A flat tire is a common, often quick-to-fix issue that affects vehicle mobility but generally requires minimal repair costs. A blown engine, however, signifies severe mechanical failure, leading to extensive and expensive repairs or complete engine replacement. Recognizing the difference helps prioritize immediate action and budget planning.
Table of Comparison
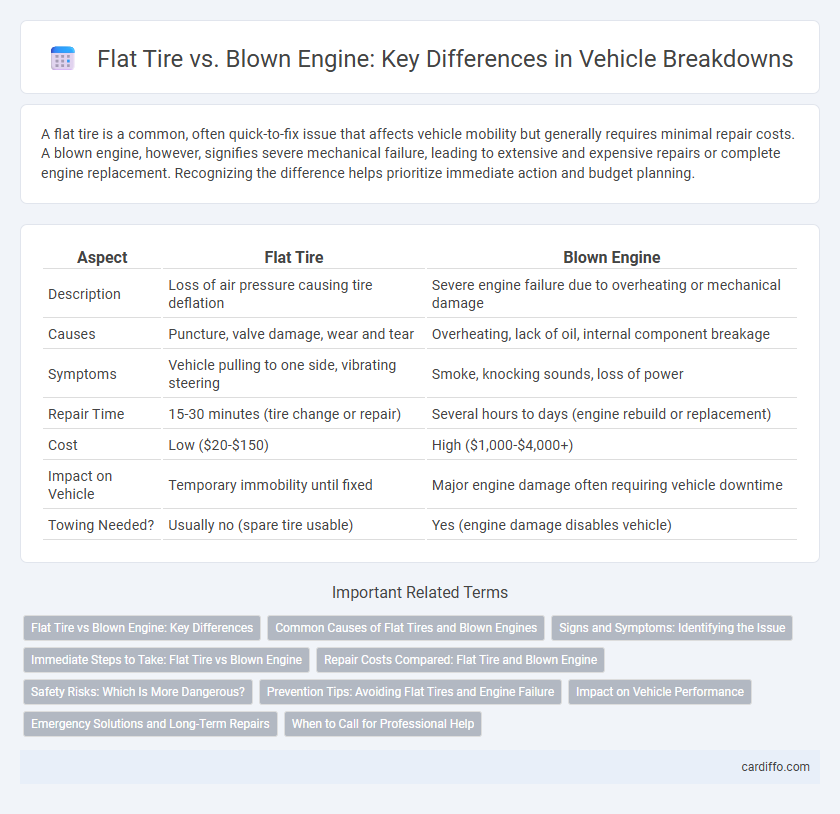
| Aspect | Flat Tire | Blown Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Loss of air pressure causing tire deflation | Severe engine failure due to overheating or mechanical damage |
| Causes | Puncture, valve damage, wear and tear | Overheating, lack of oil, internal component breakage |
| Symptoms | Vehicle pulling to one side, vibrating steering | Smoke, knocking sounds, loss of power |
| Repair Time | 15-30 minutes (tire change or repair) | Several hours to days (engine rebuild or replacement) |
| Cost | Low ($20-$150) | High ($1,000-$4,000+) |
| Impact on Vehicle | Temporary immobility until fixed | Major engine damage often requiring vehicle downtime |
| Towing Needed? | Usually no (spare tire usable) | Yes (engine damage disables vehicle) |
Flat Tire vs Blown Engine: Key Differences
A flat tire occurs when the rubber of the tire is punctured or deflated, causing loss of air pressure and impaired vehicle movement, while a blown engine refers to catastrophic internal damage resulting in total engine failure. Flat tires are generally easier and less costly to repair or replace compared to blown engines, which often require extensive mechanical rebuilding or engine replacement. Recognizing the symptoms such as tire pressure loss versus engine knocking or smoke helps diagnose the issue quickly and take appropriate action.
Common Causes of Flat Tires and Blown Engines
Flat tires commonly result from punctures by sharp objects like nails, improper tire pressure, or worn-out tread, leading to air loss and vehicle immobility. Blown engines often stem from overheating due to coolant leaks, lack of oil causing lubrication failure, or mechanical failures such as a broken timing belt or seized pistons. Understanding these causes helps prevent roadside breakdowns and costly repairs.
Signs and Symptoms: Identifying the Issue
A flat tire presents with sudden loss of air pressure, visible tread damage, and difficulty steering or maintaining control. A blown engine typically exhibits loud knocking noises, excessive smoke from the exhaust, and a significant drop in engine performance or power. Recognizing these distinct symptoms helps quickly diagnose whether the issue is a tire problem or a severe engine failure during a breakdown.
Immediate Steps to Take: Flat Tire vs Blown Engine
For a flat tire, immediately pull over to a safe location, activate hazard lights, and use a spare tire or call roadside assistance to replace the tire. In the case of a blown engine, stop the vehicle promptly to prevent further damage, allow the engine to cool down, and arrange for a professional tow to a repair shop. Both situations require prioritizing safety and prompt action tailored to the severity of the breakdown.
Repair Costs Compared: Flat Tire and Blown Engine
Repair costs for a flat tire typically range between $15 and $100, depending on whether it requires a simple patch or a full tire replacement. In contrast, repair costs for a blown engine can escalate from $3,000 to over $7,000, factoring in parts, labor, and potential engine replacement. The significant difference highlights the importance of preventive maintenance to avoid costly engine failures compared to relatively minor tire repairs.
Safety Risks: Which Is More Dangerous?
A blown engine poses greater safety risks than a flat tire due to the potential for sudden and severe mechanical failure that can lead to loss of vehicle control or engine fire. A flat tire, while inconvenient, typically allows the driver to gradually reduce speed and safely pull over, minimizing immediate danger. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing emergency responses and ensuring driver safety during breakdowns.
Prevention Tips: Avoiding Flat Tires and Engine Failure
Regularly inspect tire pressure and tread depth to prevent flat tires and maintain optimal vehicle performance. Schedule routine engine maintenance, including oil changes and coolant checks, to avoid engine failure caused by overheating or lubrication issues. Use quality tires and engine parts to enhance durability and reduce the risk of breakdowns on the road.
Impact on Vehicle Performance
A flat tire severely reduces vehicle stability and control, leading to decreased steering precision and increased stopping distances, but the engine continues to function normally. A blown engine causes a complete loss of power, rendering the vehicle immobile and requiring extensive repairs or replacement. The impact on vehicle performance from a blown engine is far more critical, resulting in total operational failure compared to the localized handling issues caused by a flat tire.
Emergency Solutions and Long-Term Repairs
Flat tire emergencies require immediate roadside solutions such as using a spare tire or tire sealant to restore mobility quickly. Blown engine breakdowns demand professional towing to a repair shop and extensive diagnostics to assess damage to components like pistons, cylinders, and the crankshaft. Long-term repairs for blown engines often involve parts replacement or complete engine rebuilds, whereas flat tire fixes mainly revolve around tire repair or replacement to ensure vehicle safety and performance.
When to Call for Professional Help
Determining when to call for professional help depends on the severity of the breakdown; a flat tire can often be temporarily fixed with a spare and basic tools, but a blown engine requires immediate towing and expert repair. Attempting to drive with a blown engine can cause further damage and increase repair costs, so contacting a roadside assistance service or mechanic is crucial. Flat tire repairs are generally quicker and less expensive, while engine failures demand comprehensive diagnostics and specialized mechanical knowledge.
Flat tire vs blown engine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com