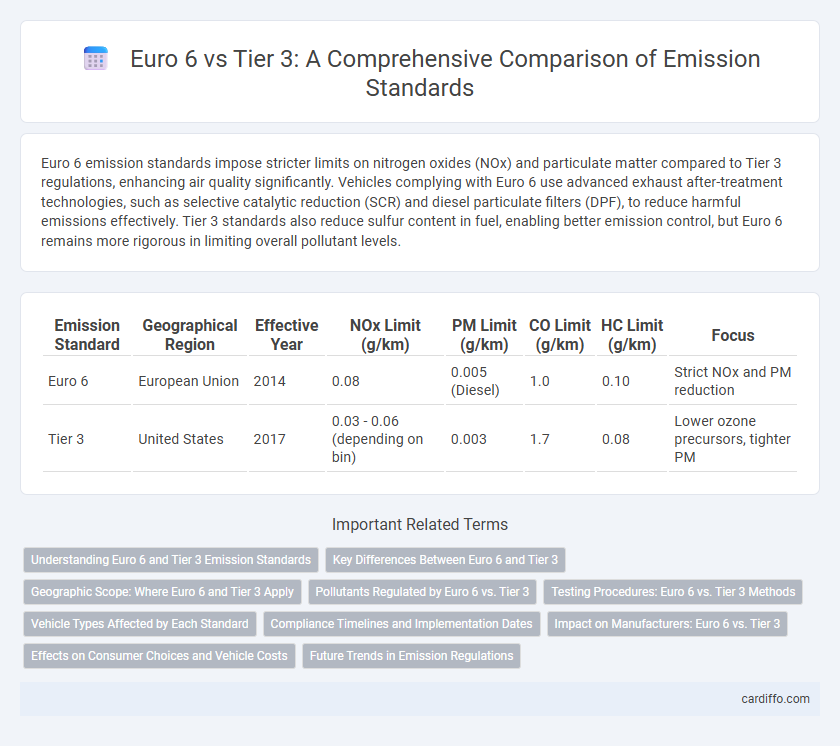
Euro 6 emission standards impose stricter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to Tier 3 regulations, enhancing air quality significantly. Vehicles complying with Euro 6 use advanced exhaust after-treatment technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF), to reduce harmful emissions effectively. Tier 3 standards also reduce sulfur content in fuel, enabling better emission control, but Euro 6 remains more rigorous in limiting overall pollutant levels.
Table of Comparison
| Emission Standard | Geographical Region | Effective Year | NOx Limit (g/km) | PM Limit (g/km) | CO Limit (g/km) | HC Limit (g/km) | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euro 6 | European Union | 2014 | 0.08 | 0.005 (Diesel) | 1.0 | 0.10 | Strict NOx and PM reduction |
| Tier 3 | United States | 2017 | 0.03 - 0.06 (depending on bin) | 0.003 | 1.7 | 0.08 | Lower ozone precursors, tighter PM |
Understanding Euro 6 and Tier 3 Emission Standards
Euro 6 emission standards set stringent limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter for vehicles, significantly reducing air pollutants compared to previous regulations. Tier 3 standards, implemented by the US EPA, impose comprehensive controls on both exhaust and evaporative emissions, targeting lower levels of nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Understanding the distinct regulatory scopes and pollutant thresholds of Euro 6 and Tier 3 is essential for automotive manufacturers to ensure compliance and minimize environmental impact.
Key Differences Between Euro 6 and Tier 3
Euro 6 emission standards primarily target nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) reductions in passenger vehicles across Europe, enforcing stricter limits than previous Euro norms. Tier 3 standards, implemented by the US Environmental Protection Agency, emphasize comprehensive reductions in greenhouse gases and ozone precursors with tighter limits on NOx, PM, and sulfur content in fuel, applicable to both light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles. Key differences include the geographic scope, with Euro 6 focused on European markets and Tier 3 on the US, alongside variations in test procedures and specific pollutant thresholds.
