Water pump failure causes engine overheating and coolant leaks, risking severe engine damage if not addressed promptly. Fuel pump failure results in inadequate fuel delivery, leading to engine stalling, poor performance, and starting difficulties. Identifying symptoms quickly ensures timely repairs, preventing costly breakdowns and maintaining vehicle reliability.
Table of Comparison
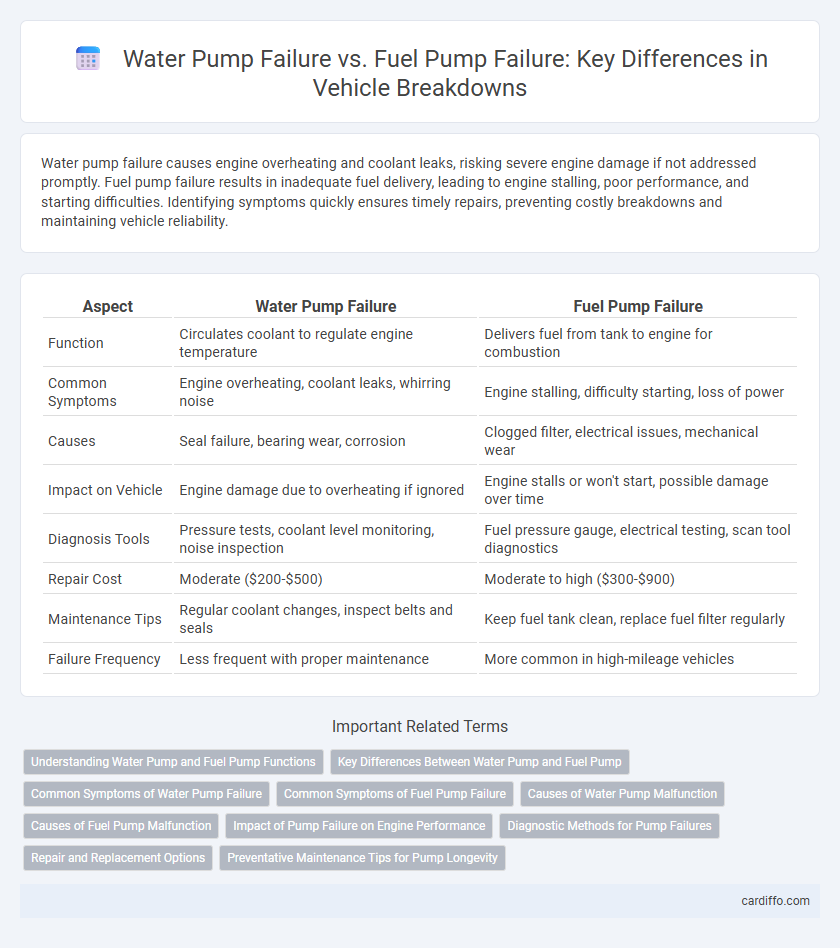
| Aspect | Water Pump Failure | Fuel Pump Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature | Delivers fuel from tank to engine for combustion |
| Common Symptoms | Engine overheating, coolant leaks, whirring noise | Engine stalling, difficulty starting, loss of power |
| Causes | Seal failure, bearing wear, corrosion | Clogged filter, electrical issues, mechanical wear |
| Impact on Vehicle | Engine damage due to overheating if ignored | Engine stalls or won't start, possible damage over time |
| Diagnosis Tools | Pressure tests, coolant level monitoring, noise inspection | Fuel pressure gauge, electrical testing, scan tool diagnostics |
| Repair Cost | Moderate ($200-$500) | Moderate to high ($300-$900) |
| Maintenance Tips | Regular coolant changes, inspect belts and seals | Keep fuel tank clean, replace fuel filter regularly |
| Failure Frequency | Less frequent with proper maintenance | More common in high-mileage vehicles |
Understanding Water Pump and Fuel Pump Functions
Water pump failure disrupts the engine's cooling system by preventing coolant circulation, leading to overheating and potential engine damage. Fuel pump failure causes a loss of fuel pressure, resulting in engine stalling or failure to start due to insufficient fuel delivery. Understanding the distinct roles of the water pump in temperature regulation and the fuel pump in fuel supply is essential for diagnosing and preventing vehicle breakdowns.
