The Start-Stop System significantly reduces emissions by automatically shutting off the engine when the vehicle is stationary, preventing unnecessary fuel consumption and pollutant release. In contrast, idling causes continuous fuel burning and increases harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. By minimizing engine running time during stops, the Start-Stop System enhances air quality and contributes to lower overall carbon footprints.
Table of Comparison
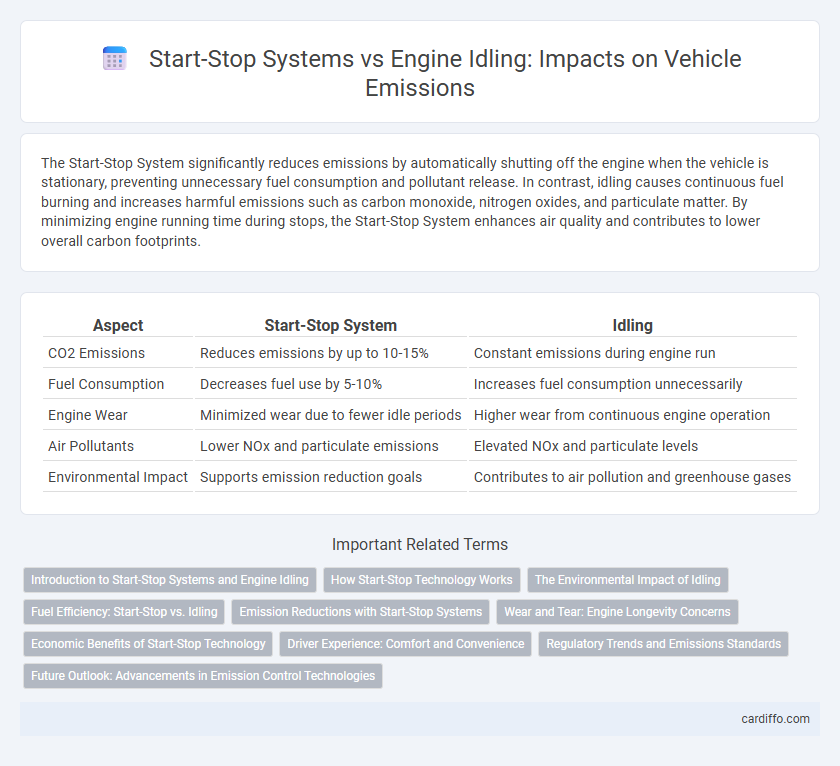
| Aspect | Start-Stop System | Idling |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions | Reduces emissions by up to 10-15% | Constant emissions during engine run |
| Fuel Consumption | Decreases fuel use by 5-10% | Increases fuel consumption unnecessarily |
| Engine Wear | Minimized wear due to fewer idle periods | Higher wear from continuous engine operation |
| Air Pollutants | Lower NOx and particulate emissions | Elevated NOx and particulate levels |
| Environmental Impact | Supports emission reduction goals | Contributes to air pollution and greenhouse gases |
Introduction to Start-Stop Systems and Engine Idling
Start-stop systems automatically shut off the engine when a vehicle is stationary, reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to traditional engine idling. Engine idling, where the engine runs while the vehicle is not moving, contributes significantly to unnecessary carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions. By minimizing idling time, start-stop technology supports improved air quality and enhanced fuel efficiency in urban driving conditions.
How Start-Stop Technology Works
Start-stop technology reduces vehicle emissions by automatically shutting off the engine when the car is stationary and restarting it instantly when needed. Sensors monitor factors such as battery charge, engine temperature, and brake pressure to determine optimal shutdown and restart moments, minimizing fuel consumption and pollutants. This system significantly decreases idling emissions by preventing unnecessary engine operation during stops.
The Environmental Impact of Idling
Idling engines emit significant amounts of carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Start-stop systems reduce harmful emissions by automatically shutting off the engine during stops, lowering fuel consumption and greenhouse gas output. This technology effectively mitigates the environmental impact of traditional idling, improving urban air quality and reducing carbon footprints.
Fuel Efficiency: Start-Stop vs. Idling
The Start-Stop system significantly improves fuel efficiency by automatically shutting off the engine during idle periods, reducing unnecessary fuel consumption. In contrast, idling keeps the engine running, leading to continuous fuel usage and increased emissions. Studies show vehicles with Start-Stop technology can reduce fuel consumption by up to 10% in urban driving conditions compared to traditional idling.
Emission Reductions with Start-Stop Systems
Start-stop systems significantly reduce vehicle emissions by shutting off the engine during idle periods, preventing unnecessary fuel combustion and lowering carbon dioxide (CO2) output. Compared to traditional idling, these systems can reduce emissions by up to 10-15%, contributing to improved air quality and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Implementing start-stop technology in urban traffic conditions where idling is frequent maximizes these emission reduction benefits.
Wear and Tear: Engine Longevity Concerns
Start-stop systems reduce engine idling time, significantly decreasing wear and tear on critical components like pistons and cylinder walls, which enhances engine longevity. Conventional idling keeps the engine running without load, causing increased fuel consumption and accelerated degradation of engine oil and parts. Studies show that vehicles equipped with start-stop technology experience less mechanical stress, leading to longer engine life and lower maintenance costs over time.
Economic Benefits of Start-Stop Technology
Start-stop technology significantly reduces fuel consumption by shutting off the engine during idle periods, leading to lower fuel expenses for drivers and fleet operators. By minimizing unnecessary fuel burn, this system decreases carbon dioxide emissions and improves engine efficiency, contributing to long-term economic savings. Enhanced durability of engine components due to reduced idling also lowers maintenance costs, amplifying the overall financial benefits of adopting start-stop systems.
Driver Experience: Comfort and Convenience
The Start-Stop system enhances driver comfort by automatically shutting off the engine during extended stops, reducing cabin noise and vibration without manual intervention. It contributes to convenience by seamlessly restarting the engine when the driver releases the brake, ensuring smooth transitions without delays. Unlike traditional idling, this technology minimizes unnecessary fuel consumption and emissions, improving the overall driving experience in urban traffic conditions.
Regulatory Trends and Emissions Standards
Start-stop systems significantly reduce emissions by shutting down the engine during idle periods, aligning with increasingly stringent regulatory trends targeting urban air quality improvement. Emissions standards such as Euro 6d and EPA Tier 3 emphasize lower CO2 and NOx outputs, promoting technologies that minimize idling pollution. Regulatory bodies worldwide incentivize vehicle manufacturers to adopt start-stop technology to meet these evolving standards and reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions from passenger and commercial vehicles.
Future Outlook: Advancements in Emission Control Technologies
Start-stop systems significantly reduce emissions by automatically shutting off the engine during idling, cutting fuel consumption and harmful pollutants such as CO2 and NOx. Emerging advancements in emission control technologies, including improved catalytic converters and advanced sensors, further optimize engine performance and reduce exhaust emissions during both idling and active driving. Future outlooks emphasize integrating start-stop technology with electrification and AI-powered predictive controls to achieve near-zero emission vehicles and comply with increasingly stringent global emission standards.
Start-Stop System vs Idling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com