Euro 6 emission standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter emissions compared to Euro 5, improving air quality and public health. Vehicles compliant with Euro 6 feature advanced exhaust after-treatment technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF). These improvements result in cleaner combustion and lower environmental impact, making Euro 6 a critical step forward in emission regulations.
Table of Comparison
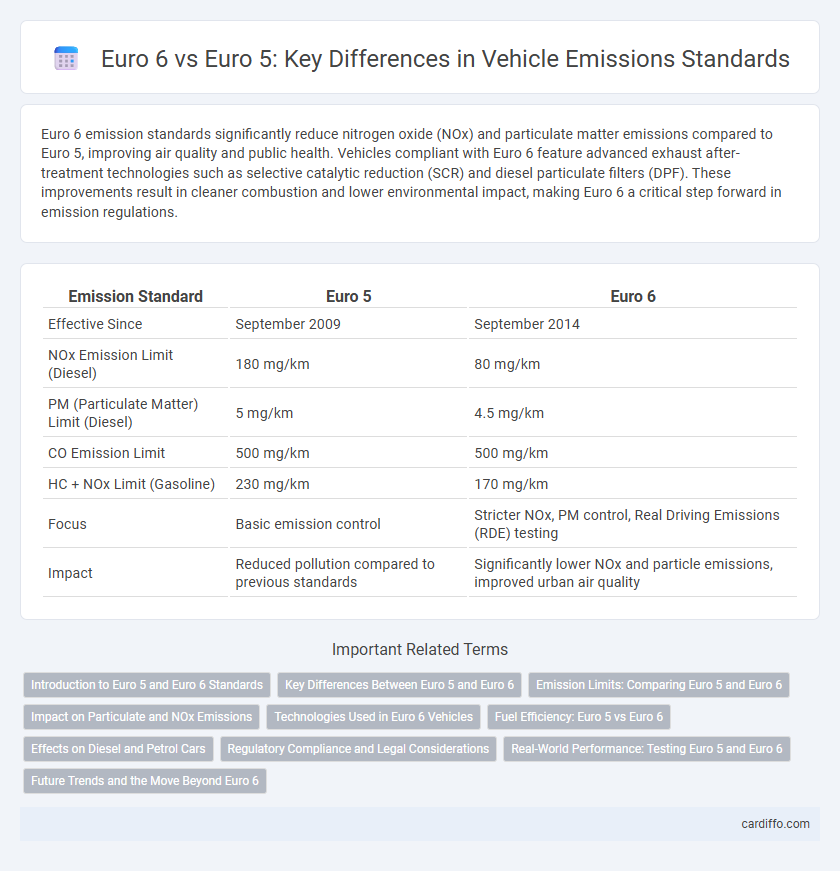
| Emission Standard | Euro 5 | Euro 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Effective Since | September 2009 | September 2014 |
| NOx Emission Limit (Diesel) | 180 mg/km | 80 mg/km |
| PM (Particulate Matter) Limit (Diesel) | 5 mg/km | 4.5 mg/km |
| CO Emission Limit | 500 mg/km | 500 mg/km |
| HC + NOx Limit (Gasoline) | 230 mg/km | 170 mg/km |
| Focus | Basic emission control | Stricter NOx, PM control, Real Driving Emissions (RDE) testing |
| Impact | Reduced pollution compared to previous standards | Significantly lower NOx and particle emissions, improved urban air quality |
Introduction to Euro 5 and Euro 6 Standards
Euro 5 and Euro 6 standards define limits for vehicle emissions, targeting significant reductions in nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and hydrocarbons to improve air quality. Euro 5, introduced in 2009, marked a major step in controlling diesel particulate emissions by enforcing particulate filters, while Euro 6, implemented in 2014, tightened NOx limits specifically for diesel engines to reduce smog and health risks. These regulations drive advancements in engine technology and exhaust after-treatment systems across Europe to meet stricter environmental performance criteria.
