Mechanical failure occurs when physical components such as gears, bearings, or shafts wear out or break, leading to impaired function or complete stoppage. Electrical failure involves issues like short circuits, blown fuses, or faulty wiring that disrupt power flow and electronic control systems. Differentiating between mechanical and electrical failures ensures targeted diagnostics and effective repair strategies to minimize downtime.
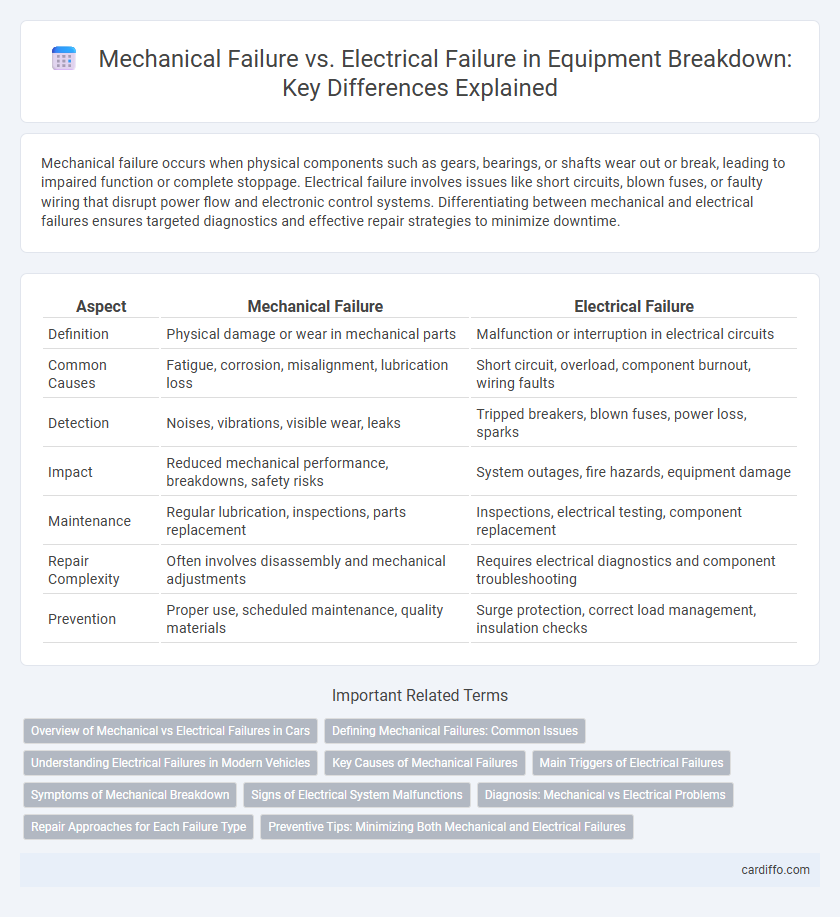
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mechanical Failure | Electrical Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical damage or wear in mechanical parts | Malfunction or interruption in electrical circuits |
| Common Causes | Fatigue, corrosion, misalignment, lubrication loss | Short circuit, overload, component burnout, wiring faults |
| Detection | Noises, vibrations, visible wear, leaks | Tripped breakers, blown fuses, power loss, sparks |
| Impact | Reduced mechanical performance, breakdowns, safety risks | System outages, fire hazards, equipment damage |
| Maintenance | Regular lubrication, inspections, parts replacement | Inspections, electrical testing, component replacement |
| Repair Complexity | Often involves disassembly and mechanical adjustments | Requires electrical diagnostics and component troubleshooting |
| Prevention | Proper use, scheduled maintenance, quality materials | Surge protection, correct load management, insulation checks |
Overview of Mechanical vs Electrical Failures in Cars
Mechanical failures in cars typically involve issues with the engine, transmission, brakes, or suspension components, causing breakdowns due to wear, overheating, or physical damage. Electrical failures often stem from battery problems, alternator malfunctions, faulty wiring, or sensor errors, leading to starting issues or malfunctioning electronic systems. Understanding the distinct symptoms and repair needs of mechanical versus electrical failures is essential for accurate diagnostics and timely vehicle maintenance.
