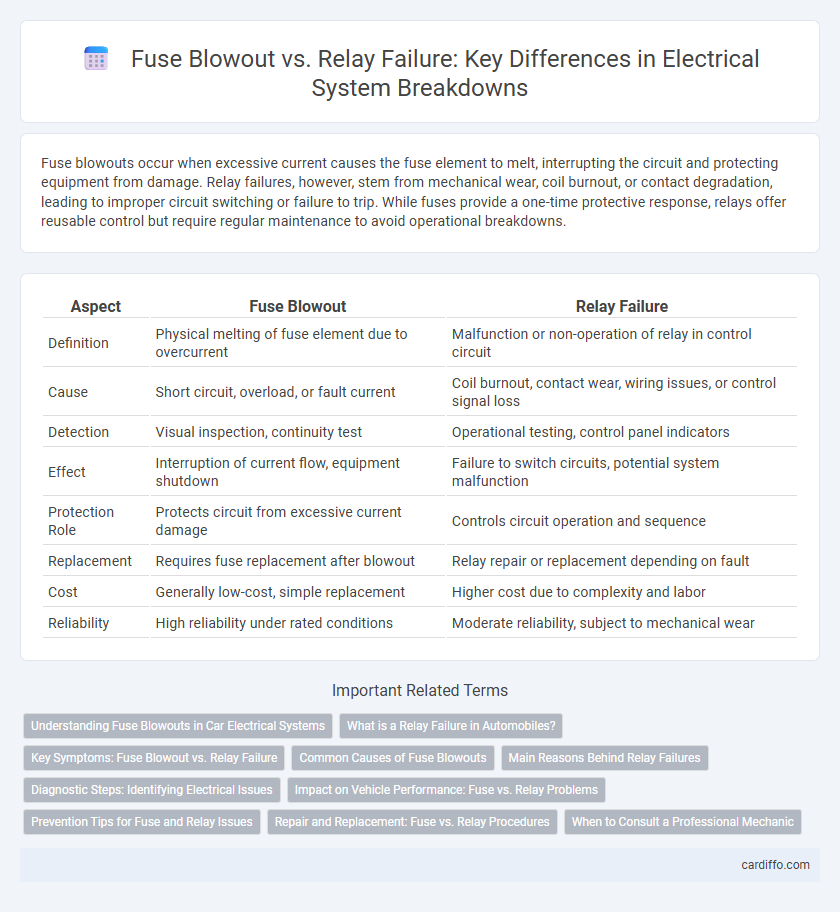
Fuse blowouts occur when excessive current causes the fuse element to melt, interrupting the circuit and protecting equipment from damage. Relay failures, however, stem from mechanical wear, coil burnout, or contact degradation, leading to improper circuit switching or failure to trip. While fuses provide a one-time protective response, relays offer reusable control but require regular maintenance to avoid operational breakdowns.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fuse Blowout | Relay Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical melting of fuse element due to overcurrent | Malfunction or non-operation of relay in control circuit |
| Cause | Short circuit, overload, or fault current | Coil burnout, contact wear, wiring issues, or control signal loss |
| Detection | Visual inspection, continuity test | Operational testing, control panel indicators |
| Effect | Interruption of current flow, equipment shutdown | Failure to switch circuits, potential system malfunction |
| Protection Role | Protects circuit from excessive current damage | Controls circuit operation and sequence |
| Replacement | Requires fuse replacement after blowout | Relay repair or replacement depending on fault |
| Cost | Generally low-cost, simple replacement | Higher cost due to complexity and labor |
| Reliability | High reliability under rated conditions | Moderate reliability, subject to mechanical wear |
Understanding Fuse Blowouts in Car Electrical Systems
Fuse blowouts in car electrical systems occur when excessive current overloads the circuit, causing the fuse to melt and interrupt power flow. This protective mechanism prevents damage to sensitive components and wiring by isolating the fault, often triggered by short circuits, faulty wiring, or malfunctioning devices. Understanding fuse blowouts is crucial for diagnosing electrical failures, as they differ from relay failures, which typically involve mechanical or coil issues within the relay itself.
