ABS failure occurs when the anti-lock braking system malfunctions, causing the wheels to lock up during braking and increasing the risk of skidding. Traction control failure affects the vehicle's ability to prevent wheel spin during acceleration, leading to reduced stability and control on slippery surfaces. Understanding these differences helps diagnose specific issues and ensures appropriate repairs for safer driving.
Table of Comparison
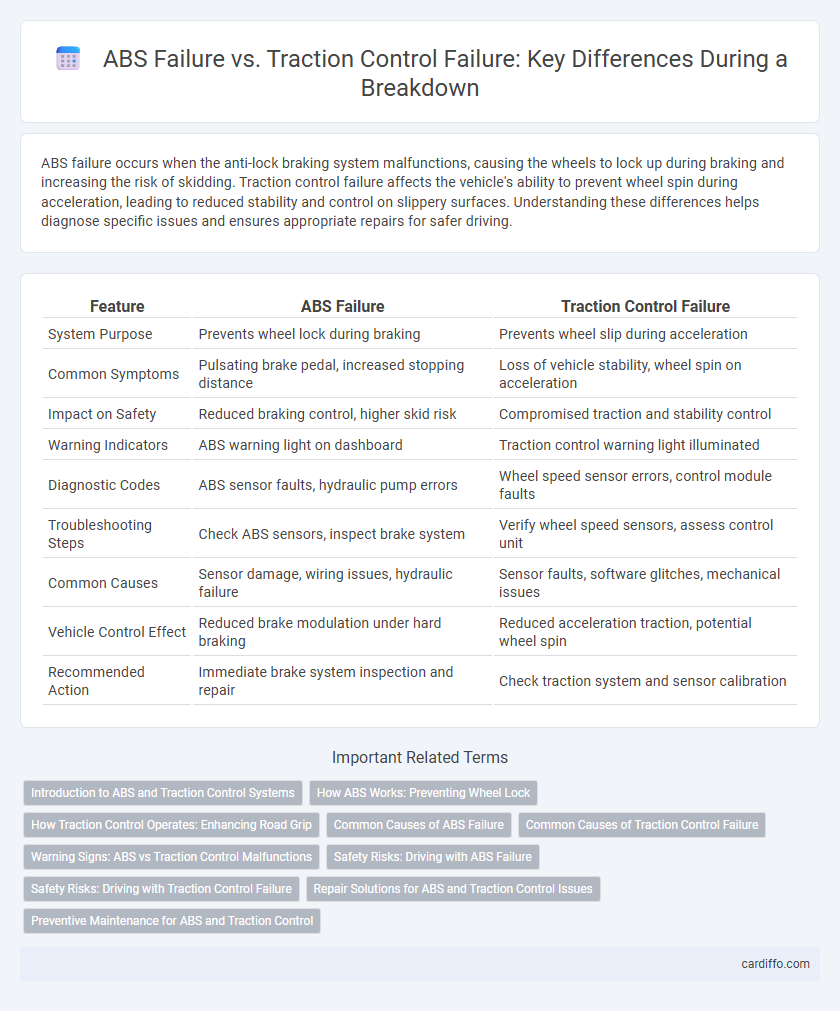
| Feature | ABS Failure | Traction Control Failure |
|---|---|---|
| System Purpose | Prevents wheel lock during braking | Prevents wheel slip during acceleration |
| Common Symptoms | Pulsating brake pedal, increased stopping distance | Loss of vehicle stability, wheel spin on acceleration |
| Impact on Safety | Reduced braking control, higher skid risk | Compromised traction and stability control |
| Warning Indicators | ABS warning light on dashboard | Traction control warning light illuminated |
| Diagnostic Codes | ABS sensor faults, hydraulic pump errors | Wheel speed sensor errors, control module faults |
| Troubleshooting Steps | Check ABS sensors, inspect brake system | Verify wheel speed sensors, assess control unit |
| Common Causes | Sensor damage, wiring issues, hydraulic failure | Sensor faults, software glitches, mechanical issues |
| Vehicle Control Effect | Reduced brake modulation under hard braking | Reduced acceleration traction, potential wheel spin |
| Recommended Action | Immediate brake system inspection and repair | Check traction system and sensor calibration |
Introduction to ABS and Traction Control Systems
Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) prevent wheel lockup during sudden braking by modulating brake pressure, enhancing vehicle control and reducing stopping distances on slippery surfaces. Traction Control Systems (TCS) manage wheel spin during acceleration by adjusting engine power or applying brakes to individual wheels, improving grip on uneven or slippery terrain. Failures in ABS often result in compromised braking efficiency and increased stopping distance, while TCS failures lead to reduced traction and potential loss of vehicle stability during acceleration.
