A wet ignition system uses a lubricated environment to enhance electrical conductivity and reduce wear on components, making it more resistant to corrosion and providing smoother operation in high-moisture conditions. In contrast, a dry ignition system relies on air insulation, which tends to be simpler and lighter but may suffer from increased wear and moisture-related failures. Choosing between them depends on specific performance needs, environmental exposure, and maintenance considerations in the pet industry.
Table of Comparison
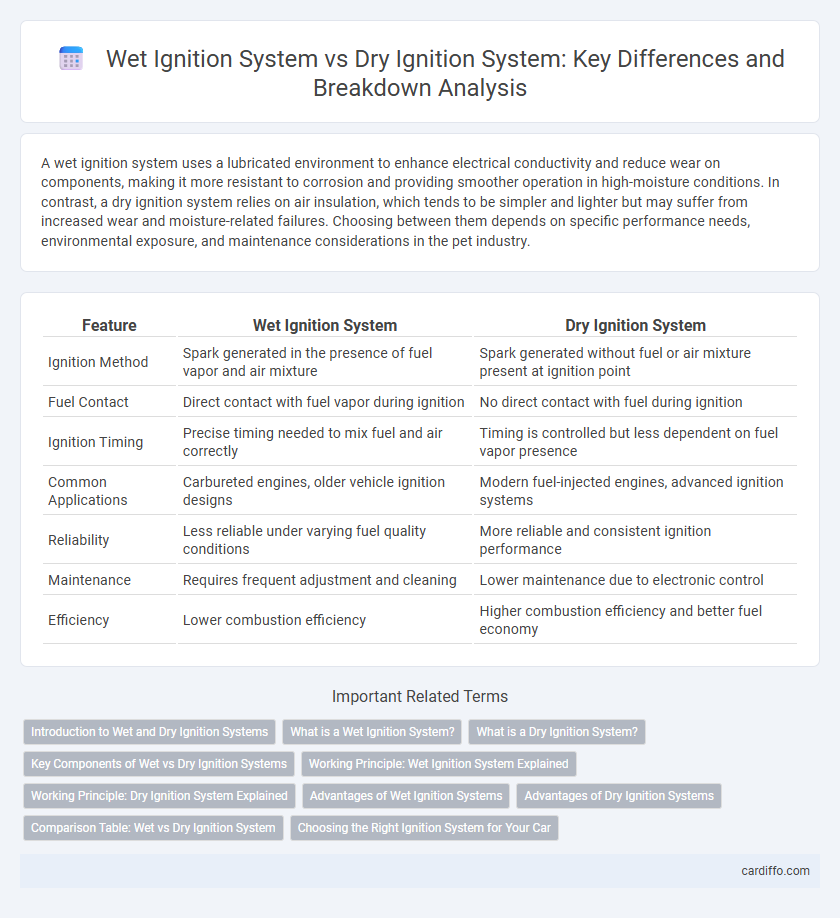
| Feature | Wet Ignition System | Dry Ignition System |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Method | Spark generated in the presence of fuel vapor and air mixture | Spark generated without fuel or air mixture present at ignition point |
| Fuel Contact | Direct contact with fuel vapor during ignition | No direct contact with fuel during ignition |
| Ignition Timing | Precise timing needed to mix fuel and air correctly | Timing is controlled but less dependent on fuel vapor presence |
| Common Applications | Carbureted engines, older vehicle ignition designs | Modern fuel-injected engines, advanced ignition systems |
| Reliability | Less reliable under varying fuel quality conditions | More reliable and consistent ignition performance |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent adjustment and cleaning | Lower maintenance due to electronic control |
| Efficiency | Lower combustion efficiency | Higher combustion efficiency and better fuel economy |
Introduction to Wet and Dry Ignition Systems
Wet ignition systems utilize a fuel mixture combined with air before spark ignition, enhancing combustion efficiency in certain engines. Dry ignition systems, in contrast, ignite air-fuel mixtures without the presence of excess liquid fuel, promoting faster spark generation and reduced misfire rates. These fundamental differences impact engine performance, emissions, and maintenance requirements significantly.
