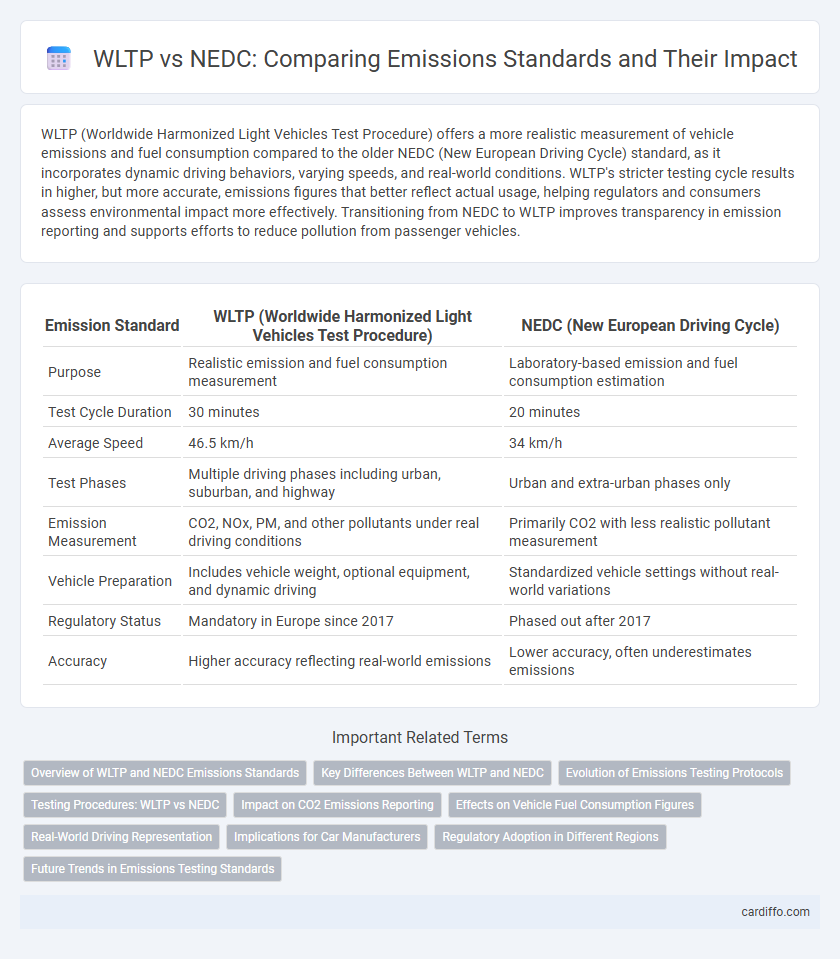
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) offers a more realistic measurement of vehicle emissions and fuel consumption compared to the older NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) standard, as it incorporates dynamic driving behaviors, varying speeds, and real-world conditions. WLTP's stricter testing cycle results in higher, but more accurate, emissions figures that better reflect actual usage, helping regulators and consumers assess environmental impact more effectively. Transitioning from NEDC to WLTP improves transparency in emission reporting and supports efforts to reduce pollution from passenger vehicles.
Table of Comparison
| Emission Standard | WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) | NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Realistic emission and fuel consumption measurement | Laboratory-based emission and fuel consumption estimation |
| Test Cycle Duration | 30 minutes | 20 minutes |
| Average Speed | 46.5 km/h | 34 km/h |
| Test Phases | Multiple driving phases including urban, suburban, and highway | Urban and extra-urban phases only |
| Emission Measurement | CO2, NOx, PM, and other pollutants under real driving conditions | Primarily CO2 with less realistic pollutant measurement |
| Vehicle Preparation | Includes vehicle weight, optional equipment, and dynamic driving | Standardized vehicle settings without real-world variations |
| Regulatory Status | Mandatory in Europe since 2017 | Phased out after 2017 |
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy reflecting real-world emissions | Lower accuracy, often underestimates emissions |
Overview of WLTP and NEDC Emissions Standards
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides a more accurate and realistic measurement of vehicle emissions compared to the older NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) standard, reflecting real driving conditions and broader testing parameters. WLTP covers a wider range of driving scenarios, including varied speeds and accelerations, resulting in higher but more reliable CO2 and pollutant emission figures. NEDC, developed in the 1980s, often underestimated emissions due to its simplified and repetitive driving cycles, leading to discrepancies in fuel consumption and pollutant reporting.
