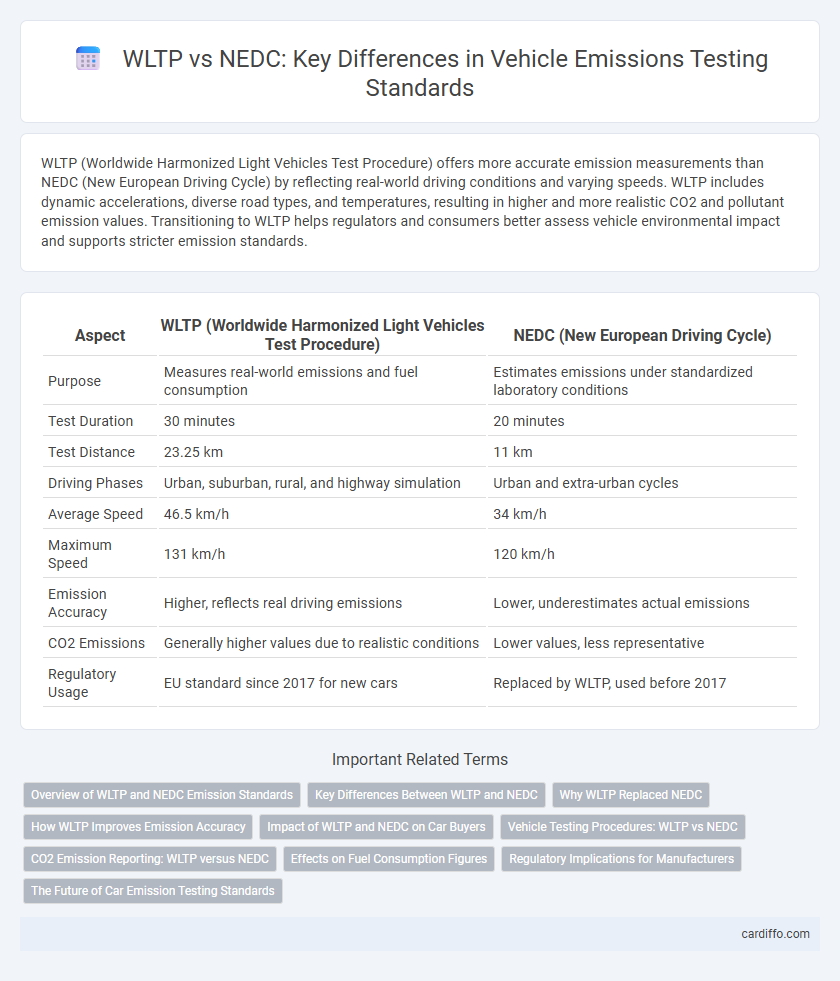
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) offers more accurate emission measurements than NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) by reflecting real-world driving conditions and varying speeds. WLTP includes dynamic accelerations, diverse road types, and temperatures, resulting in higher and more realistic CO2 and pollutant emission values. Transitioning to WLTP helps regulators and consumers better assess vehicle environmental impact and supports stricter emission standards.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) | NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures real-world emissions and fuel consumption | Estimates emissions under standardized laboratory conditions |
| Test Duration | 30 minutes | 20 minutes |
| Test Distance | 23.25 km | 11 km |
| Driving Phases | Urban, suburban, rural, and highway simulation | Urban and extra-urban cycles |
| Average Speed | 46.5 km/h | 34 km/h |
| Maximum Speed | 131 km/h | 120 km/h |
| Emission Accuracy | Higher, reflects real driving emissions | Lower, underestimates actual emissions |
| CO2 Emissions | Generally higher values due to realistic conditions | Lower values, less representative |
| Regulatory Usage | EU standard since 2017 for new cars | Replaced by WLTP, used before 2017 |
Overview of WLTP and NEDC Emission Standards
The WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides more realistic and stringent emission standards compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle), reflecting actual driving conditions with variable speeds and driving phases. WLTP measures pollutant emissions and fuel consumption with improved accuracy, significantly reducing discrepancies between test results and real-world performance. The transition from NEDC to WLTP supports regulatory goals to lower vehicle emissions, aiding in the reduction of CO2 and nitrogen oxides (NOx) across the automotive sector.
