Turbocharged engines enhance fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for better fuel combustion and increased power output from smaller engine sizes. Naturally aspirated engines, while simpler and often more reliable, typically consume more fuel due to less efficient air intake and lower power density. The advanced engineering of turbocharged systems generally results in improved miles per gallon and reduced emissions compared to naturally aspirated counterparts.
Table of Comparison
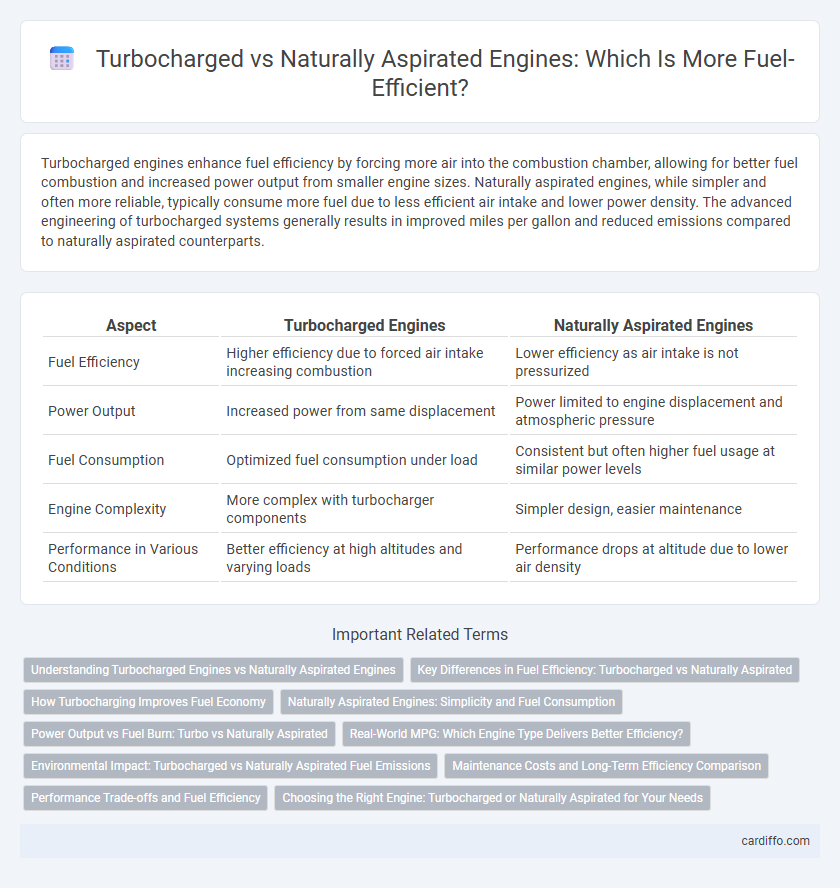
| Aspect | Turbocharged Engines | Naturally Aspirated Engines |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher efficiency due to forced air intake increasing combustion | Lower efficiency as air intake is not pressurized |
| Power Output | Increased power from same displacement | Power limited to engine displacement and atmospheric pressure |
| Fuel Consumption | Optimized fuel consumption under load | Consistent but often higher fuel usage at similar power levels |
| Engine Complexity | More complex with turbocharger components | Simpler design, easier maintenance |
| Performance in Various Conditions | Better efficiency at high altitudes and varying loads | Performance drops at altitude due to lower air density |
Understanding Turbocharged Engines vs Naturally Aspirated Engines
Turbocharged engines enhance fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in improved power output from smaller engine sizes compared to naturally aspirated engines, which rely solely on atmospheric pressure. This increased air intake allows turbocharged engines to deliver higher torque at lower RPMs, optimizing fuel consumption during acceleration and cruising. In contrast, naturally aspirated engines typically consume more fuel to achieve similar power levels due to their less efficient air intake system.