Geographic Scope: Where Euro 6 and Tier 3 Apply
Euro 6 emission standards primarily apply across the European Union and several other European countries, regulating pollutants from new vehicles sold within this region. Tier 3 standards are enforced mainly in the United States, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) implementing these regulations to reduce tailpipe emissions nationwide. Geographic scope distinctions between Euro 6 and Tier 3 highlight regional approaches to lowering automotive emissions and improving air quality.
Pollutants Regulated by Euro 6 vs. Tier 3
Euro 6 standards regulate emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons (HC) more stringently than Tier 3, with Euro 6 setting tighter limits especially on NOx and PM for diesel engines. Tier 3 focuses on reducing tailpipe emissions primarily of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter but with less rigorous thresholds compared to Euro 6, aiming at improving air quality through smoother transition phases. Euro 6 also introduces particle number (PN) limits, targeting the reduction of ultrafine particles that Tier 3 does not explicitly regulate.
Testing Procedures: Euro 6 vs. Tier 3 Methods
Euro 6 testing procedures emphasize real driving emissions (RDE) to ensure vehicles meet nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter limits under real-world conditions, while Tier 3 focuses on federal test procedures (FTP) with stricter tailpipe emission standards tested in laboratory settings. Euro 6 utilizes Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS) for on-road testing, capturing a broader range of driving scenarios, whereas Tier 3 relies predominantly on standardized dynamometer tests. These contrasting testing methodologies reflect Euro 6's approach to reducing discrepancies between lab and real-world emissions and Tier 3's goal of lowering ambient air pollutants through more stringent lab-based evaluations.
Vehicle Types Affected by Each Standard
Euro 6 emission standards primarily target passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, enforcing stricter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to previous regulations. Tier 3 standards apply broadly to both passenger vehicles and light trucks, emphasizing lower tailpipe emissions to improve air quality in urban environments. The implementation of Euro 6 affects mainly European markets, while Tier 3 is predominantly enforced in the United States, reflecting regional regulatory priorities on vehicle emissions.
Compliance Timelines and Implementation Dates
Euro 6 emission standards, enforced across the European Union, mandated full compliance for all new vehicles starting September 2015, with progressive phases targeting heavy-duty diesel vehicles by 2019. Tier 3 standards, implemented by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), began to apply to passenger cars and light trucks from January 2017, with a complete phase-in period extending through 2025 for full fleet compliance. Both regulations aim to reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter but differ in their specific timelines and vehicle categories covered.
Impact on Manufacturers: Euro 6 vs. Tier 3
Euro 6 emission standards impose stricter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to Tier 3, pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced after-treatment technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF). Tier 3 regulations emphasize reductions in tailpipe emissions but allow slightly higher thresholds, resulting in lower immediate compliance costs but less stringent environmental impact. Manufacturers face increased R&D expenses and production adjustments under Euro 6, which drive innovations in engine calibration and exhaust management systems to meet more rigorous emissions targets.
Effects on Consumer Choices and Vehicle Costs
Euro 6 emission standards impose stricter limits on nitrogen oxides and particulate matter compared to Tier 3, leading to increased manufacturing costs passed on to consumers through higher vehicle prices. Vehicles compliant with Euro 6 often incorporate advanced exhaust after-treatment technologies, influencing buyer preferences towards more fuel-efficient and environmentally conscious options despite elevated upfront costs. Consumers balance these higher initial expenses against long-term savings from improved fuel economy and reduced emission-related penalties.
Future Trends in Emission Regulations
Euro 6 emission standards impose stricter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) compared to Tier 3, reflecting a significant progression in reducing vehicular pollutants. Future trends indicate a shift toward even lower emission thresholds, emphasizing the adoption of advanced technologies like electric and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles to meet global climate goals. Regulatory bodies are increasingly integrating real-driving emissions (RDE) testing to ensure compliance beyond laboratory conditions, enhancing air quality standards worldwide.
Euro 6 vs Tier 3 Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com