Key Differences Between WLTP and NEDC
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) offers more realistic emission and fuel consumption data compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle), which often underestimated pollutant levels. WLTP incorporates dynamic driving patterns, varied speeds, and real-world conditions, resulting in higher accuracy for CO2 and NOx emissions measurement. NEDC's simplified cycle fails to represent true driving scenarios, leading to less reliable data for regulatory compliance and consumer information.
Why WLTP Replaced NEDC
WLTP replaced NEDC because it provides more accurate and realistic vehicle emission measurements by reflecting contemporary driving conditions, speeds, and road types. Unlike NEDC, WLTP accounts for variations in temperature, vehicle weight, and optional equipment, leading to more precise CO2 and pollutant emission data. This shift ensures better regulatory compliance and helps consumers make informed decisions based on reliable environmental impact assessments.
How WLTP Improves Emission Accuracy
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) improves emission accuracy by providing more realistic driving cycles that reflect everyday vehicle usage, including varying speeds, accelerations, and ambient conditions. Unlike the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle), WLTP incorporates dynamic driving behaviors and longer test durations, resulting in emissions and fuel consumption data that better represent real-world scenarios. This enhanced precision aids regulators and manufacturers in setting stricter standards and developing cleaner vehicle technologies.
Impact of WLTP and NEDC on Car Buyers
The transition from NEDC to WLTP testing has significantly impacted car buyers by providing more accurate and realistic emissions and fuel consumption data. WLTP results in higher reported CO2 values, influencing taxation, insurance costs, and purchase decisions, while offering greater transparency on real-world vehicle performance. This shift encourages consumers to choose more environmentally friendly cars, affecting market demand and promoting cleaner technologies.
Vehicle Testing Procedures: WLTP vs NEDC
The Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) offers a more accurate representation of real-world driving emissions compared to the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) by incorporating variable speeds, dynamic acceleration, and a broader range of driving conditions. WLTP testing involves longer test durations with more realistic temperature settings, resulting in higher and more precise emission values for pollutants such as CO2 and NOx. This enhanced methodology improves the reliability of vehicle emission standards and regulatory compliance assessments across different global regions.
CO2 Emission Reporting: WLTP versus NEDC
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides more accurate and realistic CO2 emission data compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle) by simulating real-world driving conditions. WLTP results typically show higher CO2 emission values due to stricter testing parameters including varying speeds, acceleration, and road gradients. Diesel and gasoline vehicles exhibit different emission profiles in WLTP, making it a crucial standard for regulatory compliance and consumer transparency in Europe.
Effects on Fuel Consumption Figures
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) provides more realistic fuel consumption figures compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle), reflecting real-world driving conditions such as variable speeds and accelerations. Vehicles tested under WLTP typically show higher fuel consumption figures, emphasizing increased transparency and accuracy for emissions legislation compliance. This shift encourages manufacturers to improve engine efficiency and emissions control technologies to meet stricter environmental standards.
Regulatory Implications for Manufacturers
The Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) imposes stricter and more realistic emission testing standards compared to the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC), leading to significant regulatory adjustments for manufacturers. Compliance with WLTP requires advanced calibration of engine control units and adoption of cleaner technologies to meet tighter CO2 and NOx limits. Manufacturers face increased development costs and must ensure transparency in emission reporting to adhere to evolving regulatory frameworks promoting environmental sustainability.
The Future of Car Emission Testing Standards
WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure) offers more accurate and representative emission measurements compared to the outdated NEDC (New European Driving Cycle), reflecting real-world driving conditions and pollutant levels. Future car emission testing standards will increasingly rely on WLTP data to enforce stricter emission limits and support global efforts to reduce carbon footprints. Enhanced sensor technologies and on-road testing methodologies are expected to complement WLTP, ensuring transparent and reliable vehicle emissions monitoring worldwide.
WLTP vs NEDC Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com