Misfire occurs when the engine's air-fuel mixture fails to ignite properly, causing rough idling, loss of power, and increased emissions. Backfire happens when unburned fuel combusts in the exhaust system, producing a loud popping sound and potential damage to exhaust components. Both issues signal underlying engine problems that require prompt diagnosis and repair to prevent further vehicle breakdown.
Table of Comparison
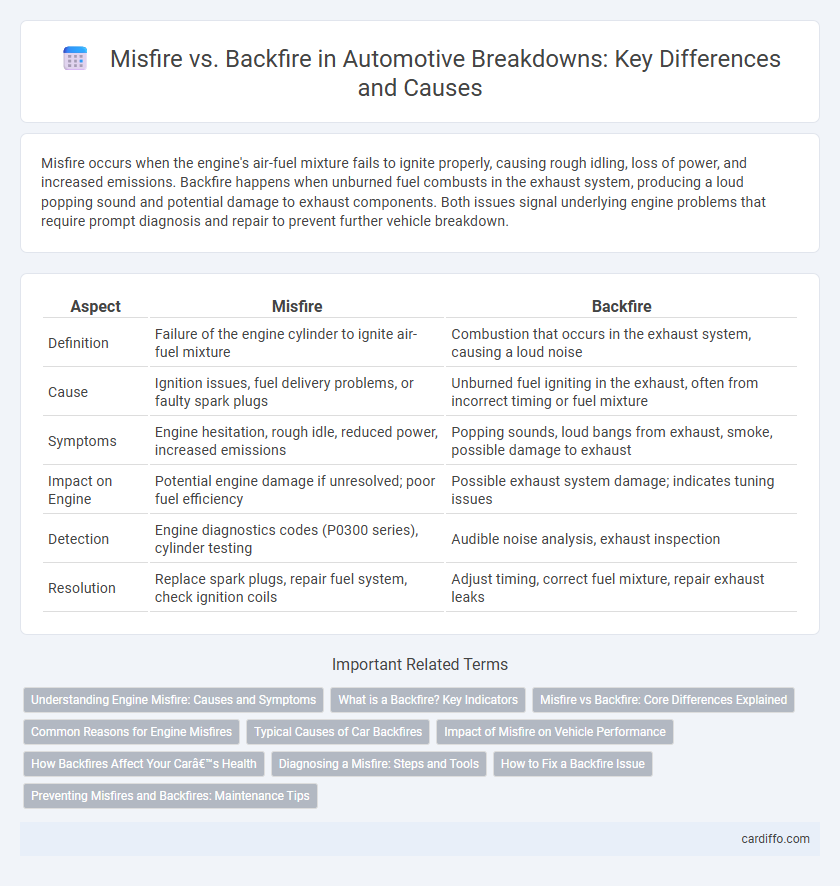
| Aspect | Misfire | Backfire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure of the engine cylinder to ignite air-fuel mixture | Combustion that occurs in the exhaust system, causing a loud noise |
| Cause | Ignition issues, fuel delivery problems, or faulty spark plugs | Unburned fuel igniting in the exhaust, often from incorrect timing or fuel mixture |
| Symptoms | Engine hesitation, rough idle, reduced power, increased emissions | Popping sounds, loud bangs from exhaust, smoke, possible damage to exhaust |
| Impact on Engine | Potential engine damage if unresolved; poor fuel efficiency | Possible exhaust system damage; indicates tuning issues |
| Detection | Engine diagnostics codes (P0300 series), cylinder testing | Audible noise analysis, exhaust inspection |
| Resolution | Replace spark plugs, repair fuel system, check ignition coils | Adjust timing, correct fuel mixture, repair exhaust leaks |
Understanding Engine Misfire: Causes and Symptoms
Engine misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to ignite the fuel-air mixture properly, causing incomplete combustion. Common causes include faulty spark plugs, ignition coil issues, clogged fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks, leading to rough engine performance, reduced power, and increased emissions. Detecting misfire symptoms like engine hesitation, uneven idling, and check engine light activation is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair.
What is a Backfire? Key Indicators
A backfire occurs when unburned fuel ignites in the exhaust system, producing a loud popping or banging sound, often accompanied by visible flames or smoke from the tailpipe. Key indicators include irregular engine idling, reduced power, and a strong smell of fuel or exhaust fumes. Backfires can result from issues such as incorrect ignition timing, a faulty carburetor, or a clogged air filter.
Misfire vs Backfire: Core Differences Explained
Misfire occurs when the fuel in an engine cylinder fails to ignite properly, causing loss of power and rough idling, whereas backfire happens when unburned fuel ignites in the exhaust system, producing a loud popping noise and potential damage. Misfires typically indicate issues with spark plugs, fuel delivery, or compression problems, while backfires often result from timing errors or a lean fuel mixture. Understanding these core differences helps diagnose engine performance issues and implement precise repairs.
Common Reasons for Engine Misfires
Engine misfires commonly occur due to issues such as faulty spark plugs, clogged fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning ignition coil, which disrupt the proper combustion process. Vacuum leaks and a dirty air filter can also cause air-fuel mixture imbalances, leading to misfires. Ignoring these common causes of engine misfires may result in reduced fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
Typical Causes of Car Backfires
Car backfires are typically caused by unburned fuel igniting in the exhaust system, often due to a rich fuel mixture or faulty spark plugs. Other common causes include timing issues, such as incorrect ignition timing or a malfunctioning carburetor, which affect the combustion process. Exhaust leaks and clogged air filters also contribute to backfires by disrupting proper airflow and fuel combustion.
Impact of Misfire on Vehicle Performance
Misfire causes a significant drop in engine power and fuel efficiency, leading to rough idling and increased emissions. It disrupts the combustion process, resulting in incomplete fuel burning and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Persistent misfires can cause engine stalling and reduced acceleration, severely impacting vehicle performance and drivability.
How Backfires Affect Your Car’s Health
Backfires indicate improper combustion, causing unburned fuel to ignite in the exhaust system, leading to potential damage in the muffler and catalytic converter. Persistent backfires reduce engine efficiency and increase emissions, worsening overall vehicle performance. Ignoring backfires can result in costly repairs and compromise engine longevity.
Diagnosing a Misfire: Steps and Tools
Diagnosing a misfire involves inspecting the ignition system, fuel delivery, and engine compression to identify the root cause. Tools like an OBD-II scanner, spark plug tester, and compression gauge provide precise diagnostic data for pinpointing faulty cylinders or components. Accurate diagnosis enables targeted repairs, preventing engine damage and improving overall performance.
How to Fix a Backfire Issue
To fix a backfire issue, first inspect the ignition system for faulty spark plugs, wires, or timing problems that cause unburned fuel to ignite in the exhaust. Next, clean or replace the carburetor or fuel injectors to ensure proper fuel-air mixture and prevent excess fuel from entering the exhaust system. Finally, check for exhaust leaks or damaged components that may contribute to backfiring and repair them to restore optimal engine performance.
Preventing Misfires and Backfires: Maintenance Tips
Regularly inspecting spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors reduces the risk of engine misfires and backfires by ensuring consistent ignition and fuel delivery. Keeping the air filter clean and using high-quality fuel improve combustion efficiency and prevent incomplete burning that leads to backfires. Scheduling routine engine tune-ups and addressing vacuum leaks promptly maintain optimal engine performance and minimize breakdowns caused by misfires and backfires.
Misfire vs backfire Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com