) contains sulfur levels reduced to 15 parts per million, significantly lowering emissions of sulfur oxides and particulate matter compared to Standard Diesel, which has sulfur content up to 500 parts per million. This reduction in sulfur directly decreases acid rain and respiratory pollutants, contributing to improved air quality and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Vehicles running on ULSD also benefit from enhanced performance of advanced emission control systems like diesel particulate filters and catalytic converters, further minimizing nitrogen oxide and carbon emissions.
Vehicle Compatibility and Transitioning Fuels
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) significantly reduces sulfur content to 15 ppm, enhancing compatibility with modern diesel engines equipped with advanced emission control technologies like diesel particulate filters and catalytic converters. Standard Diesel, containing up to 500 ppm sulfur, may damage these sensitive systems and is primarily suited for older vehicles without strict emissions requirements. Transitioning from Standard Diesel to ULSD requires careful consideration of vehicle fuel system compatibility, potential need for filter replacements, and adjustments in maintenance schedules to ensure optimal engine performance and emissions compliance.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) generally costs more than Standard Diesel due to its refined processing and stricter environmental standards, with price differences ranging from 10% to 30% depending on region and supply chain dynamics. Market availability of ULSD is widespread in developed countries as regulatory mandates require its use, while Standard Diesel remains prevalent in regions with less stringent environmental policies or limited refining infrastructure. Bulk purchasing and long-term contracts can mitigate ULSD costs, but fluctuating crude oil prices continue to impact both fuel types' pricing and accessibility globally.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Diesel Delivers More Miles?
Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) improves fuel efficiency by reducing engine deposits and promoting cleaner combustion, resulting in slight mileage gains compared to standard diesel. Studies show ULSD can enhance fuel economy by approximately 1-3%, depending on engine type and driving conditions. While standard diesel offers comparable energy content, ULSD's cleaner formulation contributes to better long-term engine performance and consistent fuel economy.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) significantly enhances engine longevity by reducing sulfur-induced corrosion and deposits, which are prevalent in Standard Diesel. Vehicles using ULSD require less frequent maintenance and experience lower fuel system wear, extending the lifespan of critical components like fuel injectors and filters. Maintenance costs decrease due to fewer fuel-related repairs, making ULSD a cost-effective choice for long-term engine health.
Future Trends in Diesel Technology
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) is becoming the standard fuel due to stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing sulfur emissions, significantly lowering particulate matter and nitrogen oxides compared to standard diesel. Future trends in diesel technology emphasize advancements in fuel formulations and engine designs to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce greenhouse gases, including integration with biodiesel and renewable diesel blends. Emerging innovations focus on hybrid diesel-electric systems and the adoption of synthetic diesel fuels derived from sustainable sources to meet global decarbonization goals.
Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel vs Standard Diesel Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com