A starter issue occurs when the engine doesn't crank despite turning the key, often caused by a faulty starter motor or dead battery. An ignition issue, however, involves the engine cranking but failing to start, typically due to problems with the ignition switch, spark plugs, or fuel delivery. Differentiating these problems helps streamline diagnostics and effective repairs.
Table of Comparison
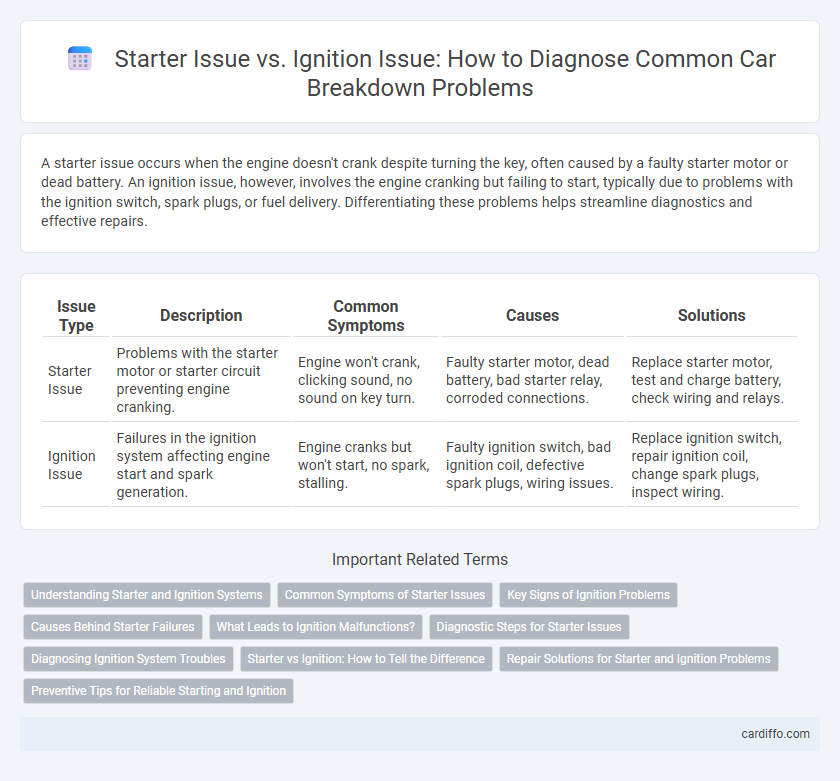
| Issue Type | Description | Common Symptoms | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starter Issue | Problems with the starter motor or starter circuit preventing engine cranking. | Engine won't crank, clicking sound, no sound on key turn. | Faulty starter motor, dead battery, bad starter relay, corroded connections. | Replace starter motor, test and charge battery, check wiring and relays. |
| Ignition Issue | Failures in the ignition system affecting engine start and spark generation. | Engine cranks but won't start, no spark, stalling. | Faulty ignition switch, bad ignition coil, defective spark plugs, wiring issues. | Replace ignition switch, repair ignition coil, change spark plugs, inspect wiring. |
Understanding Starter and Ignition Systems
Starter issues often involve mechanical failures such as a faulty starter motor, worn-out solenoid, or dead battery, which prevent the engine from cranking. Ignition issues typically relate to problems within the ignition switch, ignition coil, or spark plugs, causing the engine to crank without starting. Understanding the distinct roles of the starter system, responsible for engine cranking, and the ignition system, essential for engine ignition, helps accurately diagnose breakdown causes.
Common Symptoms of Starter Issues
Common symptoms of starter issues include a clicking noise when turning the key, a slow or labored engine crank, and complete failure to start despite a fully charged battery. Unlike ignition problems that prevent power from reaching the starter, starter issues often manifest through mechanical failures such as a worn-out solenoid or faulty starter motor. Diagnosing these symptoms quickly can prevent a complete vehicle breakdown and ensure timely repairs.
Key Signs of Ignition Problems
Key signs of ignition problems include difficulty starting the engine, frequent stalling, and unusual clicking sounds when turning the key. A faulty ignition switch may cause intermittent power loss, while ignition coil failures often result in misfiring or poor engine performance. Diagnosing these symptoms early can prevent complete breakdowns and costly repairs.
Causes Behind Starter Failures
Starter failures primarily arise from electrical faults such as a dead battery, corroded terminals, or faulty wiring that prevents sufficient current flow. Mechanical wear in the starter motor's components, including worn brushes or a damaged pinion gear, significantly contributes to ignition failure. Environmental factors like moisture and dirt infiltration can accelerate starter deterioration, leading to repeated breakdowns.
What Leads to Ignition Malfunctions?
Ignition malfunctions often result from faulty ignition coils, worn spark plugs, or a malfunctioning ignition switch disrupting the electrical flow needed to start the engine. Corroded wiring and a weak battery can also hinder the ignition process by failing to provide sufficient power. Unlike starter issues that involve the mechanical engagement of the engine, ignition problems primarily affect the electrical spark generation critical for combustion.
Diagnostic Steps for Starter Issues
Diagnosing starter issues begins with checking the battery voltage to ensure it provides at least 12.6 volts, followed by inspecting the starter relay and fuses for continuity. Testing the starter motor involves measuring voltage at the starter solenoid terminal while attempting to start the engine; absence of voltage indicates wiring or ignition switch problems. Conducting a bench test on the starter motor helps determine if it turns properly, isolating ignition issues from starter motor failures.
Diagnosing Ignition System Troubles
Diagnosing ignition system troubles involves inspecting key components such as spark plugs, ignition coils, and the ignition switch to identify faults causing engine starting failures. Testing spark plug condition and coil resistance helps detect ignition issues distinct from starter problems, which are typically related to the battery, starter motor, or solenoid. Accurate diagnosis ensures targeted repairs, preventing unnecessary replacement of starter parts when the root cause lies within the ignition system.
Starter vs Ignition: How to Tell the Difference
A starter issue typically causes a clicking sound or complete silence when turning the key, indicating the starter motor is failing to engage the engine. Ignition problems often manifest as the engine turning over but failing to start, pointing to faulty ignition switches, spark plugs, or ignition coils. Diagnosing the difference involves checking for battery power, starter motor response, and spark generation to isolate whether the issue lies in the starter system or the ignition circuit.
Repair Solutions for Starter and Ignition Problems
Repair solutions for starter problems often involve inspecting and replacing the starter motor, solenoid, or electrical connections to ensure proper power delivery. Ignition issues typically require diagnosing the ignition switch, ignition coil, or spark plugs to restore engine starting performance. Addressing both starter and ignition problems promptly prevents vehicle breakdowns and reduces repair costs.
Preventive Tips for Reliable Starting and Ignition
Regularly inspect and replace the starter motor and ignition coil to ensure reliable vehicle startup. Keep battery terminals clean and charged, as low voltage can mimic starter or ignition problems. Use quality spark plugs and maintain the ignition system to prevent misfires and improve engine ignition consistency.
Starter issue vs ignition issue Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com