Key Differences Between WLTP and NEDC
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides more realistic and accurate emission measurements than NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) by simulating real driving conditions with varied speeds, accelerations, and temperature ranges. The WLTP testing cycle is longer and covers a greater distance, including higher average and maximum speeds, resulting in higher but more representative emission values. NEDC's outdated methodology often underestimates pollutant emissions and fuel consumption, making WLTP the preferred standard for regulatory compliance and environmental impact assessment.
Evolution of Emissions Testing Protocols
The evolution of emissions testing protocols highlights a significant transition from the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) to the Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP), reflecting efforts to provide more accurate real-world vehicle emissions data. WLTP incorporates dynamic driving conditions, higher speeds, and a more comprehensive range of temperatures, leading to stricter and more realistic CO2 and pollutant measurements compared to the NEDC's outdated and simplified testing methods. This shift aims to improve regulatory compliance and environmental impact assessments, driving advancements in vehicle emission control technologies.
Testing Procedures: WLTP vs NEDC
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) offers a more accurate and realistic assessment of vehicle emissions by simulating real-world driving conditions compared to the older NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) which relies on more simplified and static laboratory cycles. WLTP incorporates dynamic factors such as variable speeds, acceleration, and a broader range of driving scenarios to better reflect actual emissions performance. The improved test design in WLTP reduces discrepancies between laboratory results and on-road emissions, providing stricter and more reliable regulatory standards for vehicle manufacturers.
Impact on CO2 Emissions Reporting
The WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides more accurate and realistic CO2 emissions data compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) standard, reflecting real-world driving conditions and vehicle performance. This results in higher reported CO2 emissions under WLTP, enabling regulators and consumers to better assess environmental impact and compliance. Enhanced precision in emissions reporting under WLTP drives manufacturers to improve fuel efficiency and reduce carbon footprints more effectively.
Effects on Vehicle Fuel Consumption Figures
WLTP emission standards provide more accurate and realistic vehicle fuel consumption figures compared to the outdated NEDC cycle, reflecting real-world driving conditions such as varying speeds and accelerations. Vehicles tested under WLTP generally show higher fuel consumption and CO2 emissions due to stricter testing protocols that incorporate dynamic driving behavior and additional equipment load. This shift improves transparency for consumers and helps manufacturers develop more efficient engines aligned with actual road performance.
Real-World Driving Representation
The WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides a more accurate real-world driving emissions representation compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) standard by incorporating dynamic driving conditions such as varied speeds, acceleration, and road gradients. WLTP better reflects real-world fuel consumption and pollutant emissions by simulating realistic driving scenarios and environmental factors. This results in more reliable emission data used for regulatory compliance and consumer information in vehicle markets.
Implications for Car Manufacturers
WLTP emissions standards require car manufacturers to provide more accurate and comprehensive data on real-world vehicle emissions compared to the outdated NEDC protocol. This shift forces manufacturers to invest in advanced testing technologies and redesign vehicles to meet stricter limits, impacting production costs and timelines. Compliance with WLTP directly influences market competitiveness, regulatory penalties, and consumer perception regarding environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Adoption in Different Regions
The Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) has been increasingly adopted by the European Union, India, and Japan to provide more accurate emissions data compared to the older New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) standard. In contrast, regions like the United States and China continue to maintain their own regulatory frameworks, such as the EPA emissions test and China's National VI standards, which align closely but are not directly based on WLTP. This divergence in regulatory adoption creates challenges for automakers aiming to meet varying emissions requirements across global markets.
Future Trends in Emissions Testing Standards
Future trends in emissions testing standards emphasize the transition from NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) to WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) due to WLTP's enhanced accuracy in reflecting real-world driving conditions. WLTP incorporates dynamic driving phases and stringent measurement protocols, providing lower tolerance intervals for pollutants like NOx and CO2 compared to the outdated NEDC. Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting WLTP and integrating RDE (Real Driving Emissions) tests to improve emission control verification, driving innovation in cleaner vehicle technologies and stricter compliance requirements.
WLTP vs NEDC emissions standards Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com