Brake line rupture poses a serious safety risk as it leads to a complete loss of braking power due to fluid leakage, while brake pad wear gradually reduces braking efficiency through friction material thinning. Recognizing symptoms like spongy brake pedals or visible fluid leaks indicates brake line issues, whereas squealing noises and reduced stopping performance typically signal worn brake pads. Timely inspection and maintenance of both components ensure reliable vehicle braking and prevent costly repairs.
Table of Comparison
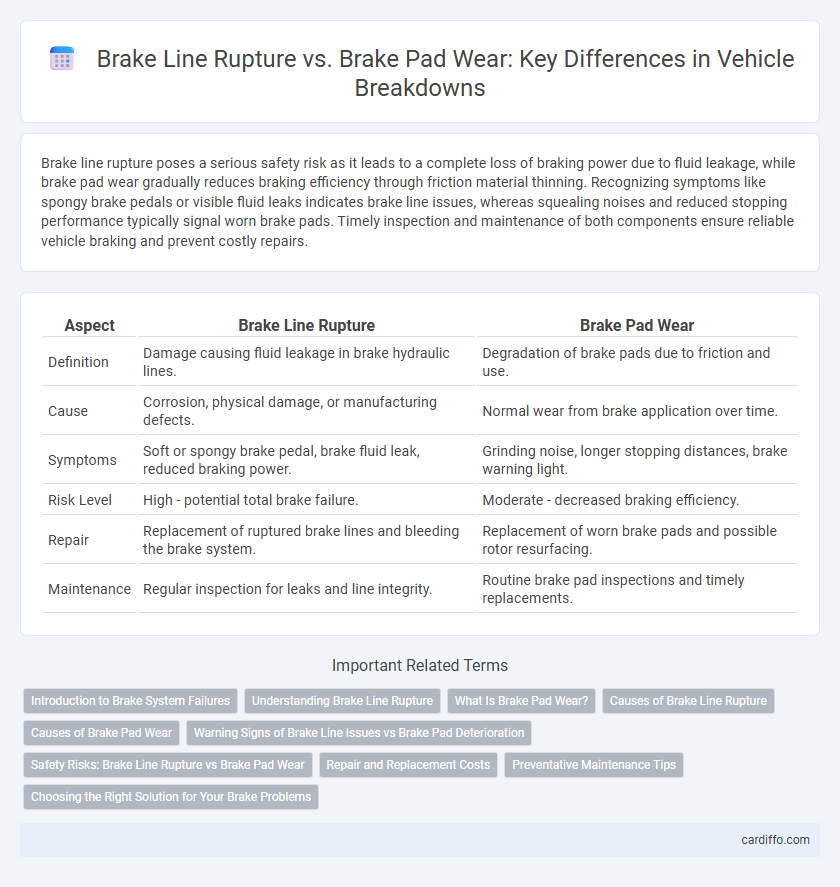
| Aspect | Brake Line Rupture | Brake Pad Wear |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Damage causing fluid leakage in brake hydraulic lines. | Degradation of brake pads due to friction and use. |
| Cause | Corrosion, physical damage, or manufacturing defects. | Normal wear from brake application over time. |
| Symptoms | Soft or spongy brake pedal, brake fluid leak, reduced braking power. | Grinding noise, longer stopping distances, brake warning light. |
| Risk Level | High - potential total brake failure. | Moderate - decreased braking efficiency. |
| Repair | Replacement of ruptured brake lines and bleeding the brake system. | Replacement of worn brake pads and possible rotor resurfacing. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection for leaks and line integrity. | Routine brake pad inspections and timely replacements. |
Introduction to Brake System Failures
Brake line rupture and brake pad wear represent critical brake system failures that significantly impact vehicle safety and performance. Brake line rupture leads to loss of hydraulic pressure, causing brake fluid leakage and diminished braking capability, often resulting in complete brake failure. In contrast, brake pad wear gradually reduces friction material thickness, lowering braking efficiency and increasing stopping distances without immediate fluid loss.
