Octane boosting increases a fuel's resistance to knocking and improves engine performance by raising the octane rating. Fuel additives, on the other hand, enhance overall fuel quality by cleaning injectors, reducing emissions, and preventing corrosion without necessarily affecting octane levels. Choosing between octane boosters and fuel additives depends on whether the priority is engine knock prevention or maintaining fuel system health.
Table of Comparison
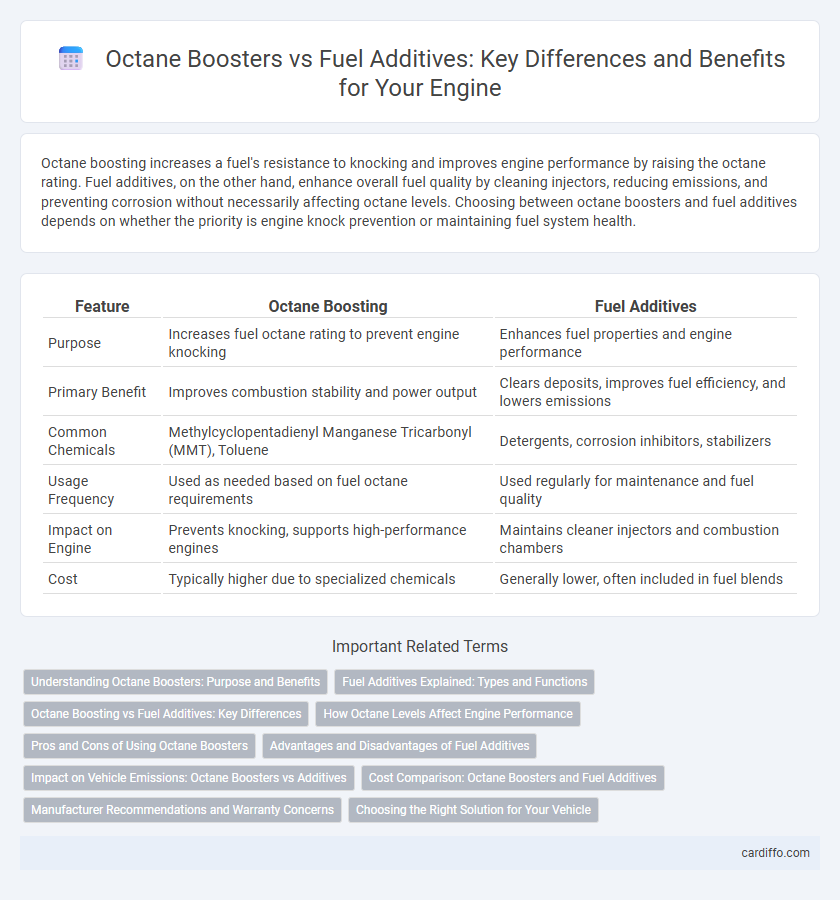
| Feature | Octane Boosting | Fuel Additives |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Increases fuel octane rating to prevent engine knocking | Enhances fuel properties and engine performance |
| Primary Benefit | Improves combustion stability and power output | Clears deposits, improves fuel efficiency, and lowers emissions |
| Common Chemicals | Methylcyclopentadienyl Manganese Tricarbonyl (MMT), Toluene | Detergents, corrosion inhibitors, stabilizers |
| Usage Frequency | Used as needed based on fuel octane requirements | Used regularly for maintenance and fuel quality |
| Impact on Engine | Prevents knocking, supports high-performance engines | Maintains cleaner injectors and combustion chambers |
| Cost | Typically higher due to specialized chemicals | Generally lower, often included in fuel blends |
Understanding Octane Boosters: Purpose and Benefits
Octane boosters increase the octane rating of gasoline, improving fuel's ability to resist engine knocking and pre-ignition in high-performance or older engines. These additives enhance combustion efficiency, allowing engines to run smoother and deliver better power output without damaging internal components. Using octane boosters can also optimize fuel economy and reduce emissions by maintaining optimal ignition timing and preventing incomplete combustion.