Defining Mechanical Failures: Common Issues
Mechanical failures in breakdowns often involve worn-out bearings, broken gears, or seized pistons, leading to loss of functionality in engines or machinery. Common issues include overheating due to lack of lubrication, misalignment of moving parts causing excessive friction, and structural fatigue from repeated stress cycles. These failures typically result in physical damage that requires component repair or replacement to restore operational integrity.
Understanding Electrical Failures in Modern Vehicles
Electrical failures in modern vehicles often stem from issues like faulty wiring, battery degradation, or malfunctioning sensors, disrupting critical systems such as engine control units and infotainment displays. Diagnosing these failures requires specialized diagnostic tools that interface with onboard computer systems to identify error codes and pinpoint the exact malfunction. Addressing electrical failures promptly is essential to prevent further complications, including vehicle immobilization and safety hazards.
Key Causes of Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures primarily result from wear and tear of components, leading to issues such as broken shafts, bearings, and gears. Insufficient lubrication, material fatigue, and misalignment also contribute significantly to mechanical breakdowns. These factors cause increased friction and stress, ultimately resulting in system malfunctions and operational downtime.
Main Triggers of Electrical Failures
Main triggers of electrical failures include short circuits, power surges, and insulation breakdowns caused by moisture or heat exposure. Corroded connections and worn-out components often disrupt current flow, leading to system malfunctions. Faulty wiring installation and overload conditions also contribute significantly to electrical system breakdowns.
Symptoms of Mechanical Breakdown
Symptoms of mechanical breakdown often include unusual noises such as grinding or knocking, visible leaks, and noticeable vibrations during operation. Reduced performance, difficulty starting the engine, and overheating are common indicators of mechanical issues. These signs differentiate mechanical failures from electrical problems, which typically involve malfunctioning lights, battery drainage, or faulty sensors.
Signs of Electrical System Malfunctions
Signs of electrical system malfunctions include dimming or flickering headlights, dashboard warning lights, and a vehicle that won't start despite a fully charged battery. Corroded battery terminals, blown fuses, and unusual smells like burning plastic also indicate potential electrical failures. Early detection of these symptoms helps prevent costly repairs and ensures vehicle safety.
Diagnosis: Mechanical vs Electrical Problems
Mechanical failure diagnosis involves inspecting physical components like gears, belts, and bearings for wear, misalignment, or damage through visual checks and manual testing. Electrical failure diagnosis requires analyzing circuits, wiring, fuses, and sensors using multimeters and diagnostic software to identify short circuits, open circuits, or faulty connections. Accurate differentiation between mechanical and electrical issues accelerates repair processes and minimizes downtime.
Repair Approaches for Each Failure Type
Mechanical failure repair primarily involves replacing worn or damaged physical components such as gears, bearings, or shafts, often requiring disassembly and thorough inspection to identify the root cause. Electrical failure repair focuses on diagnosing circuit malfunctions, damaged wiring, or faulty electronic components using specialized tools like multimeters and oscilloscopes, followed by component replacement or circuit board repairs. Tailoring repair approaches to the failure type ensures efficient restoration of functionality, minimizing downtime and preventing recurrent issues.
Preventive Tips: Minimizing Both Mechanical and Electrical Failures
Regular maintenance routines, including lubrication, tightening of bolts, and inspection of moving parts, help prevent mechanical failures by reducing wear and tear. For electrical failures, ensuring proper insulation, avoiding moisture exposure, and regularly testing circuit integrity are crucial preventive measures. Implementing diagnostic tools and timely component replacements significantly minimize the risk of both mechanical and electrical breakdowns.
Mechanical failure vs electrical failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com