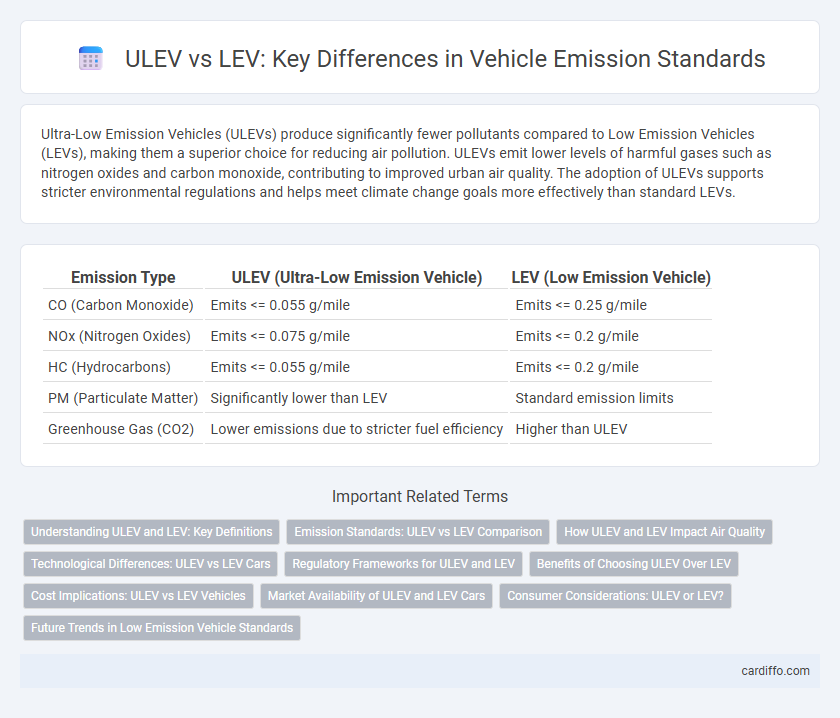
Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) produce significantly fewer pollutants compared to Low Emission Vehicles (LEVs), making them a superior choice for reducing air pollution. ULEVs emit lower levels of harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide, contributing to improved urban air quality. The adoption of ULEVs supports stricter environmental regulations and helps meet climate change goals more effectively than standard LEVs.
Table of Comparison
| Emission Type | ULEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) | LEV (Low Emission Vehicle) |
|---|---|---|
| CO (Carbon Monoxide) | Emits <= 0.055 g/mile | Emits <= 0.25 g/mile |
| NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) | Emits <= 0.075 g/mile | Emits <= 0.2 g/mile |
| HC (Hydrocarbons) | Emits <= 0.055 g/mile | Emits <= 0.2 g/mile |
| PM (Particulate Matter) | Significantly lower than LEV | Standard emission limits |
| Greenhouse Gas (CO2) | Lower emissions due to stricter fuel efficiency | Higher than ULEV |
Understanding ULEV and LEV: Key Definitions
ULEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) and LEV (Low Emission Vehicle) are classifications used to measure vehicle emissions based on regulatory standards such as those set by the California Air Resources Board (CARB). LEVs produce fewer emissions than conventional vehicles, while ULEVs have even stricter limits, emitting significantly lower levels of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons. These definitions are essential for understanding compliance requirements and environmental impact in automotive emission regulations.
Emission Standards: ULEV vs LEV Comparison
Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) emit significantly fewer pollutants than Low Emission Vehicles (LEVs), with ULEVs typically producing fewer than 0.02 grams per mile of non-methane organic gases compared to LEVs' higher limits. Emission standards set by regulatory agencies like the California Air Resources Board (CARB) require ULEVs to meet stricter thresholds for nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, ensuring cleaner air quality. These standards make ULEVs a critical focus in reducing urban air pollution and meeting future environmental targets.
How ULEV and LEV Impact Air Quality
Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) emit significantly fewer pollutants than Low Emission Vehicles (LEVs), leading to improved air quality by reducing harmful substances such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. LEVs offer moderate emission reductions but still contribute to airborne contaminants that affect respiratory health and environmental conditions. Transitioning from LEVs to ULEVs plays a pivotal role in curbing urban air pollution and mitigating climate change effects.
Technological Differences: ULEV vs LEV Cars
ULEV (Ultra Low Emission Vehicle) cars utilize advanced emission control technologies such as enhanced catalytic converters, precise fuel injection systems, and improved onboard diagnostics to drastically reduce pollutants compared to LEV (Low Emission Vehicle) models. LEV vehicles meet baseline standards by controlling emissions primarily through basic catalytic converters and less sophisticated engine management systems. The technological advancements in ULEVs enable significantly lower levels of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides, contributing to more stringent compliance with current environmental regulations.
Regulatory Frameworks for ULEV and LEV
Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) face stricter regulatory frameworks compared to Low Emission Vehicles (LEVs), as governments enforce tighter emission standards to accelerate pollution reduction. ULEV regulations often mandate lower limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, aligning with policies such as the California Air Resources Board (CARB) standards and Euro 6/7 regulations. LEV standards, while less stringent, serve as baseline compliance requirements to ensure vehicles meet minimum emission controls under frameworks like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Tier 2 and Tier 3 programs.
Benefits of Choosing ULEV Over LEV
ULEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) standards significantly reduce harmful pollutants compared to LEV (Low Emission Vehicle) standards, resulting in cleaner air and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Vehicles meeting ULEV criteria emit up to 50% fewer hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, directly contributing to improved public health and reduced environmental impact. Opting for ULEV-compliant vehicles supports stricter regulatory targets and enhances long-term sustainability in urban transportation.
Cost Implications: ULEV vs LEV Vehicles
ULEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles) typically have higher upfront costs than LEV (Low Emission Vehicles) due to advanced technology and stringent emission control systems. However, ULEVs often benefit from lower fuel consumption and reduced maintenance expenses, leading to potential long-term savings. Tax incentives, subsidies, and lower environmental fees further impact the overall cost-effectiveness of ULEVs compared to LEVs.
Market Availability of ULEV and LEV Cars
ULEV (Ultra Low Emission Vehicles) and LEV (Low Emission Vehicles) differ significantly in market availability, with LEVs being more widely accessible due to established technologies and regulatory incentives. Automakers have expanded LEV models across various segments, including hybrids and mild-hybrids, capitalizing on consumer demand and emission standards compliance. ULEV options remain more limited but are increasingly entering the market through advancements in electric and fuel cell vehicle offerings targeting ultra-low emission goals.
Consumer Considerations: ULEV or LEV?
Consumers choosing between Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) and Low Emission Vehicles (LEVs) should evaluate factors such as environmental impact, fuel efficiency, and long-term savings. ULEVs typically produce fewer pollutants, reducing carbon footprint and potentially qualifying for government incentives or tax rebates. LEVs often offer lower upfront costs but may result in higher emissions and increased fuel consumption over time.
Future Trends in Low Emission Vehicle Standards
ULEV (Ultra Low Emission Vehicle) standards are set to become more stringent, driving automakers to innovate in hybrid and electric powertrains to achieve lower tailpipe emissions. LEV (Low Emission Vehicle) classifications will progressively incorporate advanced emission control technologies like improved catalytic converters and particulate filters, aiming for near-zero emissions. Future regulations are poised to integrate real-time emission monitoring and stricter fuel economy benchmarks, accelerating the transition toward zero-emission mobility.
ULEV vs LEV Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com