Key Differences Between Euro 5 and Euro 6
Euro 6 emission standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) limits to 80 mg/km from Euro 5's 180 mg/km for diesel vehicles, enhancing air quality. Euro 6 also introduces particulate number (PN) limits for gasoline direct injection engines, which Euro 5 does not regulate. Further tightening of particulate matter (PM) limits and stricter real driving emissions (RDE) tests underscore Euro 6's advanced approach to minimizing vehicle pollution.
Emission Limits: Comparing Euro 5 and Euro 6
Euro 6 emission standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) limits to 80 mg/km for diesel vehicles, compared to Euro 5's 180 mg/km, enhancing air quality by cutting harmful pollutants. Particulate matter (PM) limits remain consistent at 4.5 mg/km, but Euro 6 introduces stricter particle number (PN) limits, targeting ultra-fine particles. These tighter Euro 6 regulations lead to cleaner exhaust emissions, ensuring vehicles comply with more stringent environmental protection goals.
Impact on Particulate and NOx Emissions
Euro 6 standards significantly reduce particulate matter (PM) emissions by implementing stricter limits and advanced particulate filters, achieving up to an 80% decrease compared to Euro 5. Nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions under Euro 6 are cut by approximately 67% through improved selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) technologies. These tighter regulations drive cleaner air quality and lower health risks associated with diesel and gasoline engine pollutants.
Technologies Used in Euro 6 Vehicles
Euro 6 vehicles employ advanced emission control technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF) to significantly reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to Euro 5 standards. Enhanced engine calibration and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems optimize combustion efficiency and lower harmful emissions. These innovations enable Euro 6 engines to meet stricter regulatory limits while maintaining fuel efficiency and performance.
Fuel Efficiency: Euro 5 vs Euro 6
Euro 6 vehicles demonstrate improved fuel efficiency compared to Euro 5 models due to advanced engine tuning and optimized exhaust after-treatment systems that reduce fuel consumption while maintaining lower emission levels. The integration of technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and enhanced fuel injection systems in Euro 6 standards contributes significantly to better miles per gallon (MPG) performance. Studies indicate that Euro 6 vehicles can achieve up to 5-8% better fuel efficiency, resulting in both economic savings and reduced environmental impact.
Effects on Diesel and Petrol Cars
Euro 6 standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in diesel cars by up to 80% compared to Euro 5, improving air quality and public health. Petrol cars under Euro 6 also experience lower particulate matter and hydrocarbon emissions, enhancing environmental performance. These stricter regulations promote cleaner engine technologies and advanced exhaust after-treatment systems in both fuel types.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
Euro 6 emission standards demand significantly lower limits for nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to Euro 5, ensuring stricter regulatory compliance for vehicle manufacturers. Non-compliance with Euro 6 can result in legal penalties, including fines and market restrictions within the European Union. Compliance with Euro 6 is essential for manufacturers to maintain market access and avoid enforcement actions under evolving environmental legislation.
Real-World Performance: Testing Euro 5 and Euro 6
Euro 6 emission standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions compared to Euro 5, demonstrating improved air quality impact in real-world driving conditions. Independent tests reveal Euro 6 vehicles emit up to 70% less NOx during highway and urban driving cycles, reflecting advanced exhaust after-treatment technologies like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF). These real-world performance metrics confirm Euro 6's effectiveness in meeting stricter regulatory limits beyond laboratory testing environments.
Future Trends and the Move Beyond Euro 6
Euro 6 emission standards significantly reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to Euro 5, setting a benchmark for cleaner vehicle technologies. Future trends indicate a shift towards Euro 7 regulations, emphasizing even stricter limits on pollutants, real driving emissions, and the integration of advanced sensors for continuous monitoring. The automotive industry is accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid powertrains to comply with these upcoming standards and achieve zero-emission targets.
Euro 6 vs Euro 5 Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com