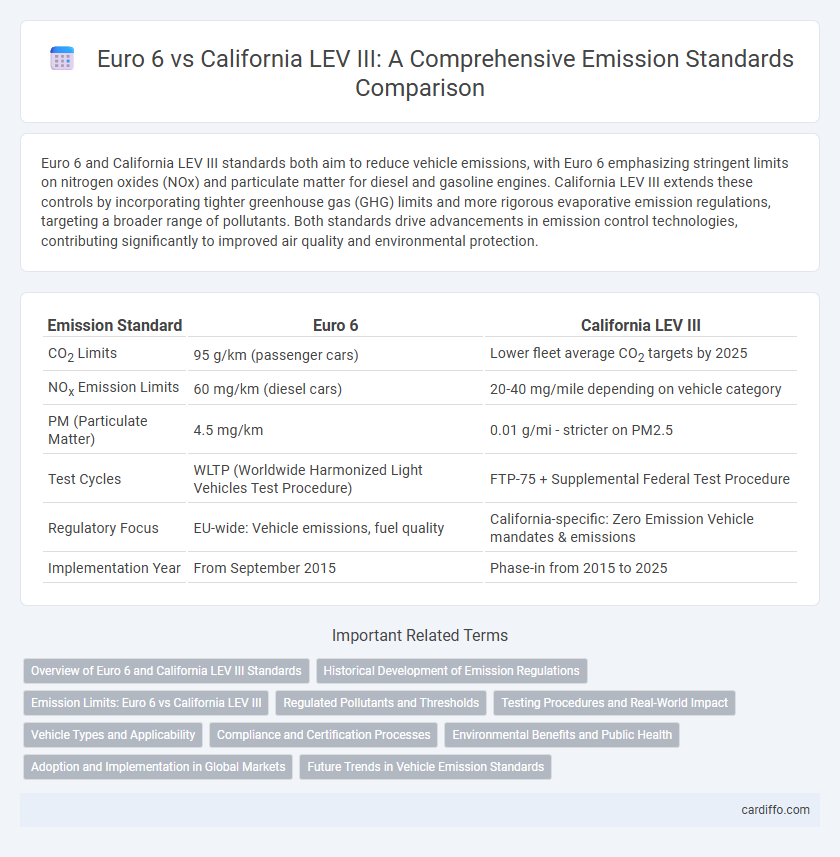
Euro 6 and California LEV III standards both aim to reduce vehicle emissions, with Euro 6 emphasizing stringent limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter for diesel and gasoline engines. California LEV III extends these controls by incorporating tighter greenhouse gas (GHG) limits and more rigorous evaporative emission regulations, targeting a broader range of pollutants. Both standards drive advancements in emission control technologies, contributing significantly to improved air quality and environmental protection.
Table of Comparison
| Emission Standard | Euro 6 | California LEV III |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Limits | 95 g/km (passenger cars) | Lower fleet average CO2 targets by 2025 |
| NOx Emission Limits | 60 mg/km (diesel cars) | 20-40 mg/mile depending on vehicle category |
| PM (Particulate Matter) | 4.5 mg/km | 0.01 g/mi - stricter on PM2.5 |
| Test Cycles | WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) | FTP-75 + Supplemental Federal Test Procedure |
| Regulatory Focus | EU-wide: Vehicle emissions, fuel quality | California-specific: Zero Emission Vehicle mandates & emissions |
| Implementation Year | From September 2015 | Phase-in from 2015 to 2025 |
Overview of Euro 6 and California LEV III Standards
Euro 6 and California LEV III are stringent vehicle emission standards designed to reduce harmful pollutants and improve air quality. Euro 6 limits nitrogen oxides (NOx) to 80 mg/km for diesel vehicles and 60 mg/km for gasoline vehicles, while LEV III targets a 75% reduction in NOx and particulate matter compared to previous California standards. Both regulations enforce limits on hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and particulate emissions, promoting cleaner combustion technologies and advanced after-treatment systems.
Historical Development of Emission Regulations
Euro 6 regulations, introduced in 2014, significantly tightened nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) limits for diesel vehicles across Europe, marking a pivotal advancement in reducing urban air pollution. California LEV III standards, phased in starting in 2015, expanded upon earlier LEV and ULEV programs by mandating stricter tailpipe emission limits and incorporating greenhouse gas (GHG) reductions, influencing nationwide emission policies in the United States. Both regulatory frameworks evolved through decades of scientific research and policy adjustments aimed at addressing health impacts related to vehicle emissions, driving innovations in automotive emission control technologies.