What is a Wet Ignition System?
A wet ignition system uses liquid fuel directly injected into the combustion chamber where it mixes with air before ignition, enhancing fuel atomization and combustion efficiency. It contrasts with a dry ignition system that relies on pre-mixed air-fuel mixture outside the chamber before intake. Wet ignition systems are commonly found in modern marine and industrial engines for improved power output and reduced emissions.
What is a Dry Ignition System?
A dry ignition system utilizes electrical components that operate without the presence of oil or other liquids, relying on air or vacuum conditions to transmit the ignition spark efficiently. This system typically features spark plugs, ignition coils, and electronic control units that function in a clean, non-lubricated environment, enhancing reliability and reducing maintenance. Dry ignition systems are common in modern vehicles due to their improved performance, ease of troubleshooting, and resistance to contamination compared to wet ignition systems.
Key Components of Wet vs Dry Ignition Systems
Wet ignition systems incorporate spark plugs with a fuel-air mixture directly in the combustion chamber, utilizing components like ignition coils, spark plugs, and fuel injectors for efficient spark generation and fuel delivery. Dry ignition systems rely on spark plugs, ignition coils, and electronic control units without direct fuel presence at the spark gap, ensuring faster ignition response and reduced fouling. Key components differences include the presence of fuel injectors in wet systems and advanced electronic controls in dry systems, impacting ignition timing and engine performance.
Working Principle: Wet Ignition System Explained
The wet ignition system operates by introducing fuel directly into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with air before ignition, allowing precise fuel atomization and efficient combustion. This system relies on a continuous fuel spray, ensuring consistent ignition and improved power output compared to dry ignition systems, which use fuel vapor or premixed air-fuel charges. The working principle centers on maintaining optimal fuel flow and spark timing to achieve a stable flame and reduce emissions.
Working Principle: Dry Ignition System Explained
The dry ignition system operates by generating a high-voltage spark through an ignition coil and electronic control unit without the use of oil or moisture, ensuring a more reliable and efficient combustion process. Unlike wet ignition systems that rely on an oil bath to cool and lubricate components, the dry system uses air cooling, which reduces maintenance and improves ignition timing precision. This mechanism enhances engine performance and fuel economy by providing consistent and rapid spark delivery under varying operating conditions.
Advantages of Wet Ignition Systems
Wet ignition systems offer superior cooling properties that reduce the risk of engine knocking and enhance combustion stability, contributing to improved engine performance. The presence of fuel mixed with air in wet systems facilitates easier ignition under varying operating conditions, ensuring reliable startup and smoother acceleration. These systems also enable simpler carburetor designs and lower manufacturing costs compared to dry ignition systems, making them a cost-effective solution for many internal combustion engines.
Advantages of Dry Ignition Systems
Dry ignition systems offer enhanced reliability by eliminating moisture-related issues that commonly affect wet ignition components. They reduce maintenance requirements due to their sealed design, preventing corrosion and minimizing wear from environmental exposure. Improved performance consistency and longer service life make dry ignition systems ideal for harsh operating conditions.
Comparison Table: Wet vs Dry Ignition System
The wet ignition system utilizes liquid fuel mixed with air before reaching the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel atomization for efficient ignition and smoother engine operation. In contrast, the dry ignition system involves direct fuel injection into the combustion chamber, resulting in better fuel economy and reduced emissions. Key comparison factors include fuel delivery method, combustion efficiency, maintenance requirements, and emission levels, with wet systems generally requiring more maintenance due to fuel residue, while dry systems offer improved environmental performance.
Choosing the Right Ignition System for Your Car
Selecting the ideal ignition system for your car involves comparing wet and dry ignition systems based on performance, maintenance, and environmental conditions. Wet ignition systems offer superior cooling and are less prone to overheating, making them suitable for high-performance engines and demanding conditions. Dry ignition systems are lighter, require less maintenance, and perform efficiently in moderate climates, providing an optimal balance for everyday vehicles.
Wet ignition system vs dry ignition system Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com