Key Differences Between Water Pump and Fuel Pump
Water pump failure primarily causes engine overheating due to coolant circulation disruption, whereas fuel pump failure leads to engine stalling or starting problems because of insufficient fuel delivery. Water pumps circulate coolant through the engine's cooling system to maintain optimal temperature, while fuel pumps supply fuel from the tank to the engine for combustion. Diagnosing water pump issues often involves checking for coolant leaks and temperature spikes, whereas fuel pump failure is identified through fuel pressure tests and engine performance issues.
Common Symptoms of Water Pump Failure
Common symptoms of water pump failure include coolant leakage near the front-center of the car, engine overheating due to inadequate coolant circulation, and a high-pitched whining noise coming from the pump area. These issues result from a worn-out bearing or a damaged impeller inside the water pump, which disrupts the efficient flow of coolant through the engine. If left unaddressed, water pump failure can lead to severe engine damage and costly repairs.
Common Symptoms of Fuel Pump Failure
Common symptoms of fuel pump failure include engine sputtering at high speeds, difficulty starting the vehicle, and a noticeable loss of power or acceleration during driving. The fuel pump may also cause the engine to stall frequently or fail to start completely if it cannot deliver adequate fuel pressure. Monitoring fuel pressure and warning lights can help diagnose fuel pump issues before leading to a breakdown.
Causes of Water Pump Malfunction
Water pump failure primarily results from worn-out bearings, damaged seals, and corrosion caused by coolant contamination or improper coolant mixture. Overheating and coolant leaks accelerate the degradation of the impeller and housing, reducing the pump's efficiency and leading to engine overheating. Unlike fuel pump failure, which is often due to clogged filters or electrical issues, water pump malfunction is closely tied to mechanical wear and coolant system maintenance lapses.
Causes of Fuel Pump Malfunction
Fuel pump malfunction commonly stems from contaminated fuel, causing clogged filters and impaired fuel flow. Electrical issues such as faulty wiring or a failing fuel pump relay disrupt the power supply, leading to pump failure. Wear and tear from prolonged usage or heat exposure often result in internal pump component damage, reducing fuel delivery efficiency.
Impact of Pump Failure on Engine Performance
Water pump failure causes engine overheating by disrupting coolant circulation, leading to potential engine damage and reduced performance. Fuel pump failure interrupts fuel delivery, causing engine stalling, misfires, and loss of power. Both failures critically impair engine efficiency but affect different systems essential for optimal combustion and cooling.
Diagnostic Methods for Pump Failures
Diagnostic methods for water pump failure primarily involve pressure testing the cooling system, inspecting coolant levels and leaks, and checking for unusual noises or overheating symptoms. Fuel pump failure diagnostics include fuel pressure testing, listening for pump operation sounds, and examining fuel filter condition and electrical connections. Both failures require targeted inspection tools like pressure gauges and diagnostic scanners to accurately identify pump performance issues.
Repair and Replacement Options
Water pump failure typically requires inspection of the impeller and seals, with repair options including gasket replacement or housing repair, while replacement involves installing a new pump to restore coolant circulation and prevent engine overheating. Fuel pump failure demands diagnosing fuel pressure issues and potential electrical faults, and repair may involve replacing filters or wiring, but most cases necessitate full fuel pump replacement to ensure proper fuel delivery and engine performance. Choosing between repair and replacement depends on the extent of damage and cost-effectiveness, with fuel pumps often requiring complete replacement more frequently than water pumps.
Preventative Maintenance Tips for Pump Longevity
Regular inspection of seals, bearings, and pressure levels in water pumps prevents overheating and corrosion, ensuring optimal performance and preventing unexpected breakdowns. Monitoring fuel quality and replacing fuel filters at recommended intervals minimizes clogging and wear in fuel pumps, extending their operational lifespan. Implementing scheduled maintenance routines and using manufacturer-approved lubricants reduces the risk of pump failure, supporting long-term reliability and efficiency.
Water pump failure vs fuel pump failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com