Understanding Brake Line Rupture
Brake line rupture causes a sudden loss of hydraulic pressure, leading to complete brake failure, whereas brake pad wear results in reduced braking efficiency over time. The brake line consists of flexible, high-pressure tubes that can crack or burst due to corrosion, physical damage, or excessive wear, necessitating immediate replacement to ensure safety. Recognizing signs like a spongy brake pedal or fluid leaks helps diagnose rupture early, preventing potentially catastrophic breakdowns.
What Is Brake Pad Wear?
Brake pad wear occurs when the friction material on brake pads thins due to repeated use, reducing braking efficiency and increasing stopping distances. Unlike brake line rupture, which causes a sudden loss of hydraulic pressure and brake failure, brake pad wear is gradual and can be monitored through visual inspection or sensor alerts. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn brake pads are essential to ensure safe vehicle operation and prevent damage to brake rotors.
Causes of Brake Line Rupture
Brake line rupture primarily occurs due to corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, road salt, and debris, which weakens the metal tubing over time. Physical damage from road hazards or improper installation can also lead to brake line failure. Unlike brake pad wear, which results from friction and heat, brake line rupture directly compromises brake fluid pressure, causing a critical loss of braking ability.
Causes of Brake Pad Wear
Brake pad wear primarily results from friction generated during braking, causing gradual thinning of the pads over time. Factors such as frequent braking, aggressive driving, and exposure to rough road conditions accelerate this wear by increasing heat and pressure on the brake pads. Unlike brake line rupture, which is caused by hydraulic fluid leaks or corrosion, brake pad wear is a normal maintenance issue driven by mechanical contact and usage patterns.
Warning Signs of Brake Line Issues vs Brake Pad Deterioration
Brake line rupture warning signs include a sudden loss of brake fluid, a spongy brake pedal, and visible brake fluid leaks near the wheels or under the vehicle. In contrast, brake pad deterioration is indicated by squealing or grinding noises, reduced braking efficiency, and visible thinning of the brake pads during inspection. Identifying these distinct symptoms early helps prevent brake system failure and ensures vehicle safety.
Safety Risks: Brake Line Rupture vs Brake Pad Wear
Brake line rupture poses a critical safety risk due to sudden and complete loss of hydraulic pressure, leading to total brake failure and increased chances of accidents. In contrast, brake pad wear results in decreased braking efficiency and longer stopping distances but typically allows some brake function to remain. Immediate inspection and repair of brake line damage are essential to prevent catastrophic failure, while worn brake pads require timely replacement to maintain effective braking performance and overall vehicle safety.
Repair and Replacement Costs
Brake line rupture repair costs typically range from $150 to $400 due to the complex labor and hydraulic system refilling involved, while brake pad replacement usually costs between $100 and $300 depending on vehicle type and pad quality. Brake line damage often requires immediate professional attention as it poses critical safety risks, whereas worn brake pads can sometimes be serviced with routine maintenance. Choosing high-quality replacement parts can increase upfront expenses but enhance long-term braking performance and safety.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Brake line rupture and brake pad wear require distinct preventative maintenance to ensure vehicle safety and performance. Regularly inspect brake lines for cracks, corrosion, and leaks, replacing any damaged sections promptly to prevent dangerous fluid loss and brake failure. Monitor brake pad thickness, replacing pads before they reach the minimum thickness specified by manufacturers to maintain effective stopping power and avoid damage to rotors.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Brake Problems
Brake line rupture demands immediate replacement of the damaged lines to restore hydraulic pressure and ensure brake functionality, while brake pad wear primarily requires timely pad replacement to maintain effective braking performance. Identifying the specific brake issue through visual inspection or professional diagnostics is crucial for selecting the correct repair method and preventing further damage. Regular maintenance schedules and monitoring brake fluid levels significantly reduce the risk of both brake line failure and excessive pad wear, optimizing overall vehicle safety.
Brake line rupture vs brake pad wear Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com