Key Differences in Fuel Efficiency: Turbocharged vs Naturally Aspirated
Turbocharged engines deliver higher fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for more complete fuel burning and improved power output per unit of fuel compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure, often resulting in lower fuel efficiency due to less optimized air-fuel mixture and reduced combustion efficiency. The increased torque and power density of turbocharged engines also enable smaller engine sizes, further enhancing fuel economy.
How Turbocharging Improves Fuel Economy
Turbocharging improves fuel economy by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, allowing for a more efficient burn of fuel and increased power output from smaller engines. This leads to reduced fuel consumption compared to naturally aspirated engines, which rely solely on atmospheric pressure for air intake. Modern turbocharged engines achieve higher thermal efficiency and lower emissions, making them a preferred choice for enhanced fuel efficiency in both passenger vehicles and commercial applications.
Naturally Aspirated Engines: Simplicity and Fuel Consumption
Naturally aspirated engines maintain fuel efficiency through their straightforward design, lacking forced induction components such as turbochargers or superchargers. This simplicity results in fewer moving parts, reducing mechanical losses and maintenance costs while promoting steady fuel consumption under moderate driving conditions. Although naturally aspirated engines typically deliver lower power density, their predictable fuel usage and reliability make them suitable for drivers prioritizing consistent efficiency over peak performance.
Power Output vs Fuel Burn: Turbo vs Naturally Aspirated
Turbocharged engines deliver higher power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in better fuel efficiency under load compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines often consume more fuel to achieve similar power levels because they rely solely on atmospheric pressure for air intake. The enhanced air-fuel mixture control in turbocharged systems optimizes combustion, reducing fuel burn while maximizing power output.
Real-World MPG: Which Engine Type Delivers Better Efficiency?
Turbocharged engines generally achieve higher real-world MPG compared to naturally aspirated engines due to their ability to deliver increased power from smaller displacement, resulting in better fuel combustion and reduced fuel consumption. Studies show turbocharged vehicles can improve fuel efficiency by 10-20% under typical driving conditions, especially during highway cruising where turbochargers maximize fuel-air mixture optimization. Naturally aspirated engines often consume more fuel as they rely on engine size rather than forced induction to generate power, leading to lower miles per gallon on average.
Environmental Impact: Turbocharged vs Naturally Aspirated Fuel Emissions
Turbocharged engines enhance fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in better fuel atomization and reduced fuel consumption, which lowers CO2 emissions compared to naturally aspirated engines. Naturally aspirated engines typically emit higher levels of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO) due to less precise fuel combustion. Optimizing turbocharged engine performance plays a critical role in minimizing environmental impact by improving fuel economy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Maintenance Costs and Long-Term Efficiency Comparison
Turbocharged engines often deliver superior fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, which enhances power output without significantly increasing fuel consumption. Maintenance costs for turbocharged systems tend to be higher due to complex components such as turbochargers, intercoolers, and additional cooling requirements, which may require specialized care and more frequent servicing. Naturally aspirated engines typically offer lower long-term maintenance expenses and more predictable reliability but can fall short in fuel economy compared to turbocharged counterparts in similar performance classes.
Performance Trade-offs and Fuel Efficiency
Turbocharged engines enhance fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, enabling smaller displacement engines to produce higher power outputs compared to naturally aspirated engines. However, turbochargers often generate increased heat and require additional fuel to maintain performance under boost, which can reduce overall fuel economy during aggressive driving. Naturally aspirated engines provide more linear power delivery and typically offer better reliability and fuel efficiency in steady, low-load conditions but sacrifice peak power and torque available from turbocharged configurations.
Choosing the Right Engine: Turbocharged or Naturally Aspirated for Your Needs
Turbocharged engines deliver superior fuel efficiency by extracting more power from less fuel compared to naturally aspirated engines, making them ideal for drivers seeking performance without compromising economy. Naturally aspirated engines offer simpler mechanics and consistent power delivery, preferred for reliability and maintenance ease in long-term use. Evaluating driving habits, performance expectations, and maintenance preferences ensures selecting the right engine aligns with fuel efficiency goals and overall vehicle needs.
Turbocharged Fuel Efficiency vs Naturally Aspirated Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com