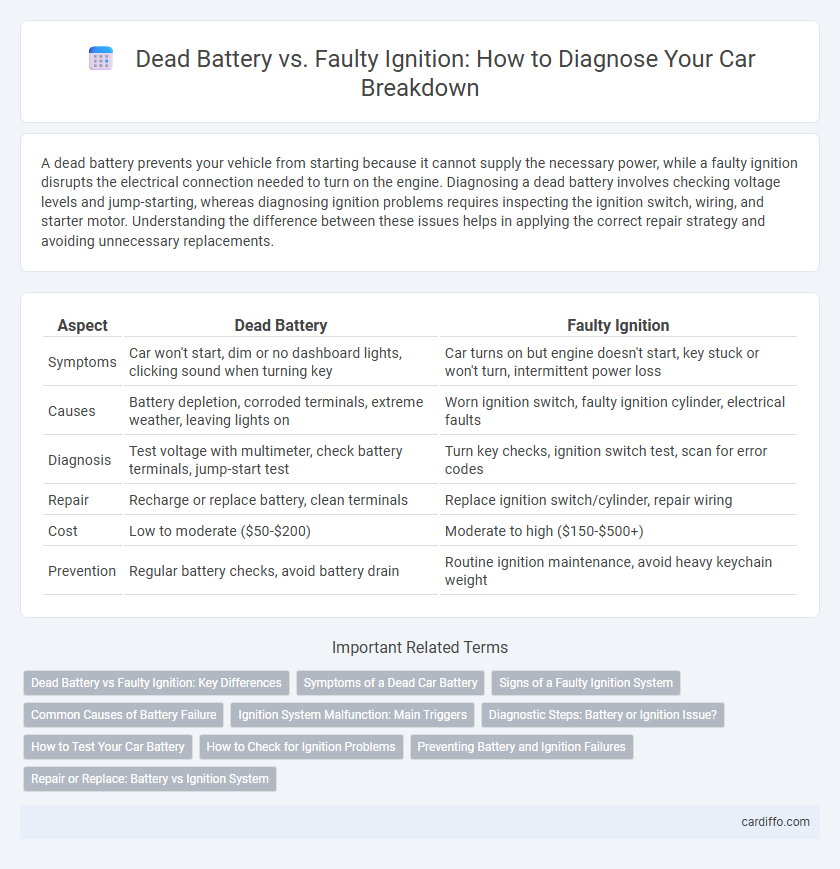
A dead battery prevents your vehicle from starting because it cannot supply the necessary power, while a faulty ignition disrupts the electrical connection needed to turn on the engine. Diagnosing a dead battery involves checking voltage levels and jump-starting, whereas diagnosing ignition problems requires inspecting the ignition switch, wiring, and starter motor. Understanding the difference between these issues helps in applying the correct repair strategy and avoiding unnecessary replacements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dead Battery | Faulty Ignition |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Car won't start, dim or no dashboard lights, clicking sound when turning key | Car turns on but engine doesn't start, key stuck or won't turn, intermittent power loss |
| Causes | Battery depletion, corroded terminals, extreme weather, leaving lights on | Worn ignition switch, faulty ignition cylinder, electrical faults |
| Diagnosis | Test voltage with multimeter, check battery terminals, jump-start test | Turn key checks, ignition switch test, scan for error codes |
| Repair | Recharge or replace battery, clean terminals | Replace ignition switch/cylinder, repair wiring |
| Cost | Low to moderate ($50-$200) | Moderate to high ($150-$500+) |
| Prevention | Regular battery checks, avoid battery drain | Routine ignition maintenance, avoid heavy keychain weight |
Dead Battery vs Faulty Ignition: Key Differences
A dead battery typically results in no response when turning the key, with dim or no dashboard lights, while a faulty ignition may show dashboard lights but fail to start the engine or cause intermittent power issues. Diagnosing a dead battery involves checking voltage levels, often below 12.4 volts, whereas ignition problems require assessment of the ignition switch, starter relay, or key cylinder. Understanding these distinctions helps in performing targeted repairs and avoiding unnecessary replacements.
Symptoms of a Dead Car Battery
A dead car battery often causes symptoms such as dim headlights, a clicking sound when turning the key, and the engine failing to start. Electrical components like the radio, interior lights, and dashboard indicators may also fail to power on. These signs differentiate a dead battery from a faulty ignition, where the engine may crank but not start.
Signs of a Faulty Ignition System
A faulty ignition system manifests through symptoms such as difficulty starting the engine, repeated stalling, and a dim or flickering dashboard light. Unlike a dead battery, which results in no power or clicking sounds when turning the key, ignition problems often produce intermittent electrical issues and unusual noises from the ignition switch. Early detection of ignition faults can prevent complete breakdowns and avoid costly repairs by addressing issues like worn spark plugs, ignition coil failure, or damaged wiring.
Common Causes of Battery Failure
Common causes of battery failure include corrosion on terminals, which impedes electrical flow, and prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures that degrade battery components. Frequent short trips prevent the battery from fully charging, while leaving lights or accessories on when the engine is off quickly drains power. A faulty alternator also contributes to battery failure by failing to replenish the battery's charge during operation.
Ignition System Malfunction: Main Triggers
Ignition system malfunctions often stem from worn-out ignition coils, faulty spark plugs, or a defective ignition switch, disrupting the engine's ability to start. Corrosion or poor electrical connections within the ignition circuitry further impede the spark generation critical for combustion. Diagnosing these main triggers promptly can prevent complete breakdowns and costly repairs.
Diagnostic Steps: Battery or Ignition Issue?
Check the battery voltage using a multimeter; a reading below 12.4 volts indicates a weak or dead battery requiring replacement or recharge. Inspect ignition system components such as the ignition switch, starter relay, and spark plugs for signs of wear or malfunction. Perform a jump-start test to confirm if the car starts with external power, helping isolate whether the issue is related to the battery or the ignition system.
How to Test Your Car Battery
To test your car battery, start by turning off all electrical components and using a digital multimeter to measure the voltage; a fully charged battery should read about 12.6 volts. If the reading is below 12.4 volts, the battery may be discharged or defective, indicating a possible dead battery rather than a faulty ignition. Perform a load test by cranking the engine and observing the voltage drop; if it falls below 10 volts during cranking, the battery likely needs replacement.
How to Check for Ignition Problems
To check for ignition problems, start by turning the key to the "on" position and observe the dashboard lights; if they fail to illuminate, the ignition switch may be faulty rather than the battery being dead. Next, listen for a clicking sound when turning the key, as a single click often indicates a bad ignition relay or starter solenoid instead of battery issues. Finally, testing the ignition coil and examining wiring connections with a multimeter can reveal faults that cause ignition failure and differentiate these from a dead battery scenario.
Preventing Battery and Ignition Failures
Regular maintenance of your vehicle's electrical system, including checking battery voltage and cleaning terminals, significantly reduces the risk of dead battery incidents. Inspecting the ignition system components such as spark plugs, ignition coils, and wiring for wear or damage prevents faulty ignition failures. Using quality parts and ensuring timely replacements help maintain reliable starting performance and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Repair or Replace: Battery vs Ignition System
Repairing a dead battery typically involves a straightforward replacement with a new or reconditioned battery, restoring full power to the vehicle's electrical system. Faulty ignition systems often require more complex diagnostics to identify issues with components such as the ignition switch, starter motor, or ignition coil, and may necessitate partial repairs or complete replacement of faulty parts. Choosing between battery replacement and ignition system repair depends on precise fault detection, cost-effectiveness, and the vehicle's overall condition to ensure reliable starting and operation.
Dead battery vs faulty ignition Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com