Diesel emissions generally contain higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to gasoline emissions, which primarily release more carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons. Diesel engines tend to produce more soot and black smoke, contributing to air quality issues and respiratory problems. Gasoline engines emit lower particulate matter but release more carbon dioxide (CO2), impacting greenhouse gas accumulation.
Table of Comparison
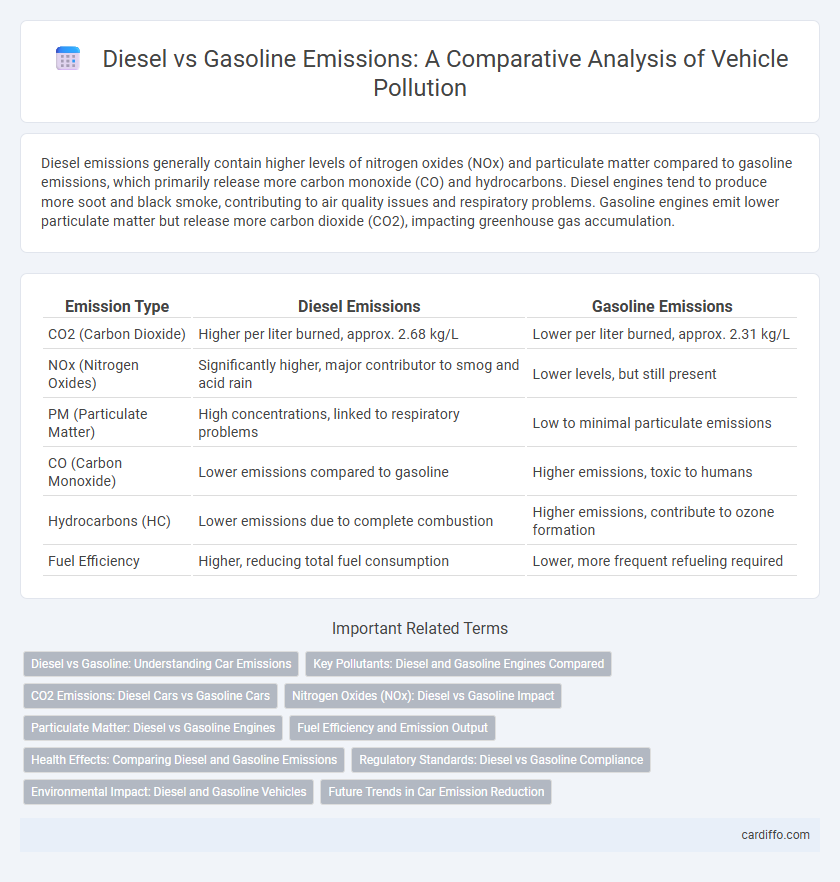
| Emission Type | Diesel Emissions | Gasoline Emissions |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) | Higher per liter burned, approx. 2.68 kg/L | Lower per liter burned, approx. 2.31 kg/L |
| NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) | Significantly higher, major contributor to smog and acid rain | Lower levels, but still present |
| PM (Particulate Matter) | High concentrations, linked to respiratory problems | Low to minimal particulate emissions |
| CO (Carbon Monoxide) | Lower emissions compared to gasoline | Higher emissions, toxic to humans |
| Hydrocarbons (HC) | Lower emissions due to complete combustion | Higher emissions, contribute to ozone formation |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher, reducing total fuel consumption | Lower, more frequent refueling required |
Diesel vs Gasoline: Understanding Car Emissions
Diesel emissions typically contain higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to gasoline emissions, which primarily release carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC). Diesel engines tend to be more fuel-efficient, producing less carbon dioxide (CO2) per mile, but their NOx and particulate emissions contribute significantly to smog and respiratory problems. Gasoline engines emit lower NOx and particulates but generate more CO and unburned hydrocarbons, affecting urban air quality differently than diesel vehicles.
Key Pollutants: Diesel and Gasoline Engines Compared
Diesel engines emit higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), contributing significantly to air pollution and respiratory problems, while gasoline engines typically produce more carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC). The fine particulate emissions from diesel combustion are linked to increased cardiovascular and lung diseases, making diesel a major concern in urban air quality management. Gasoline engines, although emitting lower PM levels, contribute more to smog formation due to higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
CO2 Emissions: Diesel Cars vs Gasoline Cars
Diesel cars typically emit about 15-20% less CO2 per kilometer compared to gasoline cars due to higher fuel efficiency and greater energy content of diesel fuel. However, diesel engines may produce higher levels of other pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, impacting overall air quality. Despite lower CO2 emissions, stricter regulations and advancements in gasoline engine technology continue to shift consumer preferences.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Diesel vs Gasoline Impact
Diesel engines emit significantly higher levels of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) compared to gasoline engines due to their higher combustion temperatures and lean burn operation. NOx contributes to air pollution problems such as smog and respiratory issues, with diesel vehicles being major sources in urban areas. Advances in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology have helped reduce NOx emissions from diesel vehicles, but gasoline engines generally produce lower NOx levels inherently.
Particulate Matter: Diesel vs Gasoline Engines
Diesel engines emit higher levels of particulate matter (PM) due to the combustion of heavier fuel oils, producing soot and fine particles linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Gasoline engines generate fewer PM emissions but tend to produce more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon monoxide, which also impact air quality. Advances in diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and gasoline direct injection (GDI) technology aim to reduce PM emissions across both engine types.
Fuel Efficiency and Emission Output
Diesel engines typically offer higher fuel efficiency compared to gasoline engines due to their higher compression ratios and energy content per liter of diesel fuel. Emission output from diesel engines includes lower carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per mile but higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), which contribute to air pollution and respiratory issues. Gasoline engines emit less NOx and PM but generally produce more CO2 per unit of fuel burned, impacting greenhouse gas levels differently than diesel engines.
Health Effects: Comparing Diesel and Gasoline Emissions
Diesel emissions contain higher levels of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which are linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and an increased risk of lung cancer. Gasoline emissions typically produce more volatile organic compounds and carbon monoxide, contributing to smog formation and acute respiratory irritation. Prolonged exposure to diesel exhaust poses more severe chronic health risks compared to gasoline exhaust, due to its finer particulate content and carcinogenic compounds.
Regulatory Standards: Diesel vs Gasoline Compliance
Diesel emissions typically face stricter regulatory standards due to higher nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter outputs compared to gasoline engines. Governments enforce rigorous compliance measures such as Euro 6 and Tier 3 standards, which mandate advanced after-treatment technologies like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for diesel vehicles. Gasoline engines primarily focus on limiting carbon monoxide (CO) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), resulting in different emission control strategies under regulations like LEV III and Euro 6 standards.
Environmental Impact: Diesel and Gasoline Vehicles
Diesel emissions typically contain higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which contribute significantly to air pollution and respiratory problems. Gasoline emissions, while generally producing less particulate matter, emit higher amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons, leading to smog formation and ozone depletion. The overall environmental impact of diesel vehicles is often more severe due to the toxicity and persistence of NOx and fine particles in the atmosphere.
Future Trends in Car Emission Reduction
Diesel emissions historically produce higher nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter compared to gasoline emissions, which primarily release more carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. Future trends in car emission reduction focus on advanced selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems for diesel and improved three-way catalytic converters for gasoline engines, alongside increased adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles. Stricter global emission standards such as Euro 7 and the integration of real-time emissions monitoring technologies are driving innovation in reducing both diesel and gasoline exhaust pollutants.
Diesel emissions vs Gasoline emissions Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com