A radiator leak often results in slow coolant loss and overheating due to cracks or corrosion, requiring sealant or replacement. A coolant hose burst causes rapid coolant spillage, leading to immediate engine overheating and potential damage. Identifying the source quickly is essential to prevent costly repairs and maintain engine health.
Table of Comparison
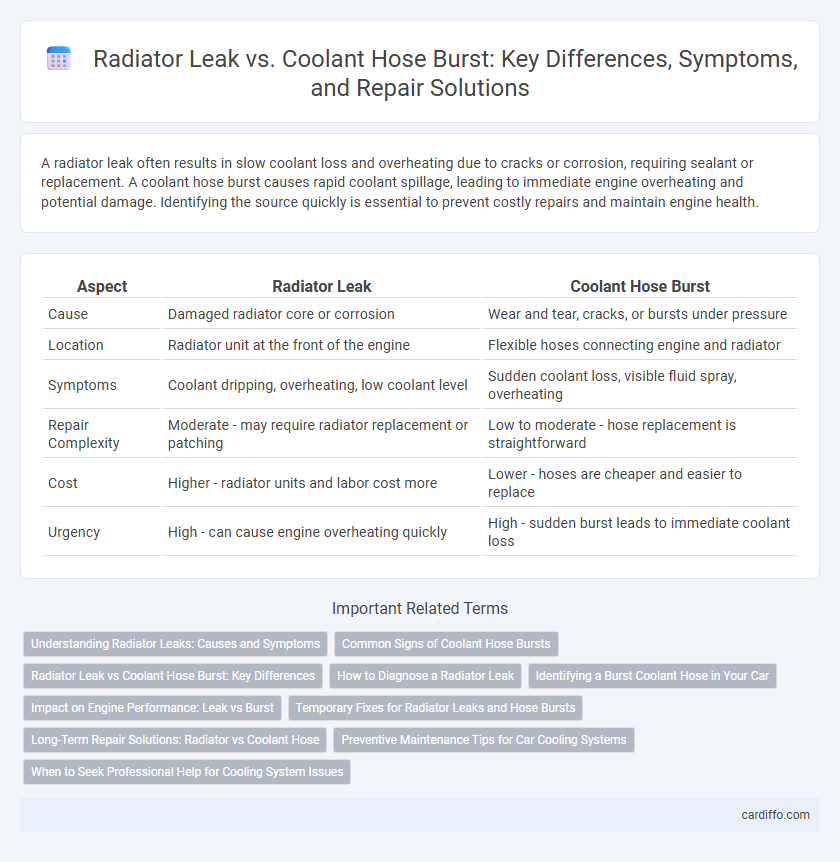
| Aspect | Radiator Leak | Coolant Hose Burst |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Damaged radiator core or corrosion | Wear and tear, cracks, or bursts under pressure |
| Location | Radiator unit at the front of the engine | Flexible hoses connecting engine and radiator |
| Symptoms | Coolant dripping, overheating, low coolant level | Sudden coolant loss, visible fluid spray, overheating |
| Repair Complexity | Moderate - may require radiator replacement or patching | Low to moderate - hose replacement is straightforward |
| Cost | Higher - radiator units and labor cost more | Lower - hoses are cheaper and easier to replace |
| Urgency | High - can cause engine overheating quickly | High - sudden burst leads to immediate coolant loss |
Understanding Radiator Leaks: Causes and Symptoms
Radiator leaks often result from corrosion, physical damage, or degraded seals, leading to coolant loss and engine overheating. Symptoms include visible coolant puddles under the vehicle, a sweet smell, and fluctuating engine temperature gauge readings. Early detection is crucial to prevent engine damage and costly repairs.
Common Signs of Coolant Hose Bursts
Coolant hose bursts often present with visible coolant spraying or pooling under the vehicle, accompanied by a sweet, antifreeze odor. Engine overheating and sudden drops in coolant levels on the reservoir gauge are key indicators of a hose failure. Unlike radiator leaks, which may cause slow, consistent drips, hose bursts typically result in rapid and noticeable coolant loss.
Radiator Leak vs Coolant Hose Burst: Key Differences
Radiator leak and coolant hose burst differ primarily in their sources and symptoms; a radiator leak originates from cracks or corrosion in the radiator itself, causing slow but consistent coolant loss, while a coolant hose burst results from hose deterioration or sudden pressure spikes, leading to rapid coolant leakage. Temperature fluctuations and visible coolant puddles often indicate a radiator leak, whereas a burst hose typically causes immediate overheating and steam due to abrupt coolant loss. Diagnosing these issues promptly is crucial to prevent engine damage and ensure proper cooling system function.
How to Diagnose a Radiator Leak
To diagnose a radiator leak, inspect the radiator and surrounding components for visible signs of coolant puddles or wet spots, especially around the radiator seams and connections. Perform a pressure test on the cooling system to identify drops in pressure that indicate a leak location. Look for dried coolant residue or corrosion, which often signals slow leaks distinct from the sudden failure of a coolant hose burst.
Identifying a Burst Coolant Hose in Your Car
A burst coolant hose in your car causes sudden coolant leaks, visible as puddles under the vehicle and a drop in engine temperature. Inspect hoses for visible cracks, bulges, or soft spots that indicate imminent failure. Unlike radiator leaks, a burst hose often leads to rapid engine overheating and steam emissions from the engine bay.
Impact on Engine Performance: Leak vs Burst
Radiator leaks cause gradual coolant loss, leading to insufficient engine cooling and potential overheating over time, which reduces engine efficiency and risks long-term damage. Coolant hose bursts result in sudden, significant coolant loss, causing rapid engine temperature spikes that can immediately impair engine performance and may lead to severe engine failure. Both conditions disrupt optimal engine temperature regulation but differ in onset speed and severity of impact on engine functionality.
Temporary Fixes for Radiator Leaks and Hose Bursts
Temporary fixes for radiator leaks include using radiator sealant products designed to bond and seal small cracks or holes, providing a short-term solution to prevent coolant loss. For coolant hose bursts, applying flexible repair tape or hose repair kits can temporarily stop leaks and restore pressure, allowing you to drive safely to a mechanic. Both methods are emergency measures and should be followed by professional repairs to avoid engine overheating or further damage.
Long-Term Repair Solutions: Radiator vs Coolant Hose
Radiator leaks require comprehensive long-term repair solutions such as full radiator replacement or professional sealant application to prevent recurring coolant loss and engine overheating. In contrast, coolant hose bursts are often resolved by replacing the damaged hose with high-quality, heat-resistant hoses designed for durability and flexibility. Ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance of both components significantly reduces the risk of future breakdowns and extends vehicle cooling system lifespan.
Preventive Maintenance Tips for Car Cooling Systems
Routine inspection of the radiator and coolant hoses is essential to prevent leaks and bursts that can cause engine overheating. Using high-quality coolant and replacing hoses and radiator components at manufacturer-recommended intervals enhances system durability and reduces the risk of breakdowns. Flushing the cooling system periodically removes contaminants, ensuring efficient heat transfer and prolonging the life of both the radiator and hoses.
When to Seek Professional Help for Cooling System Issues
Seek professional help immediately if you notice coolant pooling under the vehicle, overheating engine temperature, or a persistent drop in coolant levels, as these signs indicate a radiator leak or hose burst. A certified mechanic can accurately diagnose the source of the leak, repair or replace damaged components, and perform a thorough cooling system flush to prevent engine damage. Delaying repairs increases the risk of engine overheating, leading to costly repairs or complete engine failure.
Radiator leak vs coolant hose burst Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com