What is a Relay Failure in Automobiles?
Relay failure in automobiles occurs when the electrical relay, responsible for controlling high-current circuits using a low-current signal, malfunctions due to coil burnout, contact corrosion, or internal wear. This failure prevents critical systems such as the fuel pump, headlights, or starter motor from operating, leading to vehicle breakdowns. Unlike fuse blowouts that protect circuits by breaking under overload, relay failures disrupt circuit activation and require relay replacement to restore functionality.
Key Symptoms: Fuse Blowout vs. Relay Failure
Key symptoms of a fuse blowout include an immediate loss of power to the circuit and visible physical damage such as a melted or broken fuse element. Relay failure is characterized by intermittent or no switching action, often accompanied by clicking sounds or a lack of response despite control signals. Identifying these specific symptoms helps differentiate between fuse blowout and relay failure for effective troubleshooting.
Common Causes of Fuse Blowouts
Fuse blowouts commonly occur due to electrical overloads, short circuits, and aging components that cause excessive current flow beyond the fuse rating. Environmental factors such as high temperature and vibrations also contribute significantly to fuse degradation and sudden failure. Proper circuit design and regular maintenance help prevent fuse blowouts by ensuring the fuse rating matches the load requirements.
Main Reasons Behind Relay Failures
Relay failures often stem from coil burnout, contact erosion, and mechanical wear caused by frequent switching operations and voltage spikes. Poor maintenance and improper installation can exacerbate issues, leading to overheating and insulation breakdown. These factors differ from fuse blowouts, which primarily result from overcurrent conditions rather than mechanical or coil-related faults.
Diagnostic Steps: Identifying Electrical Issues
Diagnosing electrical issues requires distinguishing between fuse blowout and relay failure by first inspecting the fuse for visible signs of damage or continuity loss using a multimeter. Next, test the relay by checking for clicking sounds during activation and measuring coil resistance to ensure proper operation. Accurate identification through these diagnostic steps prevents misdiagnosis and ensures targeted repair of electrical system faults.
Impact on Vehicle Performance: Fuse vs. Relay Problems
Fuse blowouts cause immediate loss of electrical function in critical vehicle systems, such as lighting, ignition, or fuel pumps, leading to sudden performance failure and vehicle shutdown. Relay failures result in inconsistent or intermittent component operation, like erratic starting or malfunctioning accessories, causing unreliable vehicle performance and potential safety hazards. Diagnosing fuse versus relay issues is crucial for maintaining vehicle reliability and preventing prolonged downtime.
Prevention Tips for Fuse and Relay Issues
Prevent fuse blowouts and relay failures by regularly inspecting electrical systems for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections. Implement proper circuit protection with correctly rated fuses and relays that match the load requirements to avoid overcurrent damage. Maintain clean and dry contact points, and replace faulty components promptly to enhance system reliability and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Repair and Replacement: Fuse vs. Relay Procedures
Repair and replacement procedures for fuse blowouts involve quickly identifying the blown fuse and replacing it with one of the same amperage rating to restore circuit protection. Relay failure requires diagnosing the defective relay, often testing coil resistance and contacts, followed by removing the faulty unit and installing a compatible replacement relay. Proper handling of both components minimizes downtime and ensures reliable electrical system operation in industrial or automotive applications.
When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
Consult a professional mechanic immediately when a fuse blowout occurs repeatedly or if electrical components fail after replacing the fuse, as this may indicate underlying circuit issues. Relay failure symptoms such as intermittent electrical operation or no response from controlled devices require expert diagnosis to prevent further system damage. Prompt consultation helps ensure accurate troubleshooting and safe, reliable vehicle performance.
Fuse blowout vs relay failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com