Lead replacement petrol contains additives that mimic the anti-knock properties of traditional leaded fuel without the harmful effects of lead, offering a safer alternative for older engines. Unleaded petrol, formulated without lead additives, is designed for modern vehicles with catalytic converters, promoting cleaner emissions and environmental protection. Both fuels aim to prevent engine knocking but differ in additive composition and compatibility with vehicle engine types.
Table of Comparison
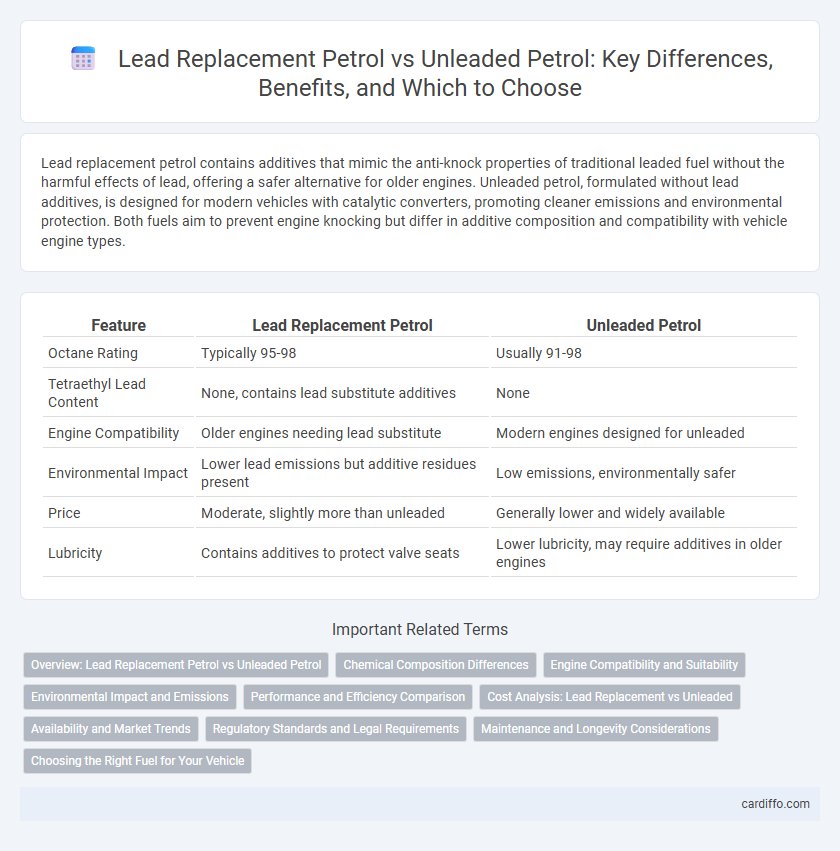
| Feature | Lead Replacement Petrol | Unleaded Petrol |
|---|---|---|
| Octane Rating | Typically 95-98 | Usually 91-98 |
| Tetraethyl Lead Content | None, contains lead substitute additives | None |
| Engine Compatibility | Older engines needing lead substitute | Modern engines designed for unleaded |
| Environmental Impact | Lower lead emissions but additive residues present | Low emissions, environmentally safer |
| Price | Moderate, slightly more than unleaded | Generally lower and widely available |
| Lubricity | Contains additives to protect valve seats | Lower lubricity, may require additives in older engines |
Overview: Lead Replacement Petrol vs Unleaded Petrol
Lead replacement petrol contains organic additives that provide similar anti-knock properties to traditional leaded petrol without using harmful tetraethyl lead, helping to protect older engines designed for leaded fuel. Unleaded petrol, free from lead compounds, is formulated with other additives to meet modern engine requirements, improving emissions and engine performance in newer vehicles. Both fuels serve as alternatives to leaded petrol, but lead replacement petrol is often preferred for classic cars to maintain valve seat protection.
Chemical Composition Differences
Lead replacement petrol contains organolead compounds such as tetraethyllead to enhance octane rating and reduce engine knocking, while unleaded petrol relies on alternative additives like MTBE or ethanol for combustion efficiency. The chemical composition of unleaded petrol excludes toxic lead, reducing environmental and health hazards associated with lead emissions. These differences affect engine performance and emission control technologies by influencing combustion characteristics and catalyst compatibility.
Engine Compatibility and Suitability
Lead replacement petrol is formulated to work in older engines designed for leaded fuel, preventing valve seat recession and ensuring optimal performance. Unleaded petrol is compatible with modern engines equipped with hardened valve seats and advanced emission control systems, promoting cleaner combustion and lower emissions. Choosing the correct fuel depends on the engine's valve seat material and manufacturer specifications to maintain engine durability and efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Lead replacement petrol eliminates the toxic effects of tetraethyllead, significantly reducing lead pollution in air and soil, which protects ecosystems and human health. Unleaded petrol produces lower emissions of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, contributing to improved air quality and reduced smog formation. Both fuels support the reduction of harmful pollutants, but unleaded petrol offers a clearer benefit in minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable environmental practices.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Unleaded petrol offers higher combustion efficiency and cleaner engine performance compared to lead replacement petrol, which often contains additives that can reduce fuel economy. Lead replacement petrol can cause carbon buildup and fouling in spark plugs, degrading engine efficiency over time. Modern engines optimized for unleaded petrol demonstrate better acceleration, lower emissions, and improved fuel consumption rates, making unleaded petrol a more efficient and environmentally friendly choice.
Cost Analysis: Lead Replacement vs Unleaded
Lead replacement petrol generally costs more than unleaded petrol due to the additional additives required to mimic lead's anti-knock properties while meeting modern emissions standards. Unleaded petrol benefits from large-scale production and widespread adoption, resulting in lower prices at the pump compared to lead replacement fuel. Consumers seeking cost efficiency typically prefer unleaded petrol, which offers better fuel economy and reduced maintenance expenses over time.
Availability and Market Trends
Unleaded petrol dominates global fuel markets with widespread availability due to stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing lead emissions. Lead replacement petrol, containing alternative additives to improve octane rating, remains a niche product primarily in regions with limited unleaded fuel infrastructure. Market trends indicate a consistent shift toward unleaded petrol as governments and manufacturers promote cleaner, lead-free options for vehicle compatibility and public health.
Regulatory Standards and Legal Requirements
Unleaded petrol complies with stringent regulatory standards aimed at reducing toxic emissions and protecting public health, adhering to mandates set by agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union's fuel quality directives. Lead replacement petrol, formulated to meet similar environmental requirements, contains additives designed to mimic the anti-knock properties of leaded fuel without violating current legal restrictions on lead content. Both fuel types must pass rigorous testing to ensure conformity with vehicle emission regulations and fuel quality standards, ensuring market legality and environmental compliance.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Unleaded petrol reduces engine wear by preventing lead deposits that can clog valves and spark plugs, enhancing overall vehicle longevity. Lead replacement petrol, while designed to simulate leaded fuel's protective properties, may still lead to increased maintenance due to incomplete valve seat lubrication. Consistent use of unleaded petrol promotes cleaner combustion and fewer engine deposits, decreasing the frequency of costly repairs and extending engine life.
Choosing the Right Fuel for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right fuel for your vehicle involves understanding the differences between lead replacement petrol and unleaded petrol, such as their chemical composition and engine compatibility. Lead replacement petrol contains additives designed to protect older engines originally built for leaded petrol, preventing valve seat recession, while unleaded petrol is formulated for modern vehicles with catalytic converters. Using the correct fuel enhances engine performance, reduces emissions, and prolongs the life of your vehicle's engine components.
Lead Replacement Petrol vs Unleaded Petrol Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com