Emission Limits: Euro 6 vs California LEV III
Euro 6 emission standards set stringent limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) at 80 mg/km for diesel vehicles and 60 mg/km for gasoline vehicles, while California LEV III targets a more comprehensive reduction with particulate matter (PM) capped at 3 mg/mi and NOx at 0.03 g/mi, reflecting tighter control on smog-forming pollutants. LEV III incorporates stricter evaporative emission limits and a broader scope of pollutants including formaldehyde and 1,3-butadiene, surpassing Euro 6 in coverage for ozone precursors. Both standards significantly reduce vehicle emissions, but California LEV III's more aggressive limits on particulate and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) align with its goal to meet air quality improvements in urban environments.
Regulated Pollutants and Thresholds
Euro 6 standards regulate pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons (HC) with specific limits: 80 mg/km for NOx in diesel vehicles and 4.5 mg/km for PM. California LEV III imposes stricter thresholds, particularly for NOx, set at 40 mg/mile (approximately 25 mg/km) and tighter particulate limits to reduce smog-forming pollutants. Both regulations aim to significantly lower vehicular emissions, but LEV III's more rigorous limits drive advanced emission control technologies in California.
Testing Procedures and Real-World Impact
Euro 6 and California LEV III standards both enforce stringent emission testing procedures, with Euro 6 utilizing laboratory-based chassis dynamometer tests and real-driving emissions (RDE) measurements to assess pollutant output under controlled and real-world conditions. California LEV III combines laboratory testing with onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems to continuously monitor vehicle emissions and ensure compliance during regular driving scenarios. These approaches lead to improved air quality by reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), while better aligning regulatory limits with actual vehicle performance on public roads.
Vehicle Types and Applicability
Euro 6 standards primarily target passenger cars and light commercial vehicles (up to 3.5 tons), focusing on reducing NOx and particulate emissions across petrol and diesel engines within the European market. California LEV III regulations encompass a broader range of vehicle categories, including light-, medium-, and heavy-duty vehicles, with stringent emission limits applicable to gasoline, diesel, and alternative fuel vehicles sold in California and other states adopting these rules. The applicability differences reflect regional priorities and vehicle fleet compositions, influencing compliance strategies and technology adoption among manufacturers.
Compliance and Certification Processes
Euro 6 and California LEV III regulations both enforce stringent emission limits to reduce pollutants from vehicles, with Euro 6 focusing on nitrogen oxides and particulate matter for European markets, while LEV III targets broader hydrocarbon and nitrogen oxide reductions primarily in California. Compliance with Euro 6 requires manufacturers to pass laboratory and real-driving emission tests certified by European authorities, whereas LEV III mandates certification through California Air Resources Board (CARB) protocols involving rigorous durability and evaporative emissions assessments. Both standards demand extensive on-road testing and documentation, but LEV III places greater emphasis on long-term emission control system durability and greenhouse gas reporting.
Environmental Benefits and Public Health
Euro 6 and California LEV III emission standards significantly reduce pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), which are major contributors to air quality deterioration and respiratory diseases. LEV III enforces stricter limits on smog-forming emissions, leading to improved urban air quality and lower rates of asthma and cardiovascular conditions. Euro 6's stringent diesel vehicle requirements decrease toxic exhaust emissions, contributing to public health by minimizing exposure to harmful airborne contaminants.
Adoption and Implementation in Global Markets
Euro 6 standards have been widely adopted across Europe and many other regions due to stricter enforcement of vehicular emission limits, focusing primarily on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter reductions. California LEV III regulations, recognized for their rigorous greenhouse gas and smog-forming pollutant limits, are primarily implemented within North America, influencing neighboring markets through export vehicle requirements. Global market adoption reflects regional environmental priorities and regulatory frameworks, with Euro 6 leading in Europe and parts of Asia, while California LEV III drives innovation and compliance in the US and Canada.
Future Trends in Vehicle Emission Standards
Future trends in vehicle emission standards indicate a convergence between Euro 6 and California LEV III regulations, emphasizing stricter limits on nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter emissions. Enhanced real-driving emissions (RDE) testing and tighter evaporative emission controls are becoming integral to both standards, promoting cleaner air quality globally. Advancements in hybrid and electric vehicle adoption, driven by these stringent regulations, are expected to significantly reduce tailpipe emissions in the coming decade.
Euro 6 vs California LEV III Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com