Fuel Additives Explained: Types and Functions
Fuel additives enhance engine performance, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions by modifying fuel properties and combustion. Types of fuel additives include detergents that clean injectors, corrosion inhibitors that protect engine components, stabilizers that extend fuel shelf life, and anti-knock agents that prevent premature ignition. Each additive serves a specific function to optimize fuel quality and maintain engine health under various operating conditions.
Octane Boosting vs Fuel Additives: Key Differences
Octane boosting specifically targets increasing the fuel's octane rating to prevent engine knocking, thereby enhancing performance in high-compression engines. Fuel additives encompass a broader range of chemicals designed to clean engine components, improve combustion efficiency, and reduce emissions beyond just increasing octane levels. Understanding that octane boosters serve a specialized function while fuel additives provide comprehensive engine maintenance is crucial for optimizing fuel performance.
How Octane Levels Affect Engine Performance
Higher octane levels in fuel prevent engine knocking and allow for more efficient combustion under high compression, enhancing overall engine performance and longevity. Octane boosters specifically increase the fuel's resistance to knocking, enabling engines to operate at optimal timing and power output without damaging detonation. Fuel additives, while diverse in function, primarily improve fuel stability, cleanliness, and combustion efficiency but do not significantly alter the octane rating.
Pros and Cons of Using Octane Boosters
Octane boosters increase fuel's octane rating, reducing engine knocking and improving performance, particularly in high-compression or turbocharged engines. Pros include enhanced power output and protection against pre-ignition, while cons involve potential increased costs and the risk of deposits if used excessively or improperly. Unlike general fuel additives, octane boosters specifically target combustion quality, but may not address issues like fuel system cleaning or emissions reduction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuel Additives
Fuel additives enhance combustion efficiency, reduce engine deposits, and improve fuel stability, resulting in smoother engine performance and extended engine life. However, some fuel additives may cause corrosion or damage fuel system components if improperly used or over-applied, and their cost can add up over time without guaranteed performance gains. Careful selection based on engine type and manufacturer recommendations is essential to maximize benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Impact on Vehicle Emissions: Octane Boosters vs Additives
Octane boosters increase fuel octane rating, improving combustion stability and engine performance, which can reduce unburned hydrocarbons and decrease emissions of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Fuel additives, including detergents and stabilizers, enhance fuel cleanliness and combustion efficiency, leading to lower particulate matter and fewer harmful deposits in the engine. While octane boosters primarily prevent engine knock and improve power, fuel additives contribute to overall emission control by maintaining fuel system health and optimizing fuel burn.
Cost Comparison: Octane Boosters and Fuel Additives
Octane boosters generally cost between $10 to $20 per bottle, providing a quick but often short-term increase in fuel octane rating, while fuel additives range from $5 to $15 and offer broader engine benefits such as cleaning and performance enhancement. The price per gallon impact for octane boosters can be higher due to smaller volume usage and concentrated formula, whereas fuel additives, used regularly, present a more cost-effective solution for maintaining engine health. Choosing between the two depends on whether immediate octane enhancement or ongoing engine maintenance provides better value for the vehicle's performance needs.
Manufacturer Recommendations and Warranty Concerns
Manufacturers typically recommend using specific fuel additives designed to meet engine requirements, emphasizing adherence to approved octane levels to avoid potential damage. Octane boosters may temporarily enhance performance but can lead to incomplete combustion, increasing engine deposits and risking warranty claims. Following manufacturer guidelines ensures compatibility with engine systems, maintaining warranty validity and optimizing fuel efficiency.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Vehicle
Octane boosting enhances fuel's resistance to knocking by increasing its octane rating, ideal for high-performance engines requiring higher compression ratios. Fuel additives serve various purposes, such as cleaning injectors, preventing corrosion, and improving combustion efficiency, complementing octane boosters but addressing broader engine health. Selecting the right solution depends on your vehicle's manufacturer specifications, engine type, and performance needs, ensuring compatibility and optimal fuel efficiency.
Octane Boosting vs Fuel Additives Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com