How ABS Works: Preventing Wheel Lock
ABS failure occurs when the system's wheel speed sensors or hydraulic modulator malfunction, preventing the anti-lock braking system from detecting and preventing wheel lock during braking. Traction control failure happens when the system cannot accurately sense wheel slip or modulate brake pressure, leading to ineffective traction management. ABS works by rapidly pulsing brake pressure to prevent wheel lock, maintaining tire contact with the road and enabling the driver to retain steering control under heavy braking.
How Traction Control Operates: Enhancing Road Grip
Traction control operates by monitoring wheel speed sensors to detect slip and automatically adjusting engine power or applying brakes to specific wheels for enhanced road grip. This system improves vehicle stability during acceleration on slippery surfaces by preventing wheel spin. Unlike ABS, which focuses on preventing wheel lockup during braking, traction control actively manages power distribution to maintain optimal traction.
Common Causes of ABS Failure
Common causes of ABS failure include damaged wheel speed sensors, which disrupt accurate monitoring of wheel rotation necessary for anti-lock braking. Faulty ABS module or pump failures can prevent proper hydraulic pressure modulation, leading to braking system malfunction. Corroded or loose wiring connections often result in intermittent ABS signals, compromising traction control and overall vehicle stability.
Common Causes of Traction Control Failure
Traction control failure commonly results from faulty wheel speed sensors, which provide inaccurate data to the system, impairing its ability to prevent wheel slip. Electrical issues such as blown fuses, damaged wiring harnesses, or malfunctioning ABS control modules also contribute significantly to traction control malfunctions. Additionally, worn-out or damaged traction control system components, including hydraulic pumps and valves, can lead to system failure and compromised vehicle stability.
Warning Signs: ABS vs Traction Control Malfunctions
Warning signs of ABS failure include a persistent ABS warning light, unusual brake pedal behavior such as pulsation or increased effort, and prolonged stopping distances. Traction control malfunctions often trigger the traction control warning light, wheel slip during acceleration, or erratic engine power reduction. Identifying these warnings promptly helps prevent compromised vehicle stability and ensures timely repairs of the braking and traction systems.
Safety Risks: Driving with ABS Failure
Driving with ABS failure significantly increases the risk of wheel lock-up during braking, leading to reduced steering control and longer stopping distances, especially on slippery surfaces. This can result in dangerous skidding or loss of vehicle stability, elevating the likelihood of collisions in emergency braking situations. Unlike traction control failure, which primarily affects acceleration and cornering, ABS malfunction directly compromises braking safety mechanisms critical for accident avoidance.
Safety Risks: Driving with Traction Control Failure
Driving with traction control failure significantly increases the risk of skidding and loss of vehicle stability, especially on slippery or uneven road surfaces. Unlike ABS failure, which primarily affects braking efficiency, traction control failure compromises the vehicle's ability to regulate wheel spin and maintain proper grip during acceleration. This malfunction can lead to decreased handling performance, raising the likelihood of accidents in adverse driving conditions.
Repair Solutions for ABS and Traction Control Issues
Repair solutions for ABS and traction control issues often involve diagnosing faulty wheel speed sensors, wiring problems, or malfunctioning modulators. Replacing damaged ABS control modules or recalibrating traction control systems can restore proper functionality and safety. Regular system diagnostics and software updates are critical to prevent recurring failures and ensure optimal brake and traction performance.
Preventive Maintenance for ABS and Traction Control
Regular preventive maintenance of ABS and traction control systems involves inspecting wheel speed sensors, hydraulic valves, and electronic control units to prevent failures. Addressing signs such as warning lights or inconsistent braking response early reduces the risk of ABS failure, which can compromise vehicle stability. Ensuring traction control system components, including sensors and actuators, are calibrated and functioning properly helps maintain optimal vehicle handling and safety.
ABS